First Grade Unit A: PHYSICAL SCIENCE
advertisement
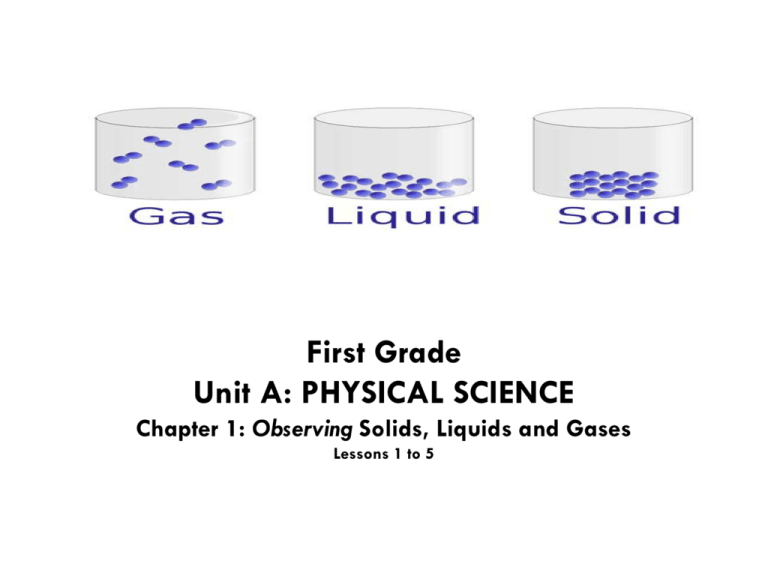
First Grade Unit A: PHYSICAL SCIENCE Chapter 1: Observing Solids, Liquids and Gases Lessons 1 to 5 Physical Science Overview Materials (matter) come in different forms. Water can be rain falling (liquid) or frozen as an ice cube (solid). When you boil (or heat up) water, you begin to see vapors (evaporate) or steam (gas). Scientists observe, compare and contrast the attributes of materials. Materials can then be classified (sorted and put together) based on their forms (or states). Scientist compare properties such as shape, size and motion of materials to decide whether they are solids, liquids or gases. Scientist experiment with mixing, cooling and heating solids, liquids and gases noting their changes and whether or not they can be changed back. Unit A Physical Science Chapter 1 Observing Solids, Liquids & Gases Lesson 1 Lesson 2 Lesson 3 Lesson 4 Lesson 5 What is a property? What is a solid? What is a liquid? What is a gas? How are solids, liquids and gases different? Property Senses Materials Attributes Classify Solid Shape Change Balance Weight Liquid Water Size Pour Container Gas Space Air Disperse Inflate Observe Alike Different Compare Contrast The Three States of Matter (Sung to Tune of The Wheels on the Bus) The three states of matter are solid, liquid, gas Solid, liquid, gas Solid, liquid, gas The three states of matter are solid, liquid, gas All day long Solids (Sung to Tune of The Wheels on the Bus) The floor is a solid You can jump up and down Jump up and down Jump up and down. The floor is a solid You can jump up and down All day long Liquids (Sung to Tune of The Wheels on the Bus) Water is a liquid You can drink right down Drink right down Drink right down Water is a liquid You can drink right down All day long Gases (Sung to Tune of The Wheels on the Bus) Air is a gas You can breathe right in Breathe right in Breathe right in Air is a gas You can breathe right in All day long Properties Shape, Color, Feel, Size & More Let’s read about properties: Properties tell us about shape, color, feel, size and more. Scientist observe the properties of materials. You can be a scientist by observing not only shape, color, feel and size but also measuring an object’s weight or height. You can also observe how an object moves. You can think of ways to change an object. Insert Photo/Graphic (Minimize) 1. What is a property? 2. Describe the properties of an apple. 3. How does an apple move? 4. How does an apple change when you roll it? 5. What things could you do to change the apple? Lesson 1: What is a Property? Vocabulary • Property: Something you can observe with your senses. Properties are ways of describing things including color, feel, shape, size and more (weight, height, etc.). The size of an object is one of its properties. • Senses: The five natural powers of sight, hearing, touch, taste and smell. You can use your senses to learn about objects. • Materials: What something is made of or used for. A tissue and a piece of cloth are different materials. Matter: All things on earth are matter. Matter can be classified as a solid, liquid or gas. • Attributes: Ways to describe something’s shape, color, feel, size or more. • Classify: To put things that are alike in groups. You can classify things as a solid, liquid or gas. Property: Something you can observe with your senses. Properties are ways of describing things including color, feel, shape, size and more (weight, height, etc.). The size of an object is one of its properties. Note: Properties and attributes are synonyms (i.e., words that mean the same or almost the same) . properties Senses: The five natural powers of sight, hearing, touch, taste and smell. You can use your senses to learn about objects. . senses Materials: What something is made of or used for. A tissue (paper) and a bath towel (cloth) are different materials. Matter: All things on earth are matter. Matter can be classified as a solid, liquid or gas. . materials Attributes: Ways to describe something’s shape, color, feel, size or more. . attributes Classify: To put things that are alike in groups. Shapes can be classified many ways such as by the number of sides. classify Video Opportunity Scott Foresman Discovery Channel School Student DVD Grade 1 PHYSICAL SCIENCE: Shapes (4 minutes) Description: What shapes can you find? Did you know that you can them in nature? Look for circles, triangles, and rectangles that are all around you. Brainstorm about Properties: What are properties? Insert Photo/Graphic (Minimize) Student Response: Properties tell us about _______, _______, ________, and _______. Solids Something that has its own size and shape. Let’s read about solids: A solid has its own size and shape. A solid does not change when it is moved from place to place. Solids are objects that have weight. They can be heavy or light. Insert Photo/Graphic (Minimize) 1. Name three solids. 