Notes
advertisement

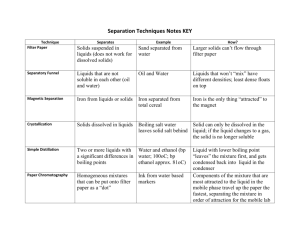
LESSON 1: What is matter? Notes: 1. Matter commonly exists in one of three states: ___________________, _____________________________, or ______________________. 2. Matter is anything that has mass ( ___________________) and volume (_________________________________________). Vocabulary: Material: The substance that something is _________________________. Matter: Anything that takes up space and has ___________________. Something that can be held in a ______________________ and ______________________ in another place. LESSON 2: Discussing the Properties of Matter Notes: 1. Some _________________________ help us clarify matter as a solid, liquid, or gas. 2. Gases do not have a definite ______________________. A gas can ___________________to fill any available space in a container. 3. Solids have a definite shape whether it’s in a _____________________ or not. 4. Liquids take up a definite amount of ________________________. It fills the _____________________ of a container. Vocabulary: Investigation: Something you do to _______________________a question. Observation: A careful description that is based on what you have _____________________________________. Powder: A solid material in the form of _________________, loose particles. Procedure: A sequence of __________________ that describes how to perform a __________________. Property: A characteristic that helps to ____________________ or identify an object, a material or a state of ________________________. State: A form, stage, or condition of something that can ____________________. LESSON 3: Exploring the Weight of Solids and Liquids Notes: 1. All _____________________takes up space (___________________________) and has mass. 2. Mass is usually measured by ___________________________. 3. Materials can be described by their ____________________________. Vocabulary: Conclusion: What you have discovered based on___________________________or other data. You should be able to support your conclusions with _________________________. Prediction: A _______________________about what you think might happen during an ____________________________ or investigation, based on what you already know. Weight: The measure of how ___________________________something is. LESSON 4: Exploring the Volume of Solids and Liquids Notes: 1. A ________________________is used to measure weight. 2. If water is poured from a tall, thin glass into a short, wide glass, the volume of water_______________________________________________. Vocabulary: Accurate: Differing only very _______________________ from the correct value. Approximation: Not exact. A guess based on actual _________________________ or counting. Displacement: The ________________________ of water pushed out of the way by an object in _________________________. Volume: The amount of ______________________ something occupies. A ____________________________ of all matter. LESSON 5: Investigating Air Notes: 1. Matter commonly exists in one of three states: solid, liquid, or _____________. 2. Matter has volume and __________________. 3. Gases can be compressed ________________________. 4. Solids and liquids can be compress very ______________________. 5. Gases _______________________if put into a larger container. Vocabulary: Air: A mixture of ______________________ that surround the earth. Compress: To press on something until it takes of ________________ space. Expand: To become _______________________, or take up a _________________ space. States of Matter: What’s Your State? (BrainPop Video to be shown after Lesson 5) Notes: 1. Liquid has a fixed ______________________, but not a fixed ______________________. 2. If you raise the __________________________ of water, the amount of energy _________________________ and the particles begin to move until the water becomes a ________________. 3. Gases __________________ to fill a container. 4. If you lower the ___________________________ of water, the water will lose energy and become a ___________________ with a definite _________________ and ______________________. Law of Conservation of Mass: Nothing Can Be Created or Destroyed (BrainPop Video to be shown after Lesson 5) Notes: 1. The Law of Conservation: Substances cannot be ___________________ or ___________________. 2. Mass is the amount of _________________ a substance has. 3. A substance with a lot of ____________ has a lot of _________________. 4. The mass of the reactants = the mass of the product. In other words, the mass of individual materials = the mass of all of the materials _______________________________. LESSON 6: A Sense of Density Notes: 1. All matter takes up _____________________(has volume) and has _______________. 2. Matter is usually ________________________ by weight. 3. Materials can be described by their ___________________________. Vocabulary: Density: How _____________________ something is for its size. Measuring Matter: Essential for Science Labs and Cookie Baking (BrainPop Video to be shown after Lesson 6) Notes: 1. _____________, ______________, and _________________ are measurements we can take of objects. 2. The ___________________ system is used for all measurements in science. 3. ______________ is how much matter an object contains. 4. __________________ is how much space an object takes up. 5. Matter ______________________ liquid. 6. ____________________ is how heavy something is for its size. LESSON 7: Heating and Cooling Solids and Liquids Notes: 1. Matter can change between _________________________. 2. One way to change a solid into a