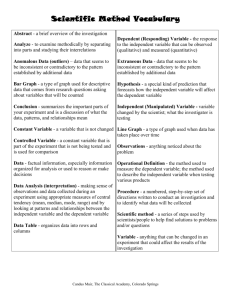
Texas Assessment of Knowledge and Skills Objective 1
advertisement

Curriculum/TAKS Alignment: Correlation of Texas Assessment of Knowledge and Skills and the Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills to the BISD Elementary Science Program Document Contains Alignment of: TAKS Objectives Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills FOSS lessons Critical comments and analysis Prepared by Michael Baldwin Elementary Science Specialist Up-dated August 1, 2006 Curriculum/TAKS Alignment: Correlation of Texas Assessment of Knowledge and Skills and the Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills to the BISD Elementary Science Program Document Contains Alignment of: TAKS Objectives Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills FOSS lessons Critical comments and analysis Yellow tab indicates objective where over 30% of BISD students missed a question Blue tab indicates an objective where FOSS materials could be supplemented Green tab indicates an objective that is developed in the Landforms kit Prepared by Michael Baldwin Elementary Science Specialist 2 2003 - 2006 Science TAKS Objectives Assessed Fifth Grade Objectives and Student Expectations Year 2003 2004 2006 Grade 5 Science Objective 1: Students will demonstrate an understanding of the nature of science. (3.1, 4.1, 5.1) The student conducts field and laboratory investigations following home and school safety procedures and environmentally appropriate and ethical practices. The student is expected to (A) Demonstrate safe practices during field and laboratory 1 25 5, 14, investigations. 35 (5.2) The student uses scientific methods during field and laboratory investigations. The student is expected to (A) Plan and implement descriptive and simple experimental 14, 25, 4 32 investigations including asking well-defined questions, formulating 37 testable hypotheses, and selecting and using equipment and technology; (B) Collect information by observing and measuring; 7, 39 7, 49 (C) Analyze and interpret information to construct reasonable 17, 20 15, 37 18, 20 explanations from direct and indirect evidence; (D) Communicate valid conclusions; and (E) Construct simple graphs, tables, maps, and charts using tools [including computers] to organize, examine, and evaluate information. (3.3, 4.3, 5.3) The student uses critical thinking and scientific problem solving to make informed decisions. The student is expected to (A) Analyze, review, [and critique] scientific explanations, including hypotheses and theories, as to their strengths and weaknesses using scientific evidence and information; (B) Draw inferences based on information [related to promotional materials] for products and services; and (C) Represent the natural world using models and identify their limitations. (5.4) The student knows how to use a variety of tools and methods to conduct science inquiry. The student is expected to (A) Collect and analyze information using tools including calculators, microscopes, [cameras, sound recorders, computers,] hand lenses, rulers, thermometers, compasses, balances, [hot plates,] meter sticks, timing devices, magnets, collecting nets, and safety goggles. 33 29 3, 24 36 10 5 4, 9 13, 38 3, 40 2 31 9, 33 33, 38 Grade 5 Science Objective 2: Students will demonstrate an understanding of the life sciences. (5.10) The student knows that likenesses between offspring and parents can be inherited or learned. The student is expected to (A) Identify traits that are inherited from parent to offspring in plants and animals; and (B) Give examples of learned characteristics that result from the influence of the environment. (5.9) The student knows that adaptations may increase the survival of members of a species. The student is expected to 4, 15 23 17 (A) Compare the adaptive characteristics of species that improve their ability to survive and reproduce in an ecosystem; 10, 28 (B) Analyze and describe adaptive characteristics that result in an organism's unique niche in an ecosystem; and 6 11 (C) Predict some adaptive characteristics required for survival and reproduction by an organism in an ecosystem. 32 36 3 16 (5.6) The student knows that some change occurs in cycles. The student is expected to (C) Describe and compare life cycles of plants and animals. 1 (3.8) The student knows that living organisms need food, water, light, air, a way to dispose of waste, and an environment in which to live. The student is expected to (A) Observe and describe the habitats of organisms within an 30 11 ecosystem; (B) Observe and identify organisms with similar needs that compete 11 with one another for resources such as oxygen, water, food, or space; (C) Describe environmental changes in which some organisms would 18 1 thrive, become ill, or perish; and (D) Describe how living organisms modify their physical environment 5 to meet their needs such as beavers building a dam or humans building a home. (2.9) The student knows that living organisms have basic needs. The student is expected to (A) Ddentify the external characteristics of different kinds of plants and 26 39 animals that allow their needs to be met; and (B) Compare and give examples of the ways living organisms depend 15 8 on each other and on their environments. (5.5) The student knows that a system is a collection of cycles, structures, and processes that interact. The student is expected to (A) Describe some cycles, structures, and processes that are found in 31 37 a simple system; and (B) Describe some interactions that occur in a simple system. 35 8 (4.6) The student knows that change can create recognizable patterns. The student is expected to (A) Identify patterns of change such as in weather, metamorphosis, 6 and objects in the sky. Grade 5 Science Objective 3: Students will demonstrate an understanding of the physical sciences. (5.8) The student knows that energy occurs in many forms. The student is expected to (A) Differentiate among forms of energy including light, heat, electrical, 2 and solar energy; (B) Identify and demonstrate everyday examples of how light is 16 13 reflected, such as from tinted windows, and refracted, such as in cameras, telescopes, and eyeglasses; (C) Demonstrate that electricity can flow in a circuit and can produce 2 19 heat, light, sound, and magnetic effects; and (D) Verify that vibrating an object can produce sound. (5.7) The student knows that matter has physical properties. The student is expected to (A) Classify matter based on its physical properties including magnetism, physical state, and the ability to conduct or insulate heat, electricity, and sound; 36 16 17 34, 38 6 27 (B) Demonstrate that some mixtures maintain the physical properties of their ingredients; (C) Identify changes that can occur in the physical properties of the ingredients of solutions such as dissolving sugar in water; and (D) Observe and measure characteristic properties of substances that remain constant such as boiling points and melting points. 21 22 7 (3.6) The student knows that forces cause change. The student is expected to 4 31, 34 40 32 9 (A) Measure and record changes in the position and direction of the 27 20 motion of an object to which a force such as a push or pull has been applied. (5.5) The student knows that a system is a collection of cycles, structures, and processes that interact. The student is expected to (A) Describe some cycles, structures, and processes that are found in 18 a simple system; and (B) Describe some interactions that occur in a simple system. 8 39 26, 29 (4.6) The student knows that change can create recognizable patterns. The student is expected to (A) Identify patterns of change such as in weather, metamorphosis, and objects in the sky. Grade 5 Science Objective 4: Students will demonstrate an understanding of the earth sciences. (5.12) The student knows that the natural world includes earth materials and objects in the sky. The student is expected to (A) Interpret how land forms are the result of a combination of constructive and destructive forces such as deposition of sediment and weathering; and 12 (C) Identify the physical characteristics of the Earth and compare them to the physical characteristics of the moon. 34 29 (5.11). The student knows that certain past events affect present and future events. The student is expected to (A) Identify and observe actions that require time for changes to be measurable, including growth, erosion, dissolving, weathering, and flow; 24 (B) Draw conclusions about "what happened before" using data such as from tree-growth rings and sedimentary rock sequences; and (C) Identify past events that led to the formation of the Earth's renewable, non-renewable, and inexhaustible resources. (5.6) The student knows that some change occurs in cycles. The student is expected to 24 (A) Identify events and describe changes that occur on a regular basis such as in daily, weekly, lunar, and seasonal cycles; and 25 (B) Identify the significance of the water, carbon, and nitrogen cycles. (4.11) The student knows that the natural world includes earth materials and objects in the sky. The student is expected to (A) Test properties of soils including texture, capacity to retain water, and ability to support life; (B) summarize the effects of the oceans on land; and (C) Identify the Sun as the major source of energy for the Earth and understand its role in the growth of plants, in the creation of winds, and in the water cycle. (3.11) The student knows that the natural world includes earth materials and objects in the sky. The student is expected to (A) Identify and describe the importance of earth materials including rocks, soil, water, and gases of the atmosphere in the local area and classify them as renewable, nonrenewable, or inexhaustible resources; (C) Identify the planets in our solar system and their position in relation to the Sun; and (D) Describe the characteristics of the Sun. (3.6) The student knows that forces cause change. The student is expected to (B) Identify that the surface of the Earth can be changed by forces such as earthquakes and glaciers. 5 23 19 3 27 12, 19 28 28 12 13, 26 22, 30 14 21, 30 (5.5) The student knows that a system is a collection of cycles, structures, and processes that interact. The student is expected to (A) Describe some cycles, structures, and processes that are found in a simple system; and (B) Describe some interactions that occur in a simple system. (4.6) The student knows that change can create recognizable patterns. The student is expected to (A) Identify patterns of change such as in weather, metamorphosis, and objects in the sky. 6 23 22 35 10, 21 Document Key This page contains an explanation of each part of the document that follows. Information on TAKS questions, TEKS, % of students picking each answer, and FOSS correlations are provided. Texas Assessment of Knowledge and Skills (TEKS) Objective 1: Students will demonstrate an understanding of the nature of science. TEKS Student Student expectation: Expectation (3.1, 4.1, 5.1) The student conducts field and laboratory investigations following home and school safety procedures and environmentally appropriate and ethical practices. TAKS Test item (A) Student expectation: demonstrate safe practices during field and laboratory from 2003 & 2004 investigations TAKS Test Items: 2003 2004 1. Which of the following would be safe to do during a lab activity? A Running in the classroom 0% B Leaving a water spill on the floor 0% C Touching hot surfaces 0% D* Following lab rules 99% 25 Which of the senses must be protected when doing an activity concerning a solar eclipse? A Touch 12% B Taste 8% C* Sight 75% D Smell 5% % of students in BISD who picked each response Study Guide/TAKS Information Booklet: Students are doing an experiment in science class. Which piece of equipment will best protect the students’ eyes during the experiment? TAKS item from either the TAKS study guide or information booklet FOSS Correlation for TEKS objective FOSS Modules: FOSS Module Solar Energy (Grade 5)Overview Mixtures and Solutions (Grade 5) FOSS Investigation/part Overview(pg 17): Safety in the Classroom Overview (pg. 17) Investigation 1/ Part 1 Investigation 2/Part 4 Investigation 4/Part 1 Investigation 4/Part 3 7 FOSS Assessment Texas Assessment of Knowledge and Skills Objective 1: Students will demonstrate an understanding of the nature of science. Student expectation: (3.1, 4.1, 5.1) The student conducts field and laboratory investigations following home and school safety procedures and environmentally appropriate and ethical practices. (A) Student expectation: demonstrate safe practices during field and laboratory investigations 2003 2004 1. Which of the following would be safe to do during a lab activity? A Running in the classroom 0% B Leaving a water spill on the floor 0% C Touching hot surfaces 0% D* Following lab rules 99% 25 Which of the senses must be protected when doing an activity concerning a solar eclipse? A Touch 12% B Taste 8% C* Sight 75% D Smell 5% % of students in BISD who picked each response 2006 TAKS 14 Students placed some frogs in a tank to study their behavior. What should the students do for safety reasons after feeding the frogs? F Wash the floor with soap and water 0% G* Wash their hands with soap and water 93% H Rinse the frog tank with cool water 4% J Rinse the frogs with cool water 2% Science Activity Students mixed a spoonful of vinegar with a small amount of baking soda in a bowl. They wrote a description of what they observed. 