2. Describe what a solid is? 3. How is a solid different than a liquid or gas? Solids • Solids keep their own shape. • Solids are easier to control. They do not flow. • Solids can be cut. • Solids when they melt become liquids. • Solids include a ball, fork, wood, bricks, ice and the Statue of Liberty. Lesson 2: What is a Solid? Vocabulary • Solid: Something that has its own shape and size. A solid does not change shape when it moved from place to place. Examples: wooden blocks, a baseball, a coin • Shape: The way something looks. A ball has a circle shape. • Change: Something becomes different through an action such as growth, mixing, cooling or heating. • Balance: A tool that can compare the weights of objects. A balance compares whether two objects are the same weight or whether one object is heavier or lighter than the other. • Weight (or Mass): How heavy something is. A balance can compare the weights of objects. Note that Mass is the amount of matter an object contains. Solid: Something that has its own shape and size. A solid does not change shape when it moved from place to place. Examples: wooden blocks, a baseball, a coin solids Shape: The way something looks. A ball has a circle shape. shape Change: Something becomes different through an action such as growth, mixing, cooling or heating. change Balance: A tool that can compare the weights of objects. A balance compares whether two objects are the same weight or whether one object is heavier or lighter than the other. balance Weight (or Mass): How heavy something is. A balance can compare the weights of objects. Note that Mass is the amount of matter an object contains. weight Observing Solids, Liquids and Gases What is a solid? Student Response: A solid is... Insert Photo/Graphic (Minimize) Liquids Liquids have their own size and take the shape of its container. Lesson 3: What is a liquid? Vocabulary • Liquid: Something that takes the shape of its container and has its own amount or size. You can pour a liquid. Examples: water, juice, oil • Water: A liquid collected in lakes, rivers, oceans and more. A liquid that plants and animals need to live. • Size: How big (or little) something is. Example: A gallon of milk is bigger than a glass of milk. • Container: An object that holds things inside it. A liquid takes the shape of its container. Examples: a glass, jar, box, and more. • Pour: The action of moving a liquid from one container to another. Let’s read about liquids: A liquid takes the shape of its container. It can be poured from one container to another changing shape but not volume (size) though it may appear to look larger or smaller. It is not. You can test this by pouring one measured cup of water into various sized containers. Insert Photo/Graphic (Minimize) 1. Name three liquids. 2. Describe what a liquid is? 3. How is a liquid different than a solid or gas? Liquids • Liquids take the shape of their container. • Liquids have a definite volume. • Liquids are difficult to control because they flow. They cannot be cut. • Liquids include: water, vinegar, orange juice, paint, gasoline. Liquid: Something that takes the shape of its container and has its own amount or size. You can pour a liquid. Examples: water, juice, oil liquids Water: A liquid collected in lakes, rivers, oceans and more. A liquid that plants and animals need to live. water Size: How big (or little) something is. Example: A gallon of milk is bigger than a glass of milk. size Container: An object that holds things inside it. A liquid takes the shape of its container. Examples: a glass, jar, box, and more. container Pour: The action of moving a liquid from one container to another. pour Observing Solids, Liquids and Gases What is a liquid? Student Response: A liquid is... Insert Photo/Graphic (Minimize) Gases . A gas takes the size and shape of its container. Let’s read about gases: Insert Photo/Graphic (Minimize) 1. Name three gases or things filled with air? 2. Describe what a gas is? 3. How is a gas different than a solid or liquid? Gases • Gases fill any available space. They