File
advertisement

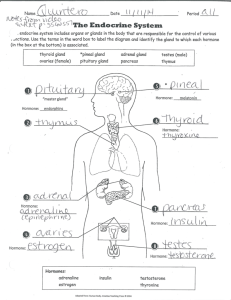
Terminology Review for Test # 2 1. Functional unit of the kidney – nephron 2. An example of a nitrogenous waste – urea, uric acid, creatine 3. Tube connecting kidney to urinary bladder - ureters 4. Blood vessel carrying blood out of glomerulus – efferent arteriole 5. Name of artery entering kidney – renal artery 6. The tubule (duct) leading out of the nephron – collecting duct 7. Hormone controlling amount of water in urine - ADH 8. Sac where urine is stored - bladder 9. Does filtrate normally contain blood cells? - no 10. Part of nephron into which blood is filtered - glomerulus 11. Outer layer of kidney where nephrons are located – renal cortex 12. Inner layer of kidney containing many blood vessels and small tubes – renal medulla 13. Central cavity in kidney where urine is collected – renal pelvis 14. Tube taking urine from bladder to body exterior - urethra 15. The 3 tubules in the nephron where most transport of “wanted” substances back into the blood occurs – PCT, DCT, collecting duct 16. Name for the substance that moves from the glomerulus into the glomerular (Bowman’s) capsule - filtrate 17. Blood vessel carrying blood out of the kidney – renal vein 18. Substance produced by kidneys that stimulates red blood cell production – erythropoietin 19. Vitamin which is activated with help from the kidneys – Vitamin D 20. Master gland of the endocrine system – pituitary gland 21. Hormone which speeds up metabolic rate - thyroxine 22. Hormone which lowers blood glucose levels - insulin 23. Hormone which stimulates the adrenal cortex - ACTH 24. Type of gland which secretes its products directly into the blood – endocrine gland GAS Health Science Prep Page 1 of 4 CHEM 2301 25. Chemical messenger which travels in the blood to a target organ or tissue hormone 26. Hormone which raises blood calcium levels - PTH 27. Hormone which stimulates sperm production – testosterone 28. Gland which has both an endocrine and an exocrine portion - pancreas 29. Gland which is large in children and decreases in size after puberty – thymus gland 30. Gland which produces melatonin - pineal gland 31. Not enough insulin causes this disorder – diabetes mellitus 32. Overproduction of GH in adults causes this disorder - acromegaly 33. Hormone which stimulates ovulation - progesterone 34. Caused by hyposecretion of thyroxine since infancy – congenital hypothroidism 35. Caused by hyposecretion of thyroxine in adults - myxedema 36. An enlarged thyroid gland – hyperthyroidism 37. Cells in the pancreas that produce hormones are called the -? Pancreatic islets 38. Two Canadians who discovered insulin 39. Disorder caused by hyposecretion of hormones from the adrenal cortex – Addison disease 40. Hormones involved in the “fight, flight, fright” response to emergencies – epinephrine, norepinephrine 41. Gland which produces hormones which help the body adapt to long-term stress – corticoids 42. Gland which produces a hormone that regulates the daily rhythm of our bodies – pineal gland 43. Disorder that results from insufficient production of growth hormone in childhood – pituitary dwarfism 44. Lobe of the pituitary that produces LH – anterior pituitary gland 45. Hormone that stimulates the production of testosterone by the testes – LH GAS Health Science Prep Page 2 of 4 CHEM 2301 46. Hormone responsible for the development of male secondary sex characteristics - testosterone 47. Hormone produced by the pancreas that raises blood glucose levels glucagon 48. Disorder caused by hypersecretion of hormones from the adrenal cortex – Crushing syndrome GAS Health Science Prep Page 3 of 4 CHEM 2301 Terminology acromegaly FSH parathyroid glands adrenal cortex giantism pineal gland adrenal medulla glomerular capsule pituitary dwarf adrenaline glomerulus pituitary gland ACTH glucagon posterior lobe (pituitary) ADH goiter progesterone aldosterone gonads prolactin ANH GH proximal convoluted tubule afferent arteriole hormone renal artery anterior lobe (pituitary) hyperthyroidism renal cortex Banting & Best insulin renal medulla calcitonin kidney renal pelvis collecting duct loop of the nephron renal vein congenital hypothyroidism LH testes corticoids MSH testosterone Cushing syndrome melatonin thymosins diabetes insipidus myxedema thymus gland diabetes mellitus nephron thyroid gland distal convoluted tubule nitrogenous waste TSH efferent arteriole noradrenaline thyroxine endocrine gland norepinephrine urea epinephrine ovaries ureter erythropoietin oxytocin urethra estrogen pancreas uric acid exocrine gland pancreatic islets urinary bladder filtrate PTH vitamin D GAS Health Science Prep Page 4 of 4 CHEM 2301