5 Which of these should the students avoid while doing this activity? A Using a metal teaspoon 3% B Using a plastic bowl 4% C Stirring the vinegar 7% D* Tasting the mixture 86% 35 This laboratory symbol shows that when performing an experiment, students need to — A avoid electricity 0% B* protect clothing 93% C keep away from food 4% D protect equipment 2% Study Guide/TAKS Information Booklet: Students are doing an experiment in science class. Which piece of equipment will best protect the students’ eyes during the experiment? 8 When entering the classroom, a student sees a lab setup. What should the student do next? A Turn on the water faucet B Cut the leaves into small pieces to prepare for the experiment C Organize the lab equipment so everything is ready to begin D* Wait for the teacher to give instructions (A) Student expectation: demonstrate safe practices during field and laboratory investigations(continued) FOSS Modules: FOSS Module Solar Energy (Grade 5)Overview Mixtures and Solutions (Grade 5) Environments (Grade 5) Models and Designs (Grade 5) FOSS Investigation/part Overview(pg 17): Safety in the Classroom FOSS Assessment Overview (pg. 17) Investigation 1/ Part 1 Investigation 2/Part 4 Investigation 4/Part 1 Investigation 4/Part 3 Overview (pg. 17) Investigation 4/Part 2 Overview (pg. 17) Investigation 2/Part 1 Investigation 3/Part 2 Investigation 4/Part 1 **Program needs supplemental assessments for Science Safety. 5.2 The student uses the scientific methods during field and laboratory investigations. (A) plan and implement descriptive and simple experimental investigations including asking well-defined questions, formulating testable hypotheses, and selecting and using equipment and technology. TAKS Test Items: 2003 2004 4 On a warm day water was accidentally spilled onto a metal tabletop. Later in the day, the water was gone. The most likely explanation is that someone wiped the water up or that — F germs drank the water 0% G the table absorbed the water 7% H all the water spilled onto the floor 3% J* the water evaporated into the air 90% 14 Which of these questions can be answered from the results of this experiment? F Do beans need light in order to grow? 9% G Can beans grow faster in groups of eight? 2% H* Does seawater affect bean growth? 72% J How much water is needed for beans to grow? 16% 9 25 Which of these would be the best way to find whether a softball will roll down a hill faster than a basketball? A Determining which of the balls has the greater mass 16% B* Observing the balls rolling down the same section of a hill at the same time 61% C Throwing the balls into the air at the same time to see which goes higher 4% D Dropping the balls from the same height and observing which hits the ground first 21% Students need practice designing experiments. (FOSS) Content covered well in Insects and Structures of Life kits. ants 37 This experiment was probably set up to answer which of the following questions? A What is the mass of the ants? 1% B* Will ants go to a dark or a light area? 97% C How many kinds of ants are there? 1% D Where do ants get food? 1% Study Guide/TAKS Information Booklet: Kimchi is a Korean food made from cabbage, garlic, pepper, and salt. Some students made kimchi as part of a social studies lesson. They layered the ingredients in a two-liter jar until it was full. Then the students sealed the jar. After a few hours the jar began to fill with liquid. The students guessed that the liquid was coming from the cabbage. In their science class the students decided that they would conduct an investigation to find out what caused the liquid to leave the cabbage. Which change in the investigation would have best helped the students find out what caused the liquid to leave the cabbage? A Using jars of different sizes B Using different amounts of cabbage C Leaving out one ingredient at a time D Replacing the cabbage with other vegetables 10 (Continued) 5.2 The student uses the scientific methods during field and laboratory investigations. (A) plan and implement descriptive and simple experimental investigations including asking well-defined questions, formulating testable hypotheses, and selecting and using equipment and technology. FOSS Modules: FOSS Module Solar Energy (Grade 5) FOSS Investigation/Part Investigation 3/ Part 1 Investigation 4/Part 3 Mixtures and Solutions (Grade 5) Investigation 4/ Part 4 Investigation 2/ Part 3 Investigation 3/Part 3 Investigation 4/ Part 4 Environments (Grade 5) Investigation 2/ Part 1, 2, and 3 Investigation 3/Part 1, 2, and 3 Investigation 4/ Part 1, 2, and 3 Investigation 5/ Part 1, 2, and 3 Investigation 6/ Part 1, 2, and 3 Models and Designs (Grade 5) Investigation 3/ Part 1, 2 and 3 Investigation 4/Part 1, 2 and 3 11 FOSS Assessment Investigation 3/Part 1, Observation or Journal Investigation 4/ Part 3, Observation or Journal Investigation 4/ Part 4 SS # 25 Investigation 2/Part 3 Journal Investigation 3/ Part 3 Journal Investigation 4/Part 4 SS # 14 End of Module Performance Assessment SS #’s 7 & 8 End of Module Assessment #’s 11, 14 Investigation 2/Part 4, SS # 7 Investigation 5/Part 3, Journal Investigation 5/Part 3, SS #18 Investigation 6/ Part 3, SS #21 End-of-Module Assessment #’s 17, 19, 23 Portfolio (see FOSS rubric) Investigation 2/Part 2, rubric Investigation 3/Part 2, SS # 11 Investigation 4/ Part 1, SS # 12 Investigation 4/Part 2, SS # 14 Investigation 4: No. 16 Investigation 4: Presentation rubric End-of-Module Assessment #’s 5, 6, 17 5.2 The student uses the scientific methods during field and laboratory investigations. (B) collect information by observing and measuring TAKS Test Items: 2003 7 What is the approximate diameter of this coin? A 2 millimeters 12% B* 2 centimeters 84% C 2 meters 3% D 2 kilometers 1% 39 What is the mass of these rocks? A 10 grams 28% B* 17 grams 14% C 19 grams 28% D 22 grams 29% Students need practice using balances. (FOSS) 2004 7 Making imprints of objects in clay is most useful for learning about — A weathering 4% B* fossils 74% C renewable resources 14% D the rock cycle 8% 40 The graph shows how many individuals were found in a beetle colony. How many more beetles than mealworms were found in this colony? F5 3% G* 8 91% H 14 2% J 32 4% Study Guide Using the centimeter ruler, measure the length of this leaf from Point A to Point B to the nearest centimeter. Record and bubble in your answer on the answer document. (continued) 12 5.2 The student uses the scientific methods during field and laboratory investigations. (B) collect information by observing and measuring FOSS Modules: FOSS Module Solar Energy (Grade 5) (temperature) Mixtures and Solutions (Grade 5) (mass, volume) Environments (Grade 5) (length, volume) Models and Designs (Grade 5) (length) FOSS Investigation/Part Investigation 2/Part 1 Investigation 2/Part 2 Investigation 3/Part 1 Investigation 3/Part 2 Investigation 1/Part 2 Investigation 2/ Part 1 Investigation 3/Part 1 Investigation 4/Part 1 Investigation 1/Math Extension Investigation 2/Math Extension Investigation 3/Part 2 Investigation 3/Part 3 Investigation 4/Math Extension Investigation 3/Part 2 Investigation 3/Part 3 Investigation 3/Math Extension, SS# 20 13 FOSS Assessment Investigation 2/Part 1, SS# 7, 8 Investigation 2/Part 2, SS# 10 Investigation 3/Part 1,2, 3, SS# 14, 15, 16 Investigation 4/Part 1 SS#, 21 End-of Module Assessment #’s 1, 11 Investigation 1/Part 2, SS# 4 Investigation 2/Part 1, SS# 8 Investigation 3/Part 2, SS# 12, 13 Investigation 3/Part 2, SS# 10 Investigation 3/Part 3, SS# 12 Investigation 4/Math Extension, SS 26 End-of-Module Assessment, # 12 5.2 The student uses the scientific methods during field and laboratory investigations. (C) analyze and interpret information to construct reasonable explanations from direct and indirect evidence; TAKS Test Items: 2003 2004 17 This diagram represents water in a container. What process is taking place? A Freezing 7% B Condensation 17% C Melting 4% D* Evaporation 72% 20 This plastic rain gauge is shown before and after a rainstorm. About how much rain in centimeters fell in the rain gauge during the storm? Record and bubble in your answer on the answer document. (66% correct) Students need practice measuring (FOSS, mathematics connections) 15 This table shows the movement of a snail over an 8-hour period. If the snail traveled at the same pace the entire time, how far did it travel in 6 hours? A 130 cm 2% B* 135 cm 88% C 140 cm 6% D 145 cm 5% 37 The table shows the time it took to freeze water in two different salt solutions with different salt content. According to the table — A freezing rates are the same in each trial 3% B* water with more salt takes longer to freeze 80% C water loses heat at a rate of 1°C per minute 7% D salt dissolves more quickly in small amounts of water 10% 2006 TAKS Test 18 This diagram shows some stages in the termite life cycle. Which of these is supported by the information in the diagram? F Some nymphs have wings. 1% G Some larvae lay eggs. 1% H Eggs develop into three kinds of larvae. 5% J* The queen produces the eggs. 94% 14 2006 TAKS Test (Objective 5.2 C continued) 20 The graph shows air temperatures taken at noon each day for a week. What is the difference between the highest and the lowest temperature? Record and bubble in your answer to the nearest degree on the answer document. (Grid able answer 85% correct) Paper Towel� Brand Mass of Dry� Mass of Wet� Paper Towel� (g) Paper Towel� (g) 2 4 56 X 3 4 62 Y 3 4 70 Z 2 4 38 Number of� Sheets Used W� FOSS Modules: FOSS Module Solar Energy (Grade 5) FOSS Investigation/Part Investigation 1: Part 2 Investigation 4/Part 2 Investigation 1/Math Extension Investigation 2/Math Extension Mixtures and Solutions (Grade 5) Investigation 2/Part 2 Investigation 2/Part 3 Investigation 3/Part 1 Investigation 4/Part 1 Environments (Grade 5) Investigation 3/Part 2 Investigation 4/Part 1 Models and Designs (Grade 5) Investigation 1/ Part1, 2, 3 Investigation 2/ Part 1, 2, 3 Investigation 3/ Part 1, 2, 3 15 32 Equal masses of paper towel were used to soak up water from a cup. Which question can be answered from the information above? F Which paper towel is the best buy? 9% G* Which paper towel is most absorbent? 86% H Which paper towel is the most colorful? 1% J Which paper towel is safest for the environment? 4% FOSS Assessment Investigation 1/Part 2 SS# 5 Investigation 4/Part 2, SS# 23 Investigation 4/Math Extension, SS# 35 Investigation 2/Math Extension SS# 33 End-of-Module Performance Assessment End-of-Module Assessment #’s 14, 15, 16,19 Investigation 2/Part 2, SS# 9 Investigation 2/Part 3, SS# 10 Investigation 3/Part 1, SS# 11 Investigation 4/Part 1, SS# 15 Investigation 4/Math Extension SS# 23 End-of-Module Assessment # 11 Investigation 3/Part 2 SS# 11 Investigation 4/Part 1 SS#14 Investigation 3/Math Extension SS# 25 Investigation 4/Math Extension SS#26 Investigation 5/Math Extension SS#27 Investigation 6/Math Extension SS#28 Investigation 3/Home School Connection SS# 31 End-of-Module Assessment #’s 8, 12,, 16, 17, 20 Investigation 1/Part 2, SS# 4 Investigation 2/Part 1, SS# 8 Investigation 2/Math Extension SS #19 5.2 The student uses the scientific methods during field and laboratory investigations. (D) communicate valid conclusions; and TAKS Test Items: 2003 2004 33 What conclusion can be drawn from this graph? A* A peach contains a lower percent of water than lettuce. 88% B Lettuce contains a lower percent of water than bread. 4% C A melon contains a higher percent of water than the other foods. 6% D Bread contains the highest percent of water. 2% FOSS kits develop concept very well at all grade levels. 3 The chart shows data collected when potted plants were placed in sunlight for different lengths of time. Which conclusion is best supported by the data? A The plants that received 4 hours of sunlight a day had the most leaves. 3% B The plants given less than 6 hours of sunlight a day had the thickest stems. 2% C* The plants that received 8 hours of sunlight a day grew the most. 84% D The plants given more than 10 hours of sunlight a day wilted. 6% 24 In which container will the water evaporate most quickly? 13% 3% 82% 2% 16 (continued) 5.2 The student uses the scientific methods during field and laboratory investigations. (D) communicate valid conclusions; and 2006 TAKS Test 36 Which of the following does the information in the picture support? F Candles cause fire. 5% G Corks put out fire. 2% H Fire warms glass. 8% J* Fire needs air. 86% Study Guide/TAKS Information Booklet: What do the graphs suggest about the average yearly rainfall and the average yearly temperature in Waco, Texas? A Years with lower average rainfall are warmer. B Years with lower average temperature have more rainfall. C The average temperature is not related to the average rainfall. D The average rainfall and the average temperature do not depend on the number of cloudy days. FOSS kits develop concept very well at all grade levels. 