flow easily. • Gases do not have a definite volume because they expand. • Most gases are invisible. • Gases cannot be cut. • Gases include helium, oxygen, hydrogen. • Heated water can become a gas. Lesson 4: What is a gas? Vocabulary • Gas: Something that takes the size and shape of its container. Most gases you can’t see. Examples: air, helium. • Space: Everything around or in something. Air takes up space but you cannot see it. • Air: A gas. Air is a gas that plants and animals need to live. You cannot see air. • Disperse: When air that is contained becomes not contained, it moves (or escapes) out of the container. • Inflate: To fill up or add air to something such as a tire, beach ball or balloon. Gas: Something that takes the size and shape of its container. Most gases you can’t see. Examples: air (oxygen, carbon dioxide), helium, hydrogen. gas Space: Everything around or in something. Air takes up space but you cannot see it. space Air: A gas. Air is a gas that plants and animals need to live. You cannot see air. air Disperse: When air that is contained becomes not contained, it moves (or escapes) out of the container. disperse Inflate: To fill up or add air to something such as a tire, beach ball or balloon. inflate Observing Solids, Liquids and Gases What is a gas? Student Response: A gas is... Insert Photo/Graphic (Minimize) Solids, Liquids, Gases Compare and Contrast Three Forms of Matter Solids Liquids Gases • • •Same Size •Different Shapes •Different Sizes •Different Shapes Same Size Same Shape Activity Three Forms of Matter A. What am I? B. What am I? C. What am I? •Same Size •Shape Changes •Size Changes •Shape Changes •Same Size •Same Shape Lesson 5 How are solids, liquids and gases different? Vocabulary • Observe: To use your senses to find out about an object. You can observe what you see, hear, smell, taste, or touch. You can observe and compare/contrast the properties of solids, liquids and gases. That is, how they are alike and different. • Alike: Comparing two or more things, attributes are similar or the same. • Different: Comparing two or more things, attributes are not the same. • Compare: Looking at how things are alike or the same. • Contrast: Looking at how things are different or not the same. Observe: To use your senses to find out about an object. You can observe what you see, hear, smell, taste, or touch. You can observe and compare/contrast the properties of solids, liquids and gases. That is, how they are alike and different. observe Alike: Comparing two or more things, attributes are similar or the same. alike Different: Comparing two or more things, attributes are not the same. different Compare: Looking at how things are alike or the same. These shapes are congruent. They are the same size and same shape. compare Contrast: Looking at how things are different or not the same. Here the square is different than the hexagons. contrast Vocabulary REVIEW for Unit A Physical Science Chapter 1 * Observing Solids, Liquids and Gases Lessons 1 to 5 Lesson 1 Lesson 2 Lesson 3 Lesson 4 Lesson 5 What is a property? What is a solid? What is a liquid? What is a gas? How are solids, liquids and gases different? Property Senses Materials Attributes Classify Solid Shape Change Balance Weight Liquid Water Size Pour Container Gas Space Air Disperse Inflate Observe Alike Different Compare Contrast Science Experiment Opportunity From Water to Solid (Freeze); From Solid to Liquid (Melt); From Liquid to Gas (Heat) First Grade Unit A: PHYSICAL SCIENCE Chapter 2: Changing Solids, Liquids and Gases Lessons 1 to 5 Physical Science Overview Materials (matter) come in different forms. Water can be rain falling (liquid) or frozen as an ice cube (solid). When you boil (or heat up) water, you begin to see vapors (evaporate) or steam (gas). Scientists observe, compare and contrast the attributes of materials. Materials can then be classified (sorted and put together) based on their forms (or states). Scientist compare properties such as shape, size and motion of materials to decide whether they are solids, liquids or gases. Scientist experiment with mixing, cooling and heating solids, liquids and gases noting their changes and whether or not they can be changed back. Unit A Physical Science Chapter 2 Changing Solids, Liquids & Gases Lesson 1 Lesson 2 Lesson 3 Lesson 4 How can things change? What properties of things can change? What changes How can when things cooling and are mixed? heating change things? Melt Mix Heat Cool Forms (states) Flexibility