Plasmolysis and Cytolysis
advertisement

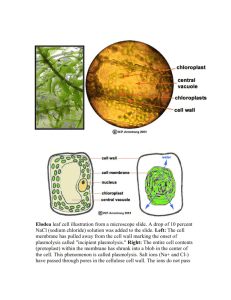
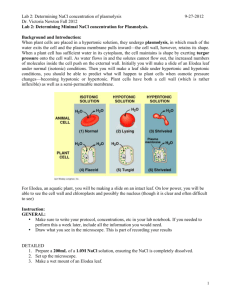
What is Elodea? Plasmolysis and Cytolysis Elodea Cell • Name three structures that are shown in this plant cell that you would not expect to find in an animal cell? • The Elodea plant has the parts that would typically be found in a plant cell. In this exercise we will identify those parts and see what happens when you subject this plant to plasmolysis. Elodea Cell Parts It is not possible to see the cell membrane because it is pushed up against the cell wall. Also, the central vacuole cannot be clearly distinguished from the cell cytoplasm. In a living elodea cell you can “roughly” tell where the vacuole is by where the moving chloroplasts are not able to go. 1 What is plasmolysis? • If you were to surround this group of plant cells with salt water then the water inside the plant would move from where there is more water (less salt) through the cell wall and membrane to the outside where there is less water (more salt). This process of water movement from a high concentration of water to a lesser concentration of water is called osmosis. When the water movement is out from a cell this form of osmosis is specifically called plasmolysis. Onion Skin Plasmolysis Note how the cell membrane draws inward pulling the cell contents along with it. Elodea Plasmolysis • This is a view of a cell that has undergone plasmolysis. It is now possible to see the cytoplasm which has contracted around the chloroplasts and the other cellular structures. Most of the water that has left the cell has been from the vacuole. Types of Solutions Hypertonic solutions contain higher concentrations of solutes than those in surrounding cells resulting in the cell shrinking in size. Hypotonic solutions contain lower concentrations of solutes than those in surrounding cells resulting in the cell swelling. Isotonic solutions contain equal concentrations of solutes than those in surrounding cells and the cell volume remains unchanged. The first figure below shows the effect of these solutions on blood cells. 2 Cytolysis/Plasmolysis What solutions were used? Normal Red Blood Cells 3