17 (continued) 5.2 The student uses the scientific methods during field and laboratory investigations. (D) communicate valid conclusions; and FOSS Modules: FOSS Module Solar Energy (Grade 5) FOSS Investigation/Part Investigation 2/Part 2 Investigation 3/Part 2 Investigation 4/Part 4 Mixtures and Solutions (Grade 5) Investigation 1/Part 1 Investigation 1/Part 2 Investigation 2/Part 2 Investigation 3/Part 2 Investigation 4/Part 2 Investigation 4/Part 4 Environments (Grade 5) Investigation 2/ Part 2 Investigation 3/Part 2 Investigation 4/Part 2 Investigation 6/Part 2, 4 Models and Designs (Grade 5) Investigation 1/Part 4 Investigation 3/Part 3 Investigation 4/Part 1 Investigation 4/Part 2 Investigation 4/Part 3 FOSS kits develop concept very well at all grade levels. 18 FOSS Assessment Investigation 2/Part 2, SS# 12 Investigation 3/Part 2, SS# 18 Investigation 4/Part 4, Presentation Investigation 1/Math Extension, SS# 31 Investigation 2/Math Extension, SS# 33 End-of-Module Assessment/Performance Assessment End-of Module Assessment #’s 3, 19 Investigation 1/Part 1, SS# 3 Investigation 1/Part 2, SS# 4 & 5 Investigation 2/Part 2, SS# 9 Investigation 3/Part 2, SS# 13 Investigation 4/Part 2, SS# 16 Investigation 4/Presentation Investigation 3/Math Extension, SS# 22 Investigation 4/Math Extension, SS# 23 End-of-Module Assessment, #’s 11, 12, 15 Investigation 2/Part 2, SS# 6 Investigation 3/Part 2, SS# 11 Investigation 4/Part 2, SS# 16 Investigation 6/Part 2, SS# 19 Investigation 6/Part 4 Presentation Investigation1/Math Extension SS# 23 Investigation 2/Math Extension SS# 24 Investigation 3/Math Extension SS# 25 Investigation 6/Math Extension, SS# 28 Home/School Connection SS# 29 Home/School Connection, SS# 31 End-of-Module Assessment #’s 10, 12, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 22, 25, 27 Investigation 1/Part 4, SS# 4 Investigation 4/Part 1, SS#12 Investigation 4/Part 2, SS# 14 Investigation 4/Part 3, Presentation Investigation 1/Math Extension SS# 18 Investigation 4/Math Extension SS# 21 End-of-Module Performance Assessment End-of-Module Assessment #’s 3, 18 Portfolio Rubric, Assessment sheet # 14 5.2 The student uses the scientific methods during field and laboratory investigations. (E) construct simple graphs, tables, maps, and charts using tools [including computers] to organize, examine, and evaluate information. 2003 TAKS Test: 29 An uncovered bowl of water was placed in the refrigerator. Each day the amount of water left in the bowl was recorded. Which graph probably shows the results? 28% 28% 29% 14% Study Guide/TAKS Information Booklet: Students need to collect data and practice making and interpreting graphs. (FOSS, mathematics connection) A student grew two plants in science class. The student recorded observations in the table above. Based on the student’s observations, what is the most likely reason that Plant 1 grew taller than Plant 2? A Plant 1 received more sunlight than Plant 2. B Plant 1 received more fresh air than Plant 2. C Plant 1 had more space to grow than Plant 2. D Plant 1 required less water to grow than Plant 2. 19 (continued) 5.2 The student uses the scientific methods during field and laboratory investigations. (E) construct simple graphs, tables, maps, and charts using tools [including computers] to organize, examine, and evaluate information. FOSS Modules: FOSS Module Solar Energy (Grade 5) FOSS Investigation/Part Investigation 1/Part 2 Investigation 2/Part 2 Investigation 3/Part 2 Mixtures and Solutions (Grade 5) Investigation 2/Part 3 Investigation3/Part 3 Investigation 4/Part 4 Environments (Grade 5) Investigation 1/Part 1 Investigation 2 Investigation 3 Investigation 4/Part 1 Investigation 4/Part 2 Investigation 5/Part 2 Investigation 5/Part 3 Investigation 6/Part 2 Investigation 6/Part 3 Models and Designs (Grade 5) Investigation 1/Part 1 Investigation 1/Part 2 Investigation 2/Part 1 20 FOSS Assessment Investigation 1/Part 2, SS# 5, 11 Investigation 2/Part 2, SS# 12 Investigation3/Part 2, SS# 17, 18 Investigation 1/Math Extension SS# 31 Investigation 2/Math Extension SS# 33 Investigation 4/Math Extension SS# 35 Investigation 1/Home/School Connection Investigation 2/Home/School Connection Investigation 3/Home/School Connection End-of-Module Performance Assessment End-of Module #’s 3, 14, 16 Investigation 2/Part 3, SS#10 Investigation 2/Math Extension, SS#21 Investigation 3/Part 3, Journal Investigation 3/Math Extension, SS# 22 Investigation 4/Part 4, Journal Investigation 4/Math Extension, SS# 23 End-of-Module #’s 11, 15 Investigation 1/Part 1, SS# 3 Investigation 1/Part 1, Journal Investigation 2/Part 1, Journal Investigation 2/Part 2, Journal Investigation 2/Part 3, Journal Investigation 2/Part 4, Journal Investigation 3/Part 1, Journal Investigation 3/Part 2, SS# 10 Investigation 3/Part 3, SS# 12 Investigation 3/Math Extension, SS# 25 Investigation 3/Home-School, SS# 31 Investigation 4/Part 1, SS#14 Investigation 4/Part 2, SS# 15 Investigation 5/Part 2, SS# 17 Investigation 5/Part 3, Journal Investigation 6/Part 2, SS# 10, 12 Investigation 6/Part 3, Journal Investigation 6/Math Extension, Journal End-of-Module, #’s 8, 12, 20, 22, 27 Investigation 1/Part 1, Journal Investigation 1/Part 2, SS# 4 Investigation 2/Part 1, SS# 8 Investigation 3/Math Extension, SS# 20 End-of-Module, #’s 2, 4, 18 (3.3, 4.3, 5.3) The student uses critical thinking and scientific problem solving to make informed decisions. The student is expected to (A) analyze, review, [and critique] scientific explanations, including hypotheses and theories, as to their strengths and weaknesses using scientific evidence and information; 2006 TAKS 10 A plant that was kept inside a house all winter was placed outside in full sunlight in the spring. The leaves of this plant soon died, and new leaves grew in their place. The new leaves were greener and thicker. Which hypothesis is best supported by this information? F Plants can learn to stay healthy. 3% G* Plants can adapt to some changes. 79% H Plants can change leaves at any time. 9% J Plants can produce weather changes. 9% Study Guide: Which statement is best supported by fossil evidence? A The types of animals on Earth have changed over time. B Human activities have been the main cause of all extinctions. C The environment has remained the same over time. D Natural disasters have sometimes destroyed all life on Earth. FOSS Modules: FOSS Module FOSS Investigation/Part FOSS Assessment Measurement Investigation 1/Part 1 Investigation 2/Part 1 Investigation 3/Part 1 Investigation 4/Part 1 Earth Materials Investigation 2/Part 2 Structures of Life (Grade 3) Investigation 2/Part 2 Electricity & Magnetism (Grade 3) (Grade 3) Human Body (Grade 4) Investigation 1/Part 3 Investigation 1/Part 1, Class Discussion Investigation 2/Part 1, Journal Investigation 3/Part 1, Journal Investigation 4/Part 1, Journal End-of-Module # 30 Investigation 2/Part 2, SS# 15 End-of-Module #16 Investigation 2/Part 2, SS# 8 End-of-Module, # 19 Investigation 1/Part 3, SS# 5 Physics of Sound Investigation 2/Part 3 Investigation 3/Part 1 Investigation 1/Part 3 Investigation 3/Part 2 Water Investigation 2/Part 3 Investigation 3/Part 2 Solar Energy (Grade 5) Mixtures and Solutions (Grade 5) Investigation 2/Part 2 Investigation 1/Part 2 Investigation 2/Part 2 Investigation 4/Part 2 Environments (Grade 5) Investigation 1/Part 2 Investigation 2/Part 2 Investigation 3/Part 2 Investigation 4/Part 2 Investigation 6/Part 2 Investigation 2/Part 3, SS# 12 Investigation 3/Part 2, SS# 17 End-of-Module # 23 Investigation 3/Part 3, SS# 10 Investigation 3/Part 1, SS# 15 Investigation 1/Part 3, SS# 5 Investigation 3/Part 2, SS# 11 End-of-Module # 22 Investigation 2/Part 2, SS# 12 Investigation 1/Part 2, SS# 5 Investigation 2/Part 2, SS# 9 Investigation 4/Part 2, SS# 16 End-of-Module, #’s 13, 15 Investigation 1/Part 2, SS# 4 Investigation 2/Part 2, SS# 6 Investigation 3/Part 2, SS# 11 Investigation 4/Part 2, SS# 16 Investigation 6/Part 2, SS# 19 End-of-Module, #’s 17, 22, 24 End-of-Module # 18 Models and Designs (Grade 5) FOSS kits develop concept very well at all grade levels. 21 (3.3, 4.3, 5.3) The student uses critical thinking and scientific problem solving to make informed decisions. The student is expected to (B) draw inferences based on information [related to promotional materials] for products and services; and TAKS Test Items: 2003 2004 5 Which of these foods would be the best choice for someone on a low-fat, low-sodium diet? A Q 14% B R 1% C * S 84% D T 1% Fact and opinion questions (Language arts connection) 13 The picture shows a bottle of the sunscreen FSC. Which of these statements indicates how well this product helps prevent skin damage? A Great for all outdoor activities 11% B Contains the finest ingredients 9% C* Sun protection factor (SPF) 30 78% D Money-back guarantee 3% 38 An advertisement for a breakfast food states that the product is “the healthiest choice.” Which of these could show that this is a valid claim? F The bar code 4% G* The nutrition information 81% H The number of grams 11% J The pictures on the box 3% 2006 TAKS 3 The table indicates the amount of time that four different brands of batteries worked in a flashlight. Which of the following statements is supported by this information? A Brand L caused the light to shine farther than the other brands tested. 1% B* Brand M lasted longer than the other brands tested. 98% C Brand N gave off a stronger light than the other brands tested. 1% D Brand O was more expensive than the other brands tested. 1% 22 5.3 B continued: 2006 TAKS Test Item: 40 The picture shows the label on a carton of orange juice. Which of these is supported by the information on the label? F Orange juice turns all vitamins into vitamin C. 4% G* Orange juice provides vitamin C to the body. 90% H Orange juice removes vitamin C from the body. 1% J Orange juice causes the body to need vitamin C. 4% FOSS Modules: FOSS Module Measurement Electricity & Magnetism (Grade 3) (Grade 3) Solar Energy (Grade 5) Mixtures and Solutions (Grade 5) Models and Designs (Grade 5) FOSS Investigation/Part Science Story “Measurement in the Marketplace” Investigation 2/Math Extension Investigation 3/Part 3 Investigation 3/Math Extension Investigation 3/Home-School Investigation 3/ Math Extension Investigation 3/Science Extension Investigation 2/Art Extension 23 FOSS Assessment Investigation 2/Math Extension, SS# 30 Investigation 3/Part 3 SS # 17 Investigation 3/Math Extension, SS# 34 Investigation 3/Home-School, SS# 38 (3.3, 4.3, 5.3) The student uses critical thinking and scientific problem solving to make informed decisions. The student is expected to (C) represent the natural world using models and identify their limitations. 2004 TAKS Test: 2 In a model of our solar system, a tennis ball is used to represent Earth. A marble would be a good representation of Mercury in this model because compared to Earth, Mercury is — F brighter 5% G lighter 3% (3rd Grade content) H* smaller 87% J more solid 6% 2006 TAKS Test: 31 This model can be used to show how the moon moves around Earth. This model also shows all of the following EXCEPT — A* the amount of light Earth reflects 78% B the land areas of Earth and the moon 7% C how the moon makes a revolution 9% D how Earth and the moon compare in size 7% Study Guide/TAKS Information Booklet: This model is an incomplete food web. This drawing could be made more complete by — A* including producers, such as grasses B changing the direction of the arrows C including nonliving things, such as rocks D connecting each organism to all the other organisms 24 (continued) (3.3, 4.3, 5.3) The student uses critical thinking and scientific problem solving to make informed decisions. The student is expected to (C) represent the natural world using models and identify their limitations. The drawing of the frog’s life cycle is a type of model. This model could be improved by — A reversing the direction of the arrows B switching the froglet and the young frog C numbering the stages, starting with the tadpoles D* showing how much time passes between the stages FOSS Modules: FOSS Module Earth Materials Structures of Life (Grade 3) Electricity & Magnetism (Grade 3) Human Body (Grade 4) Solar Energy (Grade 5) Environments (Grade 5) Models and Designs (Grade 5) FOSS Investigation/part Investigation 1/Part 1 Investigation 1/Part 3 Investigation 3/Part 3 Investigation 4/Part 2 Investigation 3/Part 1 Investigation 3/Part 2 Investigation 3/Part 3 Investigation 1/Part 2 Investigation 2/Part 2 Investigation 3/Part 1 Investigation 4 Investigation 1/Part 1 Investigation 4 Investigation 1/Parts 1-3 Investigation 2/Parts 1-3 Investigation 3/Parts 1-3 Investigation 4/Parts 1-3 Science Stories: Everyday Mysteries FOSS kits develop concept very well at all grade levels. 25 FOSS Assessment End-of-Module # 21 Investigation 3/Part 3 SS # 17 Investigation 4/Part 2, SS# 19 End-of-Module #16-17 Response #18, 19, 22 Investigation 1, SS# 4 Investigation 2, SS# 8 Investigation 3, SS# 11 Investigation 4, SS# 14 End-of-Module, #’s 2, 6, 7, 8, 10, 18, (5.4) The student knows how to use a variety of tools and methods to conduct science inquiry. The student is expected to (A) collect and analyze information using tools including calculators, microscopes, [cameras, sound recorders, computers,] hand lenses, rulers, thermometers, compasses, balances, [hot plates,] meter sticks, timing devices, magnets, collecting nets, and safety goggles. TAKS Test Items 2003 2004 4 What tool is used to find the temperature at which water boils? 