Texture Dissolve Solution Separate Freeze Evaporate Temperature Thermometer Lesson 5 What things cannot change back? REVIEW all vocabulary from Physical Science Unit A Chapters 1&2 Video Opportunity Scott Foresman Discovery Channel School Student DVD Grade 1 PHYSICAL SCIENCE: Solids, Liquids Gases (7 minutes) Description: Water exists in three states – solid, liquid and gas. Find out what makes each state unique and how temperature ((heating, cooling) causes water to change from one state to another. Science Experiment Opportunity From Water to Solid (Freeze); From Solid to Liquid (Melt); From Liquid to Gas (Heat) Draw on Prior Knowledge What are the three forms of matter? Compare and contrast the three forms. How can things change? Solids, liquids and gases can change when they are mixed, heated or cooled. Lesson 1: How can things change? Vocabulary • Melt: To change from a solid to a liquid. Solid wax (crayon) melts when it is heated. • Mix: To put (stir) two or more things together. • Heat: To increase (raise) the temperature of something. • Cool: To decrease (lower) the temperature of something. • Forms (state): Some materials change shape but not what it is made of. Example: Clay or Dough Melt: To change from a solid to a liquid. A frozen solid popsicle begins to melt when you take it out of the freezer because of the change in temperature. melt Mix: To put (stir) two or more things together. . mix Heat: To increase (raise) the temperature of something. . heat Cool: To decrease (lower) the temperature of something. cool Forms (state): Some materials change shape but not what it is made of. Example: clay or dough. . form (states) Chapter 1: How can things change? How can things change? Insert Photo/Graphic (Minimize) Student Response: Things change when they are ______, _______, or _________. What properties of things can change? Properties of color, shape, size, how things feel (texture) and move (flexibility) can change as a result of heating, cooling, and mixing. Lesson 2: What properties of things can change? Vocabulary • Flexibility: The capacity of an object to bend. Hard materials do not bend as easily as soft materials. • Texture: How something feels. Does it feel smooth or rough? Flexibility: The capacity of an object to bend. Hard materials do not bend as easily as soft materials. A wooden ruler would break if you bend it but a soft plastic ruler bends. . flexibility Texture: How something feels. Does it feel smooth or rough? The skin of a tomato is smooth but the skin of a kiwi is rough. . texture Chapter 2: What properties of things can change? What properties of things can change? Insert Photo/Graphic (Minimize) Student Response: ____, _____, _____, and how something _____ are properties that can change. What changes when things are mixed? Solids and liquids can be mixed together. Some solids dissolve or spread throughout a liquid. Lesson 3: What changes when things are mixed? Vocabulary • Dissolve: Spread throughout a liquid. Salt or sugar dissolves when it is mixed with water. • Solution: A mixture in which one substance (solute) dissolves in another (solvent). • Separate: Opposite of dissolve. Some things dissolved can be separated (e.g., salt and water) others cannot (e.g., paint). Dissolve: Spread throughout a liquid. Salt or sugar dissolves when it is mixed with water. . dissolve Solution: A mixture in which one substance (solute) dissolves in another (solvent). solution Separate: Opposite of dissolve. Some things dissolved can be separated (e.g., salt and water) others cannot (e.g., paint). . separate Chapter 3: What changes when things are mixed? What changes when things are mixed? Insert Photo/Graphic (Minimize) Student Response: ______ and _____ can be mixed. Some solids ______ when they are _____ with liquids. How can cooling and heating change things? Liquids such as water can turn into solids when cooled and back when heated. When water is heated it evaporates changing from a liquid to a gas. The gas can become a liquid again. Lesson 4: How can cooling and heating change things? Vocabulary • Freeze: To change from a liquid to a solid. Water freezes when it gets very cold. • Evaporate: Change from a liquid to a gas. Heat from the sunlight causes water to evaporate. • Temperature: How hot or cold something is. You can measure the temperature of air. • Thermometer: A tool that measures temperature. Temperature tells you how hot or cold. The numbers on a thermometer show the temperature. • Order: Decide or tell what is first, next