20-1, Practice Problems
advertisement

20-1, PracticeProblems
&
1. What is the oxidation number of each
(c) SOr?
elementin (a) HrSO4&) H2S2O7
6. What is the.'oxidation number of each
elementin (a)MBaN2(b) FeCl, (c) BaSOn?
2. What is the oxidation number of each
element in (a) H,PO4 (b) P4O6(c) KHtPOn?
7. What is the oxidation number of each
element in (a) NaHrPOn (b) NarPOn
(c) HrBor?
What is the oxidation number of each
element in (a) (a(HrPOa)2 G) CaSOn
(e) KrMnOr?
What is the oxidation number of each
element in (a) ZnCO" (b) AgrCO, (c) BaFr?
I
4. What is the oxidation number of each
element in (a) Be(OH)" (b) B(OH)q
(c) Si(OH)n?
What is the oxidation number of each
elementin (a) NHs &) SCl2(c) Sr(OH)r?
9. What is the oxidation number of each
element in (a) Mg(OH)2 &) MgClt
(c) CrCl"?
L0. What is the oxidation number of each
element in (a) Co(OH), (b) HAuClo
(c) HgSOn?
e
8
20
Chapter
@ Prentice-Hall,lnc
Name
Date
Class
20-L Practice Problems (continued)
L1. Identify the oxidizing agent and the
reducing agentin the following reaction:
C + ZClr-- CCla r
16. Identify the element that is oxidized and
the element that is reduced in the
following reaction:
2Al + 3Brr-* 2AlBrg
12. Identify the element that is oxidized and
the element that is reduced in the
following reaction:
Hr + Cl, -'+2HCl
13. Identify the oxidizing agent and the
reducing agent in the following reaction:
2P + 3CIr-+ 2PClg
L7. Identify the oxidizing agent and the
reducing agent in the following reaction:
Pb + 2HCl -r PbCl, + H"
L8. Identify the element that is oxidized and
the element that is reduced in the
following reaction:
SiO, + 2C --+Si + 2CO
14. Identify the element that is oxidized and
the element that is reduced in the
following reaction:
19. Identify the oxidizing agent and the
reducing agent in the following reaction:
COr+2Mg+2MgO+C
C+HrO--+CO+Hz
15. Identify the oxidizing agent and the
reducing agentin the following reaction:
Fe + 3C1"--+2FeCl"
20. Identify the element that is oxidized and
the element that is reduced in the
following reaction:
H2SO4+ Zn-+ ZnSOn + H,
O Prentice-Hall,
Inc.
l
Chapter2} 9
tttffR0GtIMtSTRY
PRAOIII
PROBtI|4S
UseTable23.2 to soluethe following problems in your notebook.
(ItLp(lTtNTtAtS
stfft(lN
zt.l ilAtt-(ttt!AND
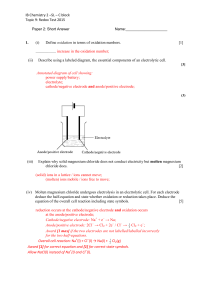
l. Determine the cell reaction, the standard cell potential (Eleil)and the half-cell
that acts as the cathode for the voltaic cells composed of the following halfcells.
a. Mgz+(aq)+ 2e- -+ Mg(s)
Clr(g) + 2e- -->ZCI- (aq)
b. Ni2+(aq)+ 2e- -+ Ni(s)
Ag+ (aq) + e- --+Ag(s)
c. MnOn-(aq) + BIH+(aq)+ 5e- --Mnz*(aq) + 4HzO(I)
Cd2+(aq) + 2e- -+ Cd(s)
d. Brr(/) * 2e- -->2Br- {aq)
Na+(aq) f e- --+Na(s)
e. ZH+(aq) + Ze- --->Hr(g;)
MnO2(s) + 4H+(aq) + 2e- --' Mn2+ {aq) + ZH.O(I)
2. Calculate E!"u to determine whether the following redox reactions are
spontaneousas written.
a. Snz+(aq)+ Ba(s)-+ Sn(s) + Baz*(aq)
b. z\g+(aq) + 2Cl-(aq)'+ 2Ag(s)+ Cl2€)
c. Zn(s) + FzG) --+ZF-{aq)+ Znz+(aq)
d. 2li(s) + Co2+(aq)-->zLi+(aq)+ Co(s)
e. 2I- (aq) + K+(aq) --+ Iz(s) + K(s)
C{t uU^*'^q
o
E'{o'
d {eaL T lo
*
9nr e) +
&o*l*ps
tl
o
o
Pfrbl'^
E
'tr
n
Jo)
5 n n[tp, + 9t?tE)
,
o
.9
o
c
g
"l
oyidatrcn
9 a,rs--
ft d,""A.'n
?:-\H:
1Jnt
&,, ( aLl
Ar
<
Sqr st 't- 3 "nlop) '--
'1
+ sLe -
an re)
F' , + ? , 7 a /
Eu'-o,l t"t{
PalaH t 1nrt)V :+e,?bV
( 9po"fa'. e o'> )
ReuiewModule / Chapters21-24
59
1
Name
Date
Class
2l-2 PracticeProblems
"1., Calculate the standard cell potential
produced by a voltaic cell consisting of a
nickel electrode in contact with a solution
of Ni2* ions and a silver electrode in
contact with a solution of Ag+ ions.