5% 0% 9 Earthworm B is how many centimeters longer than Earthworm A? A 1.5 cm 5% B* 2.0 cm 81% C 3.0 cm 5% D 5.5 cm 9% 0% 92% 33 The pans in this balance are at the same height. According to this information, the mass of the rock sample is — A* 170 grams 76% B 180 grams 3% C 200 grams 10% D 230 grams 10% 9 Which tools are needed to find how mass affects the distance these boxes will slide? A Ramp, thermometer 4% B* Balance, ruler 76% C Stopwatch, ruler 13% D Balance, string 7% 2006 TAKS Items 38 A balance would be the best tool for measuring which of the following? F The texture of soil 1% G The length of a stick 4% H* The mass of a rock 94% J The color of a leaf 1% 26 (5.4 A Continued) 2006 TAKS Test Items continued 33 A diagram of an oak tree is shown above. What is the height of the tree? A 9 meters 11% B 11 meters 1% C* 18 meters 87% D 22 meters 1% FOSS Modules: FOSS Module Solar Energy (Grade 5) Mixtures and Solutions (Grade 5) Environments (Grade 5) Models and Designs (Grade 5) Equipment Used Compasses, magnetic Flashlights Clock or watch Earth globe Evaporating dishes Balances Hand lenses Fish net Beakers Meter tape balances Beakers Scissors Funnel motors Plastic cups (250 ml) Thermometers Ruler Metric spoons Beakers syringes Aquarium Hand lenses Thermometer Meter tapes Pliers d-cells Equipment not included: calculators, microscopes, and safety goggles. 27 Objective 2: The Student will demonstrate an understanding of the life sciences. (5.10) The student knows that likenesses between offspring and parents can be inherited or learned. The student is expected to (A) identify traits that are inherited from parent to offspring in plants and animals; and 2006 TAKS Africa is home to a frog that catches insects in a very unusual way. This frog, called the African clawed frog, has moist skin and is found in murky ponds and other wet environments. When the dry season starts, the frog burrows into the mud to remain moist. It stays in the burrow without eating or moving until rainfall returns. This may take up to a year. This frog cannot see well in the water or in the dark. Still, it is very successful at catching insects. When an insect lands on the surface of a pond, waves are sent across the water. The African clawed frog has many tiny detectors that sense where the waves are coming from. Many scientists believe that this frog can tell the size of the insect making the waves. And when two or more waves are made at the same time, it can tell exactly where each wave is coming from. Was that a wave? Supper’s ready! 15 Which of the following is an inherited trait in African clawed frogs? A* The location of wave detectors on the frogs 80% B The location of the frogs in a pond 11% C The number of insects eaten by the frogs in an hour 5% D The number of times the frogs look for insects in an hour 4% FOSS Modules: FOSS Module Insects (Grade 2) Structures of Life (Grade 3) Environments (Grade 5) FOSS Investigation/part Science Stories: “Variation” Investigation 2/Part 3 Investigation 3/Part 3 Investigation 3/Part 4 Investigation 4/Part 2 Science Stories: Barbara McClintock Answering Kids’ Questions Life Cycle of a Crayfish Crayfish, Snails, and Kids Science Stories: Beetles The Darkling Beetle Isopod 28 4 Which of the following characteristics of a field mouse is most likely inherited from its parents? F* Brown fur 86% G Torn ear 2% H Scar on its leg 3% J Chipped tooth 8% FOSS Assessment Investigation 2/Part 3 Investigation 3/Part 3 SS# 15 Investigation 3/Part 4 Investigation 4/Part 2, Journal End-of-Module Performance Assessment End-of-Module #’s 6, 7, (5.10) The student knows that likenesses between offspring and parents can be inherited or learned. The student is expected to (B) give examples of learned characteristics that result from the influence of the environment. TAKS Test Items 2003 23 Raccoons living in cities have learned to open lids of garbage cans. This is an example of an animal — A* adapting to its environment 77% B inheriting the ability to change its diet 6% C being tamed by humans 14% D becoming a plant eater 3% 2004 17 Which of these is an example of a learned behavior? 4% 89% 2% 6% Study Guide/TAKS Information Booklet: Coyotes learn some of their behaviors as they move around in their environment. Which behavior is most likely learned? A Running B Drinking water C* Avoiding cacti D Sleeping FOSS Modules: FOSS Module FOSS Investigation/part Structures of Life (Grade 3) Investigation 3/Part 3 Investigation 3/Part 4 Investigation 4/Part 3 Human Body (Grade 4) Science Stories: Space Race Smart Training FOSS Assessment Investigation 3/Part 4 SS# 14 Investigation4/Part 3 SS#’s 17, 18 End-of-Module Performance Assessment End-of-Module #’s 12, 17 Environments (Grade 5) Behaviors are studied more in 3rd Grade Structures of Life (Grade 3). Learned behaviors are characteristic of higher organisms with large brains. In most animals, behaviors are significantly instinctual (they are not learned) or they are a combination of learned and instinct. To teach this concept it would be better to talk about people or possibly pets. Students would be best prepared for these types of questions through news and science articles discussing the behaviors of many different animals. 29 (5.9) The student knows that adaptations may increase the survival of members of a species. The student is expected to (A) compare the adaptive characteristics of species that improve their ability to survive and reproduce in an ecosystem; 2003 TAKS Test Items: Prairie Animals 10 Which part of a jackrabbit most helps it escape predators? F* Long legs 96% G Thick fur 1% H Short tail 1% J Small head 2% 28 The African baobab tree has a huge trunk that can store as much as 100 kiloliters of water. This adaptation would be an advantage in a climate that is very — Students need to read F cold 10% G* dry 53% and discuss articles about H windy 8% many different plants J sunny 28% and animals. 2006 TAKS Test Africa is home to a frog that catches insects in a very unusual way. This frog, called the African clawed frog, has moist skin and is found in murky ponds and other wet environments. When the dry season starts, the frog burrows into the mud to remain moist. It stays in the burrow without eating or moving until rainfall returns. This may take up to a year. This frog cannot see well in the water or in the dark. Still, it is very successful at catching insects. When an insect lands on the surface of a pond, waves are sent across the water. The African clawed frog has many tiny detectors that sense where the waves are coming from. Many scientists believe that this frog can tell the size of the insect making the waves. And when two or more waves are made at the same time, it can tell exactly where each wave is coming from. Was that a wave? Supper’s ready! 16 The African clawed frog has many adaptations that help it survive. Which of these adaptations helps it survive changes in its environment? F The ability to see color 2% G The ability to detect waves 38% H* The ability to burrow 48% J The ability to eat 11% Study Guide/Information Booklet: Which animal would most likely be found in a habitat with high temperatures, few plants, and little rainfall? 30 (continued) (5.9) The student knows that adaptations may increase the survival of members of a species. The student is expected to (A) compare the adaptive characteristics of species that improve their ability to survive and reproduce in an ecosystem; Study Guide/Information Booklet: Which of these adaptations makes a tadpole more suited to live in water than on land? A Eyes B Legs C* Gills D Lungs FOSS Modules: FOSS Module Structures of Life (Grade 3) Human Body (Grade 4) Water (Grade 4) Environments (Grade 5) FOSS Investigation/part Investigation 1/Parts 1-3 Investigation 3/Parts 1-4 Investigation 4/Parts 1-4 Science Stories: Life on Earth Crayfish, Snails, and Kids FOSS Assessment Investigation 1/Parts 1-3, Journal, SS#’s 2, 3, Investigation 2/ Parts 1-3, Journal, SS#’s 7, 9 Investigation 3/Parts 1-4, Journal, SS#’s 11, 15 Investigation 4/Parts 1-4, Journal, SS#’s 19, 20 End-of-Module, #’s 1, 6, 7, 15, 18, 19, 21 Investigation 1/Part 1 Science Stories: Barn Owls Bones on the Outside Science Stories: The Pond Investigation 1/Part 1 & 2 Investigation 2 Investigation 3/Parts 1-3 Investigation 5/Parts 1-3 Investigation 6/Parts 1-3 Science Stories: Amazon Rainforest Journal Beetles The Darkling Beetle Isopods Aunties Plants Brine Shrimp The Mono Lake Story What Happens When Ecosystems Change *How Organisms Depend on Each Other 31 Investigation 1/Part 1 & 2, Journal Investigation 2/Part 1, SS# 6, Investigation 2/Part 2, Journal Investigation 2/Part 3, SS# 6 Investigation 2/Part 4, Journal Investigation 3/Parts 1-3, Journal, SS#’s 9, 10, 11 Investigation 5/Parts 1-3, Journal, SS#’s 17, 18 Investigation 6/Parts 1-3, Journal, SS#’s 9, 10, 19 End-of-Module #’s 1, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 1, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 18, 19 (5.9) The student knows that adaptations may increase the survival of members of a species. The student is expected to (B) analyze and describe adaptive characteristics that result in an organism's unique niche in an ecosystem; and 2003 2004 6 Some salamanders have a sticky tongue and a wide mouth lined with teeth. These animals most likely feed on — F* Insects and other tiny animals 74% G leaves and other plant structures 12% H algae and other microorganisms 7% J dead and decaying materials 7% Use the information below and your knowledge of science to help you answer questions 11–13. 11 As seagulls fly over the water, they sometimes dive into the water to catch prey. Which of these senses is useful to seagulls that feed in this manner? A* Sight 69% B Smell 19% C Hearing 8% D Touch 4% Study Guide/TAKS Information Booklet: Which bird has a beak that is best adapted for cracking seeds? 32 Students need to read articles about many different plants and animals. (continued) (5.9) The student knows that adaptations may increase the survival of members of a species. The student is expected to (B) analyze and describe adaptive characteristics that result in an organism's unique niche Study Guide/TAKS Information Booklet (continued): Which type of leaf is best adapted for preventing water loss? FOSS Modules: FOSS Module New Plants (Grade 1) Structures of Life (Grade 3) Water (Grade 4) Environments (Grade 5) FOSS Investigation/part Science Stories: Plants and Animals Around the World Animal Teeth Investigation 1/Part 1 Investigation 1/Part 2 Investigation 3/Part 3 Investigation 4/Part 2 Science Stories: Life on Earth Science Stories: The Pond Investigation 2/Part 3 Investigation 6/Parts 1-3 Science Stories: Amazon Rainforest Journal Darkly Beetles Isopods Brine Shrimp 33 FOSS Assessment Investigation 1/Part 1, SS# 2, 6 Investigation 1/Part 2, SS# 3, 4, 5 Investigation 3/Part 3, SS# 14, 15 Investigation 4/Part 2, SS# 18, 19 Investigation 2/Part 3 Investigation 6/Parts 1-3, Journal End-of-Module, #’s 7, 13, 15, 16, 17, 18, 26, 27 (5.9) The student knows that adaptations may increase the survival of members of a species. The student is expected to (C) predict some adaptive characteristics required for survival and reproduction by an organism in an ecosystem. 2003 2004 32 Which of the following characteristics would NOT give animals an advantage in the ocean? F* Long body hair 54% G A smooth body 9% H Structures that sense movement 15% J A strong sense of smell 21% Students need to read and discuss articles about many different animals and plants. 36 The type of penguin shown in the picture above lives in the icy lands of Antarctica. The male penguins huddle together in a tight group. They stay in these tight groups most likely because they are — F looking for the sun 62% G hiding from predators 13% H* sharing body heat 12% J fighting over a piece of food 13% Study Guide/TAKS Information Booklet Which animal would most likely be found in a habitat with high temperatures, few plants, and little rainfall? FOSS Modules: FOSS Module Insects (Grade 2) Structures of Life (Grade 3) Water (Grade 4) Environments (Grade 5) FOSS Investigation/Part FOSS Assessment Investigation 2/Part 2 Investigation 3/Part 1 Investigation 3/Part 4 Investigation 4/Part 1&2 Science Stories: “Life on Earth”, “A Change in the Environment”, “Crayfish, Snails, and Kids” Science Stories: The Pond Investigation 1/Part 2 Investigation 2/Parts 1-4 Investigation 3/Parts 1-3 Investigation 5/Parts 1-3 Investigation 6/Parts 1-3 Science Stories: Amazon Rainforest Journal Investigation 2/Part 2, Journal Investigation 3/Part 1, SS# 11, 12 34 Investigation 4/Part 1&2, Journal, SS# 18, 19, 20 Investigation 1/Part 1, Journal Investigation 2/Parts 1-4, Journal, SS# 6 Investigation 3/Parts 1-3, Journal, SS# 11 Investigation 5/Parts 1-3, Journal Investigation 6/Parts 1-3, Journal, SS# 6 End-of-Module, # 4, 6, 7, 13, 15, 22, 25, 26 Terrestrial Environments Around the World Aquatic Environments (5.6) The student knows that some change occurs in cycles. The student is expected to (C) describe and compare life cycles of plants and animals. 2006 TAKS Test 1 Which part of this life cycle shows the adult organism? A Q 1% B R 96% C S 0% D T 3% Study Guide/TAKS Information Booklet: FOSS kits develop concept very well in 2nd, 3rd and 5th grade life science kits. The pictures show the stages in the life cycle of a beetle. What would be the correct sequence for the development of the beetle? A Q, S, R, T B* R, T, Q, S C S, R, Q, T D T, S, R, Q FOSS Modules: FOSS Module New Plants (Grade 1) Insects (Grade 2) Structures of Life (Grade 3) Environments (Grade 5) FOSS Investigation/Part Activities 1-4 FOSS Assessment Activities 1-4, Journal, SS#’s 4, 5, 8, 13 Investigation 1-Mealworms Investigation 2-Waxworms Investigation 3-Milkweed Bugs Investigation 4-Silkworms Investigation 5-Butterflies Science Stories: Insect Life Cycles Investigation 2/Part 3 -Beans Science Stories: Seeds are Everywhere Life Cycle of a Crayfish Investigation 1/Parts 1-2 Investigation 5/Parts 1-3- Brine Shrimp Science Stories: Breeding Plants 35 Investigation 2/Part 3, SS# 10 Investigation 5/Parts 1-3, Journal, SS# 18 End-of-Module, # 27 (3.8) The student knows that living organisms need food, water, light, air, a way to dispose of waste, and an environment in which to live. The student is expected to (A) observe and describe the habitats of organisms within an ecosystem; 2004 TAKS TEST: 30 The picture shows the leaf and fruit of a sycamore tree. A tree like the sycamore would have the hardest time growing in an environment that is mostly — F* cold and dark 68% G warm and rainy 9% H cool and wet 7% J hot and cloudy 16% Students need to read and discuss articles about different animals and plants. FOSS Modules: FOSS Module Animals 2x2 (Kindergarten) Insects (Grade 2) Structures of Life (Grade 3) Water (Grade 4) Environments (Grade 5) FOSS Investigation/Part Activity 1/Part 3 Activity 2/Parts 1&3 Activity 3/Parts 2 & 3 Activity 4/Parts 1&4 Investigation 6 Investigation 3/Part 2 Investigation 4/Part 1& 4 Science Stories: Life on Earth *A Change in the Environment A Snail’s Journey Science Stories: The Pond Investigation 1 Investigation 2 Investigation 3 Investigation 4 Investigation 5 Science Stories: Amazon Rainforest Journal Terrestrial Environments Around the World Aquatic Environments Brine Shrimp 36 FOSS Assessment Journal Journal Investigation 3/Part 2 SS# 13 Investigation 4/Part 1& 4, SS#17, 20 End-of-Module, Performance Assessment End-of-Module, # 21 End-of-Module, Performance Assessment End-of-Module, #’s 1, 3, 4, 7, 8, 10, 11, 18 (3.8) The student knows that living organisms need food, water, light, air, a way to dispose of waste, and an environment in which to live. The student is expected to (B) observe and identify organisms with similar needs that compete with one another for resources such as oxygen, water, food, or space; 2003 TAKS TEST: 11 On the prairie the herbivores would compete most for — A oxygen 7% B space 18% C* grass 72% D soil 3% 2006 TAKS Characteristics of Four Habitats Surface Features Habitat Climate Q Hot R Cool Hills S Cool Mountains T Cold Snowdrifts Sand dunes Main Plant Types Cacti, grasses Grains, thistles Trees, blueberry bushes Algae, mosses Black Bear Needs Plant Eater in Habitat Field mouse Rabbit Beaver Habitat Forests and woodlands Food Nuts, fruits, young sprouts, insects, young mammals, and livestock Space 3 to 90 square kilometers Lemming 11 The top chart shows some characteristics of four habitats. In which habitat would a black bear most likely be found? A Q 6% B R 10% C* S 81% D T 3% FOSS Modules: FOSS Module Structures of Life (Grade 3) FOSS Investigation/part Investigation 1 Investigation 3 Science Stories: *A change in the Environment Environments (Grade 5) Investigation 1-4 Science Stories: *What is an Ecosystem *California version of Science Stories 37 FOSS Assessment Investigation 4, Part 3 Journal Summative Assessment #20 (3.8) The student knows that living organisms need food, water, light, air, a way to dispose of waste, and an environment in which to live. The student is expected to (C) describe environmental changes in which some organisms would thrive, become ill, or perish; and TAKS Test Items: 2003 2004 18 Plants can survive in a clear, closed container without animals. Animals cannot survive in a closed container without plants. Why can’t animals survive in a closed container without plants? F Plants and animals need water to survive. 8% G* Plants produce oxygen, which animals need. 85% H Plants take in and give off water; animals only take in water. 3% J Plants are stationary; most animals roam freely. 3% 1 Clearing a forest to build a shopping mall will most likely result in woodpeckers — A nesting on roofs 14% B* losing habitat 83% C laying more eggs 2% D flying slower 1% Study Guide/TAKS Information Booklet: According to the chart, what would most likely happen in an ecosystem if there were a sudden decrease in the number of bacteria and fungi? A The number of plants would increase. B The number of bees would increase. C* The amount of nutrients in the soil would decrease. D The amount of water in the air would decrease. FOSS Modules: FOSS Module Structures of Life (Grade 3) FOSS Investigation/part Investigation 2/Part 2 & 3 Investigation 3/Part 1, 2, 3 Investigation 4/Part 1 Science Stories: Life on Earth *A Change in the Environment Environments Investigation 1/Part2 (Grade 5) Investigation 3 Investigation 4 Investigation 5 FOSS Science Stories: Auntie’s Plants Water Pollution The Mono Lake Story Shrimp Aquaculture *What Happens When Ecosystems Change? *California version of Science Stories FOSS Assessment Investigation 2/Part 2 & 3, Journal Investigation 3/Part 1-3, SS# 13 Investigation 4/Part 1, Journal, SS# 17, 18 End-of-Module # 8 Investigation 1/Part2 Investigation 3 SS# 10 Investigation 4, Journal Investigation 5, Journal Investigation 6 SS# 19 Summative #11-21 38 (3.8) The student knows that living organisms need food, water, light, air, a way to dispose of waste, and an environment in which to live. The student is expected to (D) describe how living organisms modify their physical environment to meet their needs such as beavers building a dam or humans building a home. 2004 TAKS TEST: 5 Which basic need do groundhogs meet by digging tunnels in meadow soil? A Water 8% B* Shelter 77% C Light 7% D Air 7% FOSS Modules: FOSS Module Structures of Life (Grade 3) Environments (Grade 5) FOSS Investigation/part Science Story: A Change in the Environment Investigation 1/Part 2 Investigation 4/Part 2&3 Science Story: *What Happens When Ecosystems Change? Aquatic Environments *What is an Ecosystem The Mono Lake Story *California version of Science Stories 39 FOSS Assessment Investigation 1/Part 2, Journal Investigation 4/Part 2, Journal, SS# 16 (2.9) The student knows that living organisms have basic needs. The student is expected to (A) identify the external characteristics of different kinds of plants and animals that allow their needs to be met; and 2004 TAKS TEST: 26 Brightly colored flowers are most often pollinated by — F wind 8% G mammals 4% H rainfall 17% J* insects 70% 2006 TAKS Test 39 All of the characteristics listed above are useful for gathering food EXCEPT — A* 1 92% B 2 3% C 3 3% D 4 2% FOSS Modules: FOSS Module Insects (Grade 2) Structures of Life (Grade 3) The Human Body (Grade 4) Environments (Grade 5) FOSS Investigation/part Investigation 1-Mealworms Investigation 2-Waxworms Investigation 3-Milkweed Bugs Investigation 4-Silkworms Investigation 5-Butterflies Investigation 6-Other Insects Science Stories: What Makes an Insect an Insect? Investigation 1-Seeds Investigation 2-Plants Investigation 3-Crayfish Investigation 4-Land Snail Science Stories: Inside a Snail’s Shell Science stories: A Marvelous Machine The Shape of Your Shape Barn Owls Your Amazing Opposable Thumb Bones on the Outside The Frozen Man Investigation 3/Part 3 Investigation 4/Part 3 Science Stories: Amazon Rainforest Journal The Spadefoot Toad Isopods, Plankton, Brine Shrimp 40 FOSS Assessment Investigation 1, SS# 2, 3, 4, 5 Investigation 2, SS# 10 Investigation 3, SS# 11, 12, 15 Investigation 4, SS# 18, 19 End-of-Module, #’s 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 10, 11, 16, 18, 19 Science Notebook End-of-Module, #’s 25, 26, (2.9) The student knows that living organisms have basic needs. The student is expected to (B) compare and give examples of the ways living organisms depend on each other and on their Environments. TAKS Test Items: 2003 2004 Prairie Food Chain 15 If all of the fish are removed from this food web, which animal populations will most likely decrease first? A Turtles 14% B Mosquito larvae 10% C Dragonfly larvae 8% D* Pelicans 67% 8 Which of these would best complete this food chain? F Hawks 15% G Grapes 2% H Toads 4% J* Mice 79% Students need practice making and reviewing food webs in grades 3, 4, and 5. Study Guide/TAKS Information Booklet: When students drink milk, they become part of a food chain. What is the original energy source of the food chain that includes the students and the milk? A Soil B Cows C Grass D* Sunlight If all the mice were removed from this simple food chain, the rattlesnakes would most likely — A begin to starve B start eating plants C become producers D increase in number FOSS Modules: FOSS Module Structures of Life (Grade 3) Water (Grade 4) Environments (Grade 5) FOSS Investigation/part FOSS Assessment Science Stories: *A Change in the Environment The Food Web Science Stories: The Pond Investigation 1/Part 2 Investigation 4/Part 2&3 Science Stories: *How Organisms Depend on Each Other *California version of Science Stories 41 Investigation 1/Part 2, Journal Investigation 4/Part 2&3, Journal, SS# 16 (5.5) The student knows that a system is a collection of cycles, structures, and processes that interact. The student is expected to (A) describe some cycles, structures, and processes that are found in a simple system; and 2003 TAKS Test: Photosynthesis is a seventh grade TEKS objective. (7.8B) 31 In the diagram above, the label Z represents — A sugar 9% B* carbon dioxide 45% C nitrogen 30% D water vapor 16% 2006 TAKS Test: 37 In the diagram above, which of the following is represented? A Water evaporating 3% B* Energy being transferred 92% C The moon changing phase 3% D Light being reflected 2% FOSS Modules: FOSS Module FOSS Investigation/part Human Body (Grade 4) Investigation 1- Skeletal System Investigation 2- Joints Investigation 3- Muscular System Investigation 4- Coordination Science Stories: Circulatory System Muscles and Bones Water (Grade 4) Environments (Grade 5) FOSS Stories: The Water Cycle Investigation 1Part 2 Science Stories: *What is an Ecosystem *California version of Science Stories 42 FOSS Assessment Investigation 2- Joints, SS# 9, 13 Investigation 3- Muscular System SS# 18 Investigation 4- Coordination, SS# 20 End-of-Module, #’s 1, 2, 3, 6, 8, 9, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 21, 24 Investigation 1Part 2, SS# 4 Investigation 3, Part 2, SS# 11 Home/School Connection SS# 32 End-of-Module Assessment SS# 18, 19, 20 (5.5) The student knows that a system is a collection of cycles, structures, and processes that interact. The student is expected to Students need practice making and reviewing (B) describe some interactions that occur in a simple system. food webs in grades 3, 4, and 5. 2004 TAKS Test 35 Which diagram shows how energy flows through a food chain? A Producers carnivoresherbivores 10% B* Sunproducersherbivores carnivores 64% C Sunherbivores carnivores producers 12% D Carnivoreproducers herbivores 8% 2006 TAKS 8 Which organism in this food chain is a producer? F Fish 3% G* Grass 87% H Grasshopper 5% J Hawk 6% FOSS Modules: FOSS Module Human Body (Grade 4) Water (Grade 4) Environments (Grade 5) FOSS Investigation/part Investigation 1 Investigation 2 Investigation 3 Investigation 4 Science Stories: The Broken Radius Your Amazing Opposable Thumb Muscles Muscles and Bones Smart Training The Circulatory System Science Stories: The Pond The Water Cycle Investigation 1-6 Science Stories: Aquatic Environments Around the World What is an Ecosystem The Mono Lake Story Breeding Plants *What Happens When Ecosystems Change? *How Organisms Depend on Each Other 43 FOSS Assessment Investigation 1, Journal Investigation 2, Journal, SS# 9, 12 Investigation 3, Journal, SS# 18 Investigation 4, Journal, SS# 20 End of Module Assessment #’s 6, 7, 8, 9, 10,16, 23, 24, 25 Investigation 1, Journal, SS# 4 Investigation 2, Journal Investigation 3, Journal, SS# 11 Investigation 4, Journal, SS# 16 Investigation 6, Journal, SS# 19 End-of-Module Assessment #’s 1, 4, 8, 10, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 18, 19, 20, 21, 24, 25 (4.6) The student knows that change can create recognizable patterns. The student is expected to (A) identify patterns of change such as in weather, metamorphosis, and objects in the sky. 2006 TAKS Test Metamorphosis: a change in the shape or characteristics of an animal’s body as it grows 6 Which diagram shows an example of metamorphosis? F.