and last. You can put things that happen in a science activity in order. Freeze: To change from a liquid to a solid. Water freezes when it gets very cold. freeze Evaporate: Change from a liquid to a gas. Heat from the sunlight causes water to evaporate. evaporate Temperature: How hot or cold something is. You can measure the temperature of air. Insert Photo/Graphic temperature Thermometer: A tool that measures temperature. The numbers on a thermometer show the temperature. Insert Photo/Graphic thermometer Order: Decide or tell what is first, next and last. You can put things that happen in a science activity in order. order Chapter 4: How can cooling and heating change things? How can cooling change things? How can heating change things? Insert Photo/Graphic (Minimize) Student Response: Cooling can _____ water into solid _____. Heating can _____ ice back into water. Heating can cause water to __________. What things cannot change back? Heating, cooling and mixing solids, liquids and gases can change properties. Doing so, some things such as water can change from one form to another and back again; however, somethings like popped corn cannot change back. Lesson 5 What things cannot change back? Vocabulary Review all vocabulary from Unit A Physical Science: Observing and Changing Solids, Liquids and Gases • Chapter 1 Lessons 1 to 5 • Chapter 2 Lessons 1 to 4 NOTE: The following How to Make Crayons presentation will provide you with an opportunity to review the vocabulary. Let’s read about how things can change: All things are a solid, liquid or a gas. Many things can be changed. Different things can be changed by mixing them, heating them or cooling them. You can mix two liquids together. You can melt ice (solid) into a liquid. You can cook (heat) eggs changing its liquids to solids. However, once cooked, a scrambled egg cannot be turned back into its original form. Water, however, changes when heated or cooled into a gas or solid but then can be changed back to a liquid again. Insert Photo/Graphic (Minimize) 1. What are three ways that a solid, liquid or gas can be changed? Can you think of other ways? 2. What are some examples of changes from one state (or form) to another? 3. Can changes from one state to another be reversed? Unit A Physical Science Chapter 2 Changing Solids, Liquids & Gases Lesson 1 Lesson 2 Lesson 3 Lesson 4 How can things change? What properties of things can change? What changes How can when things cooling and are mixed? heating change things? Melt Mix Heat Cool Forms (states) Flexibility Texture Dissolve Solution Separate Freeze Evaporate Temperature Thermometer Lesson 5 What things cannot change back? REVIEW all vocabulary from Physical Science Unit A Chapters 1&2 How to Make Crayons Do you know how the Crayon Factory makes crayons? To make crayons, the factory uses the following materials: wax (solid), and coloring (liquid like paint or a powder). Next, the factory melts the wax by heating it up. The heat raises the temperature and the wax gets hot and melts. Some of the liquid might evaporate as steam (gas). Then you will mix in color. The color will dissolve into the liquid to make a crayon solution. The hard texture of the wax has changed and now the melted wax is more flexible (soft). The liquid wax can be poured. Here is a photograph from a crayon factory. The melted, colored wax or liquid solution is then poured into molds. Poured into the mold, the temperature decreases and the solution (wax and coloring) cools and hardens. The liquid becomes a solid again. Last, the crayons will be wrapped with a label. How to Make Crayons Thinking Map: Flow Map (Sequence) Students will draw and present (and/or write) the sequenced steps for making crayons. How to Make Crayons • • • • Do you know how to make crayons? Here is how to make _______. First, you will need ____ and ____. Second, you will _____ the wax and ___ in the coloring. • Third, you will ____ the wax into molds. • Fourth, the molds will ____. • Last, the cooled ______ will be wrapped. Vocabulary REVIEW Unit A Physical Science Changing Solids, Liquids and Gases Chapter 2 * Lessons 1 to 5 Lesson 1 Lesson 2 Lesson 3 Lesson 4 How can things change? What properties of things can change? What changes How can when things cooling and are mixed? heating change things? Melt Mix Heat Cool Forms (states) Flexibility Texture Dissolve Solution Separate Freeze Evaporate Heat Temperature Thermometer Lesson 5 What things cannot change back? REVIEW all vocabulary from Unit A Chapters 1&2