6. Caiculate the standard cell potential
produced by a voltaic cell consisting of a
nickel electrode in contact with a solution
o{ Ni2* ions and a copper electrode in
contact with a solution of Cu2+ions.
2. What is the voltage produced by a voltaic
cell consisting of an aluminum electrode in
contact with a solution of Al3+ ions and an
iron electrode in contact with a solution of
Fe2+ions?
7. A voltaic cell is constructed using
electrodes based on the following half
reactions:
M#+(aq) + 2e- --+Mn(s)
Cw2*(aq)+2e-*Cu(s)
a. Which is the anode and which is the
cathode in this cell?
3. Calculate the standard celi potential
produced by a voltaic cell consisting of a
sodium electrode in contact with a solution
of Na+ ions and a copper electrode in
contact with a solution of Cu2+ ions.
4. What is the voltage producedby a voltaic
cell consisting of a calcium electrode in
contact with a solution of Ca2* ions and a
tin electrode in contact with a solution of
Sn2* ions?
5. Avoltaic cell is constructed using electrodes
based on the following half reactions:
b. What is the standard ceil potential?
8. What is the voltage produced by a voltaic
cell consisting of a lead electrode in
contact with a solution of Pb2+ ions and
an iron electrode in contact with a
solution of Fe2* ions? Which is the anode
and which is the cathode?
9, What is the voltage produced by a voltaic
cell consisting of a zinc electrode in
contact with a solution of Znz+ ions and a
silver electrode in contact with a solution
of Ag* ions?
Pbz*(aq)+ 2e- + Pb(s)
Av3+(aq)+ 3e- * Au(s)
a. \Atrhichis the anode and which is the
cathode in this cell?
b. What is the standard cell potential?
O Prentice-Hall,
Inc
L0. Calculate the standard cell potential
produced by a voltaic cell consisting of a
goid electrode in contact with a solution
of Au3+ ions and a siiver electrode in
contact with a solution of Ag+ ions.
Which is the anode and which is the
cathode?
Chapter27 L5
.l
I
Antweft
20-1 Practice Problems, pages 8-9
Answers marked znith An asterisk denote
additionalpracticeproblemsthat appearin the
Teacher's
Edition.
* 1. a .H=+L,S =+6,0=_2
b.H=+1,S = +6,O=_2
c.S =+6,O=-2
* 2 . a.H=+1,P =+5,O=-2
b .P =+3,O=1
c. K = +1,H = +1,P = +5,O = -Z
3 . a. Ca = *2,H= *1, P = *5,O = 1
b.Ca= +2,5=+6,O=J
c.K =+1,Mn=+6,O=_2
4. a.B e= *2,O = e,H = +1
b .B =*3,O=-2,H=+1
c.S i= *4,O=1,H=+1
5 . a .N=-3,H=+l
b. S = +2,CL=-I
c.S r= *2,O=-2,H=+1
6 . a .Mg=+2,N=-3
b .Fe=+3,CI=-1
C.Ba= *2,5 = +6,O = -2
7. a. Na = *1, H = +1,P= +5,O =-2
b.Na=+1,P =+5,O=-2
C .H=*1,B = +3,O=-2
8. a .Zn=*2,C=+4,O=)
b.A g=+1,C =+4,O=-2
c. Ba= +2,F = -1
9. a .Mg-*2,O=1,H=+1
b .Mg=+2,CL=-L
c.Cr=+3,CI =-1
1"0.a. Co = +2,O = -2,H = +l
b. H = +1,Au = +3,CI= -1
c. Hg - t2,S = +6,O = -2
*L1. Oxidizing agent is Cl2; reducing
agent is C.
T12. H is oxidized;
Cl is reduced.
13. Oxidizing agent is Clr; reducing agent is P.
L4. C is oxidized; H is reduced.
15. Oxidizing agent is Cl2; reducing agent is
Fe.
15. Al is oxidized; Br is reduced.
17. Oxidizing agent is HCI; reducing agent
is Pb.
18. C is oxidized; Si is reduced.
19. Oxidizing agent is CO2; reducing agent
is Mg.
20. Znis oxidized; H is reduced.
21-2 Practice Problems,page 15
Ansrnersmarkedwith an asteriskdenoteadditional
practiceproblemsthat appearin the Teacher's
Edition.
*1. +1.06V
*2. +7.21Y
3. +3.05V
4. +2.73Y
5. a. Lead is the anodeand gold is the
cathode.
b. +1.63V
6. +0.60V
7. a. Manganeseis the anode and copperis
the cathode.
b. +1.53V
8. +0.32V. Iron is the anodeand lead is the
cathode.
9. +1.56V
10. +1.70V. Silver is the anodeand gold is the
cathode.
-)
l.^)o) EL,:, +t T gv
b)Er."it:+l.osv
L \ f u " " i{ = + l. 1 t /
J) 8".",,
' + r,74J
e ) F ' ."1 [= + l" ? _ [ y
A,a ) Eo r "l
= * ). 1 6 v
b) F..rr t
i spon)an<or5
'- 0,5t V.,nonepo.$anPo,lJ
c) Fi.n , + j. L ){ r 9 f o r " $ a n r 6 , r 9
;) e"t.r = ve .? 7 ( "t'Ja^.ro,!
€)
E o . u lt
: i. L I l(^ " ^ s p o , r { a n e a r . , S