* 92% H. 2% G. 2% J. 3% Study Guide/TAKS Information Booklet: The pictures show the stages in the life cycle of a beetle. What would be the correct sequence for the development of the beetle? A Q, S, R, T B* R, T, Q, S C S, R, Q, T D T, S, R, Q 44 (4.6) The student knows that change can create recognizable patterns. The student is expected to (A) identify patterns of change such as in weather, metamorphosis, and objects in the sky. FOSS Modules: FOSS Module Insects (Grade 2) FOSS Investigation/part Activity 1 (Mealworms) Activity 2 (Waxworms) Activity 3 (Milkweed bugs) Activity 5 (Butterflies) Activity 6 (Other Insects) Structures of Investigation 1 Life (Grade 3) Investigation 2 Water Science Stories: (Grade 4) The Pond Environments Investigation 5 (Grade 5) Science Stories: *What Happens When Ecosystems Change? The Mono Lake Story *California version of Science Stories 45 FOSS Assessment Life of a Mealworm SS# 3 Life cycle of the square Moth ss# 26 Investigation 1, SS# 3, 4 Investigation 2, SS# 8, 9, 10 Investigation 5 Objective 3: Students will demonstrate an understanding of the physical sciences. (5.8) The student knows that energy occurs in many forms. The student is expected to (A) differentiate among forms of energy including light, heat, electrical, and solar energy; TAKS 2006 2 What two forms of energy does a flame from a burning candle release? F Electrical and mechanical 0% G Chemical and electrical 1% H* Light and heat 94% J Heat and nuclear 4% Study Guide/TAKS Information Booklet: Unlike battery-powered calculators, solar calculators are powered by solar cells. Which of these energy changes is used to power a solar calculator? A Heat energy changing to chemical energy B Light energy changing to chemical energy C Light energy changing to electrical energy D Chemical energy changing to electrical energy FOSS Modules: FOSS Module Magnetism and Electricity Physics of Sound Models and Designs Solar Energy (Grade 5) FOSS Investigation/part Investigation 2/Part 1 Science Stories: Magnets and Electricity in Your Life Science Stories: *Energy Science Stories: Early Autos Investigation 2 Investigation 4 Hot Topic: Finding Out What Heat Is SS# 27 Science Stories: Solar Technology Solar Cookers in Third-World Countries Solar Power From the Wind 46 FOSS Assessment Investigation 2, SS# 12 Investigation 4/ SS# 25 (5.8) The student knows that energy occurs in many forms. The student is expected to (B) identify and demonstrate everyday examples of how light is reflected, such as from tinted windows, and refracted, such as in cameras, telescopes, and eyeglasses; 2003 TAKS Test: 16 Light traveling through a pair of eyeglasses is — F* refracted 16% G transmitted 22% H absorbed 12% J reflected 49% 2006 TAKS Test 13 A student holds a note card behind a jar of water. Which of the following best explains why the part of the note card seen through the jar looks different from the rest of the note card? A The jar reflects light hitting its surface. 15% B The water absorbs light hitting its surface. 12% C The jar scatters light passing through it. 11% D* The water bends light passing through it. 62% Study Guide/TAKS Information Booklet: A student set a glass of water next to an open textbook. When she looked through the glass, the student noticed that the writing in the book looked much bigger. This happened because light from the room was reflected off the textbook and was — A reflected off the glass B* refracted by the water C absorbed by the water D sped up by the glass FOSS Modules: FOSS Module Ideas and Inventions FOSS Investigation/part Activity 4/Parts 1-4 Science Stories: Light and Reflection Making Mirrors FOSS Assessment Activity 4, SS# 15, Reflecting on the Activity, Journal Students need to understand refraction. Ideas and Inventions (4th grade) can help develop an understanding of this concept. Review reflection and refraction in 5th grade. 47 (5.8) The student knows that energy occurs in many forms. The student is expected to (C) demonstrate that electricity can flow in a circuit and can produce heat, light, sound, and magnetic effects; and 2003 TAKS Test: 2 The wires connecting the battery and the light bulb create a closed circuit. What would happen if one of these wires were cut? F The battery would lose its charge. 5% G The glass would crack. 2% H* The light would go out. 89% J The wire would become hot. 4% 19 A student plans to make this light bulb glow. All of the following objects can be used to complete the circuit EXCEPT — A a copper penny 3% B* a plastic comb 87% C a metal clip 5% D an iron nail 5% Study Guide/TAKS Information Booklet One difference between an electromagnet and a bar magnet is that the magnetic field produced by an electromagnet can — A* be turned on and off B attract materials such as wood C be made permanent D have two north poles Which picture shows a circuit that will light the light bulbs? Unlike battery-powered calculators, solar calculators are powered by solar cells. Which of these energy changes is used to power a solar calculator? A Heat energy changing to chemical energy B Light energy changing to chemical energy C* Light energy changing to electrical energy D Chemical energy changing to electrical energy 48 Continued: (5.8) The student knows that energy occurs in many forms. The student is expected to (C) demonstrate that electricity can flow in a circuit and can produce heat, light, sound, and magnetic effects; and FOSS Modules: FOSS Module Electricity and Magnetism (Grade 3) FOSS Investigation/part Investigations 2 – 5 Science Story: Magnetism and Electricity in Your Life Physics of Sound Science Stories: (Grade 4) *Energy Models and Designs Investigation 2 (Grade 5) *California Version of Science Stories FOSS Assessment Investigation 2, SS# 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12 Investigation 3, SS# 15, 16, 17 Investigation 4, SS# 18, 19, 20 Investigation 5, SS# 5 End-of-Module Performance Assessment End of Module #’s 1, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 17 18 Investigation 1/Part 1, Journal-Inquiry Entry 49 (5.8) The student knows that energy occurs in many forms. The student is expected to (D) verify that vibrating an object can produce sound. TAKS Test Items: 2003 2004 16 Blowing through a pipe can produce a sound because the — F* air in the pipe vibrates 86% G pipe speeds up the air 7% H pipe cools the air 1% J air is absorbed by the pipe 5% 36 Sound is made when a drumstick hits the drum. This happens because the force of the drumstick on the drum causes — F* vibrations 91% G electrical currents 1% H heat energy 3% J a magnetic charge 3% 2006 TAKS Test 17 An insect that produces waves in the water also produces waves in the air. What can these air vibrations produce? A* Sound 88% B Light 1% C Oxygen 8% D Carbon 3% FOSS Modules: FOSS Module Physics of Sound (Grade 4) Models and Designs (Grade 5) FOSS Investigation/part Investigation 1/Part 3 Investigation 2 Investigation 3 Investigation 4 Science Stories: Seeing the World Through Sound Listen to This, Your Source and Receiver,r Highs and Lows Making Waves, Sound Off Moving Along, Bouncing Back *Energy Investigation 2 (Building a “humdinger”) FOSS Assessment Investigation 1/Part 3, SS# 4, 5 Investigation 2, SS# 6, 7, 8, 9, 10 Investigation 3, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17 Investigation 4, SS# 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23, 24, 25 End-of-Module Performance Assessment End-of-Module Assessment #’s 2, 3,4, 5, 6, 7, 12 Not overtly taught in 5th grade, teacher will need to review that vibrations cause the hum *California Version of Science Stories Concept is well developed in the fourth grade Sound Unit. 5th grade teachers should review that vibrations cause sound in Models and Designs, Investigation 2. 50 (5.7) The student knows that matter has physical properties. The student is expected to (A) classify matter based on its physical properties including magnetism, physical state, and the ability to conduct or insulate heat, electricity, and sound; TAKS Test Items: 2003 2004 34 Which of these is a good conductor of electricity? F Glass 5% G* Metal 79% H Rubber 10% J Plastic 6% 6 Matter can undergo changes. When water boils, a — F liquid becomes a solid 9% G solid becomes a liquid 18% H* liquid becomes a gas 72% J gas becomes a solid 1% 38 Which of the following can be attracted to a magnet? F Gold ring 16% G Glass marble 2% H* Iron needle 80% J Wool sock 1% Matter has many physical properties. Starting in 1st grade the properties of matter are emphasized in the different FOSS modules. Study Guide/TAKS Information Booklet: The river water is a solution because it — A is a liquid, which has no definite shape B* contains dissolved minerals and salts C carries sand, clay, and other sediment D is a compound made up of two elements FOSS Modules: FOSS Module Electricity and Magnetism (Grade 3) Physics of Sound (Grade 4) Water (Grade 4) Mixtures and Solutions (Grade 5) FOSS Investigation/part Investigation 1 Investigation 2 Science Stories: Magnus Gets Stuck Investigations 1-4 Science Stories: Moving Along Bouncing Back Investigation 1 Investigation 2 Investigation 3 Science Stories: Surface Tension Evaporation and Condensation Investigation 1 Investigation 2 Science Stories: Mixtures and Solutions A Salty Story Earth Elements The Metals 51 FOSS Assessment Investigation 1, SS # 3, 4, 5, 6 Investigation 2, SS# 7, 10 End-of-Module #’s 5, 7, 8, 11, 12, 15, 18 Investigation 1, SS# 3 Investigation 1, Journal Investigation 2, SS# 6, 7, 9, 10 Investigation 3, SS# 14, 15, 16, Investigation 4, SS# 18, 19, 20, 23, 24 End-of-Module #’s 6, 7, 9, 10, 11, 13, 15 Investigation 1, SS# 2, 3 Investigation 2, SS# 6, 7, 8, 9 Investigation 3, SS# 10, 11 End-of-Module #’s 1, 3, 4, 6, 7, 9, 10, 11, 12, 14, 16, 21,22 Investigation 1, SS# 2, 3 Investigation 2, SS# 10 End-of-Module #’s 3, 4, 6 (5.7) The student knows that matter has physical properties. The student is expected to (B) demonstrate that some mixtures maintain the physical properties of their ingredients; TAKS Test Items: 2003 2004 21 In an experiment salt and sand are mixed together. Which of these procedures could be used to most easily separate the salt from the sand? 73% 22 Carbon powder and iron filings are both black powders. When mixed together, they look like one black powder. Which of these would be best to use to separate the iron filings from the carbon powder? F A magnifying glass 6% G Heat 15% H* A magnet 64% J Water 15% Concept covered well in Mixtures and Solutions and in Earth Materials Kits. 7% 5% 14% 2006 TAKS 7 A company collects cans for recycling. Some cans are made of aluminum, and some are made of iron. Which of the following is the best way to separate the two types of cans? A Heat the iron cans until they melt 3% B Use scissors to cut the cans 1% C* Use a magnet to pick up the iron cans 91% D Float the cans in water 5% 52 Study Guide/TAKS Information Booklet: A student stirs together a mixture of hot water and small amounts of salt, sand, and sugar. The student then pours the mixture through a paper towel. Which substance or substances will collect on the paper towel? A Only the sugar B Only the sand C Both the salt and the sugar D Both the salt and the sand (Continued) (5.7) The student knows that matter has physical properties. The student is expected to (B) demonstrate that some mixtures maintain the physical properties of their ingredients; FOSS Modules: FOSS Module Mixtures and Solutions (Grade 5) FOSS Investigation/part Investigation 1, Part 1 Investigation 1, Part2 Investigation 1, Part 3 Investigation 1, Part 4 Science Stories: The Air You Breathe Mixtures and Solutions 53 FOSS Assessment Investigation 1, Part 1, Journal, SS # 3 Investigation 1, Part2, SS # 5 Investigation 1, Part 3, Journal Investigation 1, Part 4, Journal, SS# 7 Performance Assessment SS # 8 End of Module #’s 1, 2, 11 (5.7) The student knows that matter has physical properties. The student is expected to (C) identify changes that can occur in the physical properties of the ingredients of solutions such as dissolving sugar in water; and 2004 TAKS Test Items: 31 In an activity, 20 grams of salt are dissolved in 70 grams of pure water. The water is then heated on a hot plate. When the water evaporates completely, how much salt will be left? A 0 grams 43% B 18 grams 13% C* 20 grams 43% D 22 grams 1% 34 Crystals were grown on a string in a clean glass jar containing sugar dissolved in hot water. The crystals grew on the string for several weeks. What kind of crystals are they? F String 7% G Water 4% H Glass 8% J* Sugar 82% TAKS 2006 27 A teaspoon of clean, dry sand is added to a cup of warm saltwater. What is most likely to happen after the mixture is stirred and then placed on a table for five minutes? A The amount of water will increase. 7% Concept covered well B The salt will float to the top. 5% in Mixtures and C* The sand will settle to the bottom. 