ISA 12 Income Tax and IFRS 2 Share Based Payments
advertisement

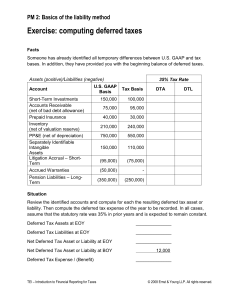
ISA 12 Income Tax ISA 12 Income Tax adopts a full provision approach to accounting for deferred taxation. It is assumed that the recovery of all assets and the settlement of all liabilities have tax consequences and that these consequences can be estimated reliably and are unavoidable. IFRS recognition criteria are generally different from those embodied in tax law and thus Temporary Difference will arise which is the difference between the Carrying Amount of an asset or a liability and its basis for taxation purposes (Tax Base). The principle is that a company will settle its liabilities and recover its assets over time and at that point the tax consequences will crystallize. Thus a change in an accounting standard will often affect the Carrying Value of an asset or a liability which in turn will affect the amount of Temporary Difference between the Carrying Value and the Tax base. This is turn will affect the amount of Deferred Taxation Provision which is the Tax Rate multiplied by the amount of Temporary Differences. The general principle is that Deferred Tax Liabilities should be recognized for all Taxable Temporary Differences and Deferred Tax Assets should be recognized for Deductible Temporary Differences, unused tax loses and unused tax credits to the extent that it is probable that taxable profit will be available against which the deductible temporary differences can be utilized. A deferred tax asset cannot be recognized when it arises from negative goodwill or the initial recognition of an asset or liability other than in a business combination. The carrying value of deferred tax assets should be reviewed at each statement of financial position date and reduced to the extent that it is no longer probable that sufficient taxable profit will be available to allow the benefit of part or all of the deferred tax asset to be utilized. The recognition of deferred tax assets result in the recognition of income in the statement of comprehensive income. This amount cannot be reported in equity as IAS 12 Income Tax does allow only deferred tax to be recognized in equity if the corresponding entry is recognized in equity. ISA 12 Income Tax and IFRS 2 Share Based Payments ISA 12 Income Tax requires the deferred tax on share options to be recognized in the Profit and Loss for the period. The difference between the tax base of the services received ( that is, the amount of tax allowance in future periods) and the carrying value of zero will be the deductible temporary difference, which results in a deferred tax asset. IFRS 2 Share Based Payments says that estimated future deduction should be based on the Option’s intrinsic value at the year end as the value at the exercise date will not be known. The Intrinsic Value is the difference between the Fair Value ( market value) of the share and the Exercise Prize of the share option. It is likely that a deferred tax asset will arise which will be the difference between the tax base of the employee’s service rendered to date and the carrying value which will be zero normally. The recognition of the deferred tax asset should be dealt with on the following basis. a) It the actual of estimated tax deduction is less than or equal to the cumulative recognized expense, then the associated tax benefits are recognized in the Statement of Comprehensive Income. b) If the actual or estimated tax deduction exceeds the cumulative recognized compensation, then the excess tax benefits are recognized directly in a separate component of equity. ISA 12 Income Tax and IAS 17 Leases Plant (asset) acquired under a Finance Lease will be recorded as PPE ( property, plant and equipment) and a corresponding liability for the obligation to pay future rentals. Rentals payable are apportioned between the finance charge and a reduction of the outstanding obligation. A temporary difference will effectively arise between the value of the plant (asset) for accounting purposes and the equivalent of the outstanding obligation as the annual rental payments qualify for Tax Relief. The tax base of the plant (asset) is the amount deducted for tax in future which is zero. The tax base of the liability is the carrying amount less any future tax deductible amount which will give a tax base of zero. Basic Computations Temporary Difference = Carrying Amount – Tax Base Liability ( Taxable Temporary Difference) Temporary Difference = Tax Base – Carrying Amount Asset ( Deductible Temporary Difference) Temporary Difference x Tax Rate = +’ve (Deferred Tax Asset) Temporary Difference x Tax Rate = -’ve (Deferred Tax Liability)