86% Solution Kit. D The cup will heat up. 2% Study Guide/TAKS Information Booklet: This experiment shows how salt water can be boiled and made into freshwater. Which statement about solutions is supported by the diagram? A The parts of a solution must have the same boiling point. B A solution is made up of only one type of particle. C A solution is formed when a liquid changes into a solid. D* The parts of a solution can be separated by a physical change. FOSS Modules: FOSS Module Mixtures and Solutions (Grade 5) FOSS Investigation/part Investigation 1, Part 1-3 Investigation 2, Part 1-4 Investigation 3, Part 1-3 Investigation 4, Part 1-4 Science Stories: Decompression Sickness Sour Power Grow Your Own Crystals The History of Rubber 54 FOSS Assessment Investigation 1, Part 1-4, Journal, SS# 5 Investigation 2, Part 1-4, Journal, SS# 9, 10 Investigation 3, Part 1-3 Journal, SS# 13 Investigation 4, Part 1-4, Journal, SS# 16 End of Module Performance Ass. SS# 7, 8 End of Module Assessment #’s 1, 3, 4, 5, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13 (5.7) The student knows that matter has physical properties. The student is expected to (D) observe and measure characteristic properties of substances that remain constant such as boiling points and melting points. TAKS Test Items: 2003 2004 40 Which of the following thermometers shows the boiling point of water in a pan? 8% 9% 32 When a chocolate bar is heated by the sun, all of the following are likely to be seen EXCEPT — F* boiling 62% G a liquid 13% H melting 12% J a change in shape 13% Concepts covered well in Measurement, Water, and Mixtures and Solutions kits. 28% 55% 2006 TAKS 9 Some students were studying properties of water. One student placed a cup containing 80 mL of water in a freezer. Another student placed an identical cup containing 40 mL of water in a different freezer. Which of the following will be the same for both cups of water? A* The temperature at which the water freezes 74% B The mass of the frozen water 6% C The time it takes the water to freeze 15% D The volume of the frozen water 6% FOSS Modules: FOSS Module Measurement (Grade 3) Water (Grade 4) FOSS Investigation/part Investigation 1- length Investigation 2- Mass Investigation 3- Volume Investigation 4- temperature Science Stories: Fahrenheit and Celsius Everything is Made of Atoms Investigation 2 Investigation 3 Science Stories Ice is Everywhere Ice History 55 FOSS Assessment Investigation 1, SS# 3, 4, 5 Investigation 2, SS# 7, 8, 9 Investigation 3, SS# 10, 11, 12 Investigation 4, SS# 13, 14, End-of-Module #’s 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23, 24, 15 26, 27, 28, 29 Investigation 2, SS# 6 Investigation 3, SS# 10 (3.6) The student knows that forces cause change. The student is expected to (A) measure and record changes in the position and direction of the motion of an object to which a force such as a push or pull has been applied. TAKS Test Items: 2003 2004 27 A car will skid more on a wet road than on a dry road. This happens because between the tires and the dry road, there is more — A gravity 24% B magnetism 14% C* friction 30% D heat 31% NOTE: Diagram at left has been modified to fit in this space. Measurements will not equal those on the original test. Gravity and friction are not well covered in the FOSS kits used by BISD. (73% correct) 20 The picture shows different points along a toy rocket’s path after it blasted off. How much height did the rocket gain between Points Q and R? Use the ruler to measure the distance to the nearest centimeter. Record and bubble in your answer on the answer document. Study Guide/TAKS Information Booklet: Several students investigated how force affects the distance a tennis ball will travel. The students used the setup below and applied a force to the tennis ball by pulling the ruler back a certain distance. Based on the students’ data table, what distance would the tennis ball be expected to travel when the ruler is pulled back 8 centimeters? Record and bubble in your answer to the nearest centimeter on the answer document. FOSS Modules: 56 FOSS Module Models and Designs (Grade 5) FOSS Investigation/part FOSS Assessment Levers are not discussed, but could Investigation 2-p. 9 be inserted into a discussion in Assessment - Teacher Investigation 2 Observation Levers and Pulleys FOSS Stories: Simple Machines Class 1 Levers Class 2 Levers Class 3 Levers BISD does not use this kit, but the FOSS book would have enough information to cover the objective. ** Concept is not well developed in the FOSS kits used by the district. (5.5) The student knows that a system is a collection of cycles, structures, and processes that interact. The student is expected to (A) describe some cycles, structures, and processes that are found in a simple system; and 2004 TAKS Test: 18 Which force is most responsible for raindrops falling to Earth? F Friction 15% G Wind 14% Gravity and friction are not well H Thrust 8% covered in the FOSS kits used by J* Gravity 63% BISD. FOSS Modules: FOSS Module Physics of Sound FOSS Investigation/part Science Stories: Scoping Out Sound Highs and Lows Your Source and Receiver *Energy Models and Designs (Grade Investigations 1- 4 5) Science Stories: Everyday Mysteries Scientists and Models The Path to Invention Mixtures and Solutions Science Stories (Grade 5) Earth Elements The Air Astronauts Breathe What is Matter Made of? *California Version of Science Stories 57 FOSS Assessment Story Questions Investigation 1, SS # 4 Investigation 2, SS# 8 Investigation 4, SS# 14 (5.5) The student knows that a system is a collection of cycles, structures, and processes that interact. The student is expected to (B) describe some interactions that occur in a simple system. TAKS Test Items: 2003 8 The picture shows the process of — F* melting 64% G boiling 16% H condensing 16% J freezing 4% Concept covered well in Water kit 2004 39 If the person in the middle lets go of the rope, in which direction would objects X and Y go? A X up, Y up 11% B X up, Y down 3% C* X down, Y down 81% D X down, Y up 5% 26 The diagram shows landfills where two communities put garbage. What is the advantage of Landfill Y? F The waste lasts longer. 17% G* The groundwater is safer. 61% H The soil contains more nutrients. 14% J The trucks move faster. 7% 29 The picture shows two bowling balls being held in position with four ropes. The box will be flipped upward if which rope is cut? A W 17% B* X 77% C Y 8% D Z 3% 58 Objective 5.5 B continued FOSS Modules: FOSS Module Water (Grade 4) Mixtures and Solutions (Grade 5) Models and Designs (Grade 5) Solar Energy (Grade 5) FOSS Investigation/part Science Stories: Evaporation and Condensation Science Stories: The Air Astronauts Breathe What is a Reaction? Investigations 1-4 Science Stories: The Path to Invention Early Autos Investigation 1-4 Science Stories: Solar Technologies Differential Heating Building Time Devices FOSS Assessment Investigation 1, SS # 4 Investigation 2, SS# 8 Investigation 4, SS# 14 End-of-Module #’s 13 Investigation 2, SS# 7 Investigation 3, SS# 15, 18 Investigation 4, SS# 22 End-of-Module #’s 4, 5, 6, 7, 10, 12, 13, 14, 16, 17, 18 (4.6) The student knows that change can create recognizable patterns. The student is expected to (A) identify patterns of change such as in weather, metamorphosis, and objects in the sky. FOSS Modules: FOSS Module Ideas and Inventions (Grade 5) Solar Energy (Grade 5) FOSS Investigation/part Science Stories: Looking at the Sky Science Stories: The Sun The Sun and the Weather Building Time Devices *Living With a Star *Terrestrial Planets *California Version of the Science Stories FOSS Assessment Weather concepts can be reviewed in the Solar Energy kit. Use the FOSS readers and www.fossweb.com . 59 Objective 4: Students will demonstrate an understanding of the earth sciences. (5.12) The student knows that the natural world includes earth materials and objects in the sky. The student is expected to (A) interpret how land forms are the result of a combination of constructive and destructive forces such as deposition of sediment and weathering; and 2003 TAKS TEST Item: 2006 TAKS TEST Item: 12 The prairie is ideal for the growth of grasses because it has rich topsoil. All of these processes help form topsoil EXCEPT — F decay of trees 20% G weathering of rocks 22% H erosion of hills 16% J* movement of oceans 41% 34 Which of these can cause sharp, rough mountains to become rounded and smooth over time? F* Wind and rain 86% G The sun’s rays 6% H Light and darkness 2% J Earth’s magnetic field 7% Study Guide/TAKS Information Booklet Concept covered in the Landforms kit. A stalactite is a feature that hangs like an icicle from the roof of a cavern. How do stalactites in limestone caverns most likely form? A Glaciers move through the cavern and deposit weathered limestone. B Wind blows through cracks in the roof and erodes some of the limestone. C An underground river flows through the cavern and dissolves some of the limestone. D* Groundwater drips through cracks in the roof and deposits limestone over time. FOSS Modules: FOSS Module Earth Materials FOSS Investigation/part Overview Investigation 2, Parts 1,2 Investigation 3, Parts 1,2, 3 Investigation 4, Parts 1,2, 3 Science Stories: Written in Stone *Where Do Rocks Come From? Landforms Investigation 2, Parts 1, 2 Investigation 3, Parts 1,2, 3 Investigation 4, Parts 1,2, 3 Science Stories: Rivers and Controlling the Flow Earthquakes, Volcanoes, and Mountains *California Version of Science Stories 60 FOSS Assessment Notebook Stream table Stream table map Journal Stream table Investigation 2, SS# 9 Investigation 3, SS# 11 Story questions (5.12) The student knows that the natural world includes earth materials and objects in the sky. The student is expected to (C) identify the physical characteristics of the Earth and compare them to the physical characteristics of the moon. 2004 TAKS Test: 29 A rock is taken from the surface of the moon and brought to Earth. What is different about this rock on Earth? A Its mass 43% B Its shape 17% C Its length 2% D* Its weight 38% FOSS Modules: FOSS Module Water (Grade 4) Landforms (5th Grade) Ideas and Inventions (5th Grade) * California Edition FOSS Investigation/part Science Stories: Moon Dreams Overview Investigation 1, Part 2, 3 Investigation 3, Part 1, 2, 3 Investigation 4, Part 1, 2 , 3 Investigation 5, Part 1, 2, 3, 4 Science Stories: Looking at the Sky (The Moon)* FOSS Assessment Journal Schoolyard Model SS# 4 Map grid SS # 5 Stream table SS# 9 Go w/flow SS# 11 **Structures of the moon are briefly discussed in the California addition of the FOSS readers. The structures of the earth are adequately covered in the FOSS landforms kit, but the comparison to the moon in not present. 61 (5.11) . The student knows that certain past events affect present and future events. The student is expected to (A) identify and observe actions that require time for changes to be measurable, including growth, erosion, dissolving, weathering, and flow; 2003 TAKS Test: 24. Which experiment would best show how different methods of plowing fields on a hill affect erosion? 12% Concept covered well in the Landforms kit. 52% 17% 18% Study Guide/TAKS Information Booklet: A student placed some clean rocks in a clear plastic jar. The jar was filled with clean water and covered with a lid. Then the student shook the jar for five minutes. The student noted that smaller pieces had broken off some of the rocks and that there was a fine grit on the bottom of the jar. Which change of Earth’s surface was the student modeling? A* Physical weathering B Chemical weathering C Erosion of sediments D Forming deltas FOSS Modules: FOSS Module FOSS Investigation/part Landforms (Grade 5) Overview (p. 7) Investigation 2, Parts 1,2 Investigation 3, Parts 1, 2, 3 Investigation 5, Part 3 Science Stories: Real People in the Grand Canyon Rivers and Controlling the Flow Shapes of the Earth The Story of Mount Shasta 62 FOSS Assessment Student Notebook Investigation 2, SS# 9 Investigation 3, SS# 11 Investigation 5, SS# 21, 22, 23, 24 Performance Assessment SS #’s 10, 11 End-of-Module Assessment #’s 3, 4, 5, 6, 8, 13 (5.11). The student knows that certain past events affect present and future events. The student is expected to (B) draw conclusions about "what happened before" using data such as from tree-growth rings and sedimentary rock sequences; and 2006 TAKS Test; 24 The rock column above shows the layers in a rock formation. The three diagrams above show the positions of fossils in different rock layers. According to this information, which fossil is the youngest? 18% % 3% 4% % 74% % 63 Study Guide/TAKS Information Booklet; Which of the pictures below shows what happened just before the shuttle in this picture took off? FOSS Modules: FOSS Module Environments (Grade 5) Solar Energy (Grade 5) Models and Designs (Grade 5) Landforms (Grade 5) FOSS Investigation/part Investigation 3 Overview Investigation 2 Science Story: Science Stories: Life on Earth 150 Million Years Ago Science Stories Rivers and Controlling the Flow Shapes of the Earth 64 FOSS Assessment Investigation 3, SS# 11 End-of-Module Assessment #’s 20, 21 Science Notebook Investigation 2, SS# 9 Investigation 2, SS# 10 End-of-Module Assessment # 14, 18 (5.11). The student knows that certain past events affect present and future events. The student is expected to (C) identify past events that led to the formation of the Earth's renewable, non-renewable, and inexhaustible resources. TAKS 2006 23 Fossil fuels formed over a long period of time because heat and pressure were applied to — A* carbon filtered through limestone 13% B organisms buried in the ground 75% C bacteria on top of the mud 5% D nitrogen mixed in the water 7% FOSS Modules: FOSS Module Earth Materials Water Landforms Mixtures and Solutions FOSS Investigation/part Science Stories: Treasure Underfoot Digging It Up Mining for Minerals Investigation 2, Parts 1,2 Investigation 3, Parts 1, 2, 3 Science Stories: Ice History Water: A Vital Resource The Power of Water Overview (p.7) Investigation 5, Parts 1, 2, 3, 4 Science Stories: Rivers and Controlling the Flow Scientists in the Canyon Science Stories: The History of Rubber The Metals 65 FOSS Assessment Science Stories Questions (5.6) The student knows that some change occurs in cycles. The student is expected to (A) identify events and describe changes that occur on a regular basis such as in daily, weekly, lunar, and seasonal cycles; and 2006 TAKS Test: 25 Which of these causes day and night on Earth? A Earth orbiting the sun 15% B The moon orbiting Earth 12% C* Earth rotating on its axis 69% D The moon blocking sunlight 5% FOSS Modules: FOSS Module FOSS Investigation/part Science Stories: Solar Energy (Grade 5) Shadows Ideas and Inventions Science Stories: (Grade 4) Looking at the Sky* Water (Grade 4) Science Stories: Wet and Dry Places * California FOSS Science Stories 66 FOSS Assessment (5.6) The student knows that some change occurs in cycles. The student is expected to (B) identify the significance of the water, carbon, and nitrogen cycles. 2003 TAKS Test Items: 2006 TAKS Test Item: 19 Which gas in the air would increase if a large number of trees were cut down? A* Carbon dioxide B Nitrogen C Oxygen D Water vapor 21 In which of these ways can volcanoes help build up new land? A By adding heat to Earth’s surface 16% B By adding gases to the atmosphere 10% C* By adding lava to Earth’s surface 63% D By adding water vapor to the atmosphere 12% Content not well developed in the FOSS kits. Study Guide/TAKS Information Booklet: An increase in the average level of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere is most likely caused by an increase in the — A extinctions of animals B plant life on Earth C* number of large forest fires D number of solar-powered homes Plants take in carbon dioxide gas and use it to make sugars. Through this process they release oxygen, which animals need. Which of the following activities could decrease the amount of oxygen released into the air? A Making sure trees are planted with every new house built B Encouraging cities to plan for more parks C* Paving more land for roads and parking lots D Better controls for air and water pollution FOSS Modules: FOSS Module Water (Grade 4) FOSS Investigation/part Science Stories: The Water Cycle Environments (Grade 5) Mixtures and Solutions Science Stories: (Grade 5) The Air You Breathe ** Carbon and Nitrogen Cycles are not discussed in FOSS kits. 67 FOSS Assessment (4.11) The student knows that the natural world includes earth materials and objects in the sky. The student is expected to (A) test properties of soils including texture, capacity to retain water, and ability to support life; TAKS Test Items: 2003 2004 3 A student wants to find out which type of soil holds the most water. He uses four identical pots with holes in the bottom. He fills each pot with a different type of soil and waters the pots with the same amount of water. How can he find out how much water stays in the soil in each pot? A By planting seeds and measuring plant growth in each pot 8% B* By measuring the amount of water that drains from each pot 62% C By observing which soil looks wettest after the water has been added to the pots 20% D By feeling the soil before and after adding water to each pot 10% 27 Similar containers were filled with different types of soil. Holes were poked into the bottom of each container, and 300 milliliters of water were added. The water that dripped out was collected and measured. According to the information in the table, which type of soil retained water best? A* Potting soil 32% B Sandy soil 4% C Gravel 57% D Clay 2% Study Guide/TAKS Information Booklet: Concept covered well in the Water and Landforms kits. Three soil samples were tested to see how much water each could hold. The same amount of water was added to each funnel of soil. Very few plants would probably grow in the clay because the water would — A* fail to reach the roots of the plants B become too cloudy C run through the soil too quickly D become poisonous to the plants 68 (continued) (4.11) The student knows that the natural world includes earth materials and objects in the sky. The student is expected to (A) test properties of soils including texture, capacity to retain water, and ability to support life; FOSS Modules: FOSS Module Pebbles, Sand, and Silt (Grade 1) Water (Grade 4) FOSS Investigation/part Investigation 4, Parts 1-3 Science Stories: What is Soil?* Testing Soil* Investigation 4, Part 1 Environments (Grade 5) Investigation 1, Part 1 Investigation 3, Parts 1-3 Investigation 6, Parts 1-3 Landforms (Grade 5) Investigation 2, Parts 1-2 Investigation 3, Parts 1-3 *California FOSS Science Stories 69 FOSS Assessment Journal Investigation 4, Part 1 SS # 16 End-of-Module # 2 Investigation 1, Part 1 SS# 4 Investigation 3, Parts 1-3 SS# 11 Home School SS# 31 End-of-Module # 16, 22, 25 Investigation 2, Part1 SS# 9 Investigation 2, Part 2 SS# 10 End-of-Module Assessment # 5 (4.11) The student knows that the natural world includes earth materials and objects in the sky. The student is expected to (B) summarize the effects of the oceans on land; and Study Guide/TAKS Information Booklet: Which landform was most likely made by the process of depositing sediments? FOSS Modules: FOSS Module Water (Grade 4) Landforms (Grade 5) FOSS Investigation/part Science Stories: Ice is Everywhere Investigation 2, Part 1-2 Investigation 3, Parts 1-3 Science Stories: Shapes of the Earth FOSS Assessment Science Notebook Investigation 2 SS# 9 Investigation 3, SS # 10 End-of-Module #’s 5, 13 **Deposition and erosion are discussed and investigated thoroughly in the landforms module in the 5th grade. The effects of the water (ice) and oceans are briefly discussed in the science story Ice is Everywhere in 4th grade. 70 (4.11) The student knows that the natural world includes earth materials and objects in the sky. The student is expected to (C) identify the Sun as the major source of energy for the Earth and understand its role in the growth of plants, in the creation of winds, and in the water cycle. 2004 TAKS Test Items: 12 The energy that causes seawater to form water vapor comes from — F the clouds 23% G underwater mountains 2% H chemical reactions in the sea 10% J* the sun 66% 19 In order for tomato plants to make their own food, their leaves must absorb — A rain 23% B* sunlight 46% C oxygen 14% D minerals 17% 2006 TAKS Test 28 Which of these supplies the energy that drives the water cycle? F* The sun 76% G The planets 1% H The oceans 21% J The moon 2% FOSS Modules: FOSS Module Water (Grade 4) Solar Energy (Grade 5) FOSS Investigation/part Science Stories: The Water Cycle FOSS Stories: The Sun and the Weather Solar Cookers in the Third World Solar Power from the Wind 71 FOSS Assessment (3.11) The student knows that the natural world includes earth materials and objects in the sky. The student is expected to (A) identify and describe the importance of earth materials including rocks, soil, water, and gases of the atmosphere in the local area and classify them as renewable, nonrenewable, or inexhaustible resources; 2004 TAKS Test Item: 28 Which of these best completes this chart? F Water 13% G Soil 21% H* Coal 62% J Sand 4% 2006 TAKS 12 Which of these is a renewable resource? F* Tree 69% G Coal 7% H Oil 6% J Wind 18% Study Guide/TAKS Information Booklet: Which of these is an inexhaustible resource? A Coal B Gold C Trees D Wind FOSS Modules: FOSS Module Earth Materials (Grade 3) FOSS Investigation/part Science Stories: Mining for Minerals Identifying Minerals Water (Grade 4) Science Stories: The Water Cycle The Power of Water Physics of Sound (Grade 4) Science Stories: *Energy Mixtures and Solutions Science Stories: (Grade 5) The Air You Breathe A Salty Story Earth Elements The Metals The History of Rubber Landforms (Grade 5) Science Stories Rivers and Controlling the Flow *California Version of Science Stories 72 FOSS Assessment (3.11) The student knows that the natural world includes earth materials and objects in the sky. The student is expected to (C) identify the planets in our solar system and their position in relation to the Sun; and 2003 TAKS Test Items: 13 Which two planets are closest to Earth? A Mercury and Saturn 9% B Mars and Jupiter 20% C Mercury and Venus 21% D* Venus and Mars 49% Information on the solar system available through www.fossweb.com 26 Which of these best represents Mars? F Q 17% G R 24% H* S 54% J T 5% FOSS Modules: FOSS Module Ideas and Inventions FOSS Investigation/part Science Stories: *Objects in the Sky Models and Designs Investigation 1 Investigation 2 Solar Energy (Grade 5) Math Extension SS #33 Science Stories: *Living With a Star *Terrestrial Planets *California Version of Science Stories FOSS Assessment Investigation 1, SS# 4 Investigation 2, SS# 8 **Astronomy objectives not well developed in Texas version of the FOSS modules. California science stories contain good explanations. Information on the solar system available at www.fossweb.com 73 (3.11) The student knows that the natural world includes earth materials and objects in the sky. The student is expected to (D) describe the characteristics of the Sun. TAKS Test Items: 2003 2004 14 The surface of the sun is made of — F* gases 60% G solids 9% H liquids 3% J energy 29% 22 Sunspots appear to be darker than the rest of the sun’s surface because they are — F partially hidden from view 13% G in the shadow of the sun’s corona 21% H* cooler than the rest of the sun’s surface 27% J made of dark-colored minerals 40% Many of the TAKS questions on this objective are fact oriented and best prepared for by reading FOSS reader and other resources about the sun. 30 Which of these would best model how the sun’s energy warms Earth? F A pot of water boiling 26% G* A heat lamp keeping food hot 50% H An oven baking bread 13% J A spoon getting hot when stirring soup 11% FOSS Modules: FOSS Module Solar Energy (Grade 5) FOSS Investigation/part FOSS Overview Science Stories: The Sun Effects of the Sun 74 FOSS Assessment (3.6) The student knows that forces cause change. The student is expected to (B) identify that the surface of the Earth can be changed by forces such as earthquakes and glaciers. 2006 TAKS Test: 30 The picture shows a kind of glacier that can be many meters thick. In this landscape, which of the following is most directly affected by this kind of glacier? F The average height of plants on the mountainside 11% G The shape of clouds that form above the glacier 5% H The average mass of trees near the lake 12% J* The shape of the valley between the mountains 71% e FOSS Modules: FOSS Module Earth Materials FOSS Investigation/part Science Stories: Postcards from the Edge *Where Do Rocks Come From? Landforms Investigation 2, Parts 1-2 Investigation 3, Parts 1-2 FOSS Science Stories: Real People in the Grand Canyon Rivers and Controlling the Flow The Story of Mount Shasta Shapes of the Earth National Parks The Eye of the Needle *California version of Science Stories 75 FOSS Assessment Investigation 2, SS# 9 Investigation 3, SS# 11 Science Notebook Rivers and Controlling the Flow-questions to explore (5.5) The student knows that a system is a collection of cycles, structures, and processes that interact. The student is expected to (A) describe some cycles, structures, and processes that are found in a simple system; and 2004 TAKS Test Items: 23 Which of these best shows the relationship between Earth, the moon, and the sun? 6% 19% 62% 13% FOSS Modules: FOSS Module Solar Energy (Grade 5) Landforms (Grade 5) FOSS Investigation/part Science Stories: Shadows Building Time Devices Effects of the Sun Differential Heating The Sun and the Weather Solar Power from the Wind Science Stories Rivers and Controlling the Flow Shapes of the Earth 76 FOSS Assessment (5.5) The student knows that a system is a collection of cycles, structures, and processes that interact. The student is expected to (B) describe some interactions that occur in a simple system. 2006 TAKS Test 22 Before a field trip to a cave, a science class studied this picture. Which two features of this cave system were most likely formed by the slow buildup of minerals from water drops? F Pool of water and trench 44% G Pool of water and stalagmite 14% H Stalactite and trench 7% J* Stalagmite and stalactite 35% FOSS Modules: FOSS Module Solar Energy (Grade 5) Landforms (Grade 5) FOSS Investigation/part Science Stories: Shadows Building Time Devices Effects of the Sun Differential Heating The Sun and the Weather Solar Power in Homes Solar Power from the Wind Science Stories Rivers and Controlling the Flow Shapes of the Earth 77 FOSS Assessment (4.6) The student knows that change can create recognizable patterns. The student is expected to (A) identify patterns of change such as in weather, metamorphosis, and objects in the sky. Science concepts. TAKS Test Items: 2003 2004 35 About how long does it take Earth to make a complete rotation on its axis? A* One day 33% B One week 7% C One month 10% D One year 50% 10 According to this information, what kind of weather is related to low air pressure? F Sunny 9% G Fair 9% H* Rainy 73% J Mild 9% 21 Tides on the Texas coast usually occur twice — A* daily 37% B weekly 21% C monthly 23% D yearly 19% Study Guide/TAKS Information Booklet: A sudden change in wind direction, air temperature, and cloud cover most likely signals a change in — A climate B landforms C seasons D weather A student saw the constellation Scorpios in the southern part of the summer sky. In the winter Scorpios was not visible at all. What causes this constellation to disappear from the winter sky? A The stars moving away from Earth B The solar winds covering the night sky C* The revolution of Earth around the sun D The orbiting of the stars in the galaxy FOSS Modules: FOSS Module Ideas and Inventions (Grade 4) Models and Designs (Grade 5) FOSS Investigation/part FOSS Assessment Looking at the Sky Science Stories: Scientists and Models Solar Energy (Grade 5) Shadows, Building Time Devices The Sun and the Weather *Predicting the Weather Landforms (Grade 5) Rivers and Controlling the Flow Shapes of the Earth Weather concepts are introduced and taught in grade 2 in the FOSS kit called Air and Weather. Weather concepts are reviewed in grade 4 (Water kit) and in Grade 5 (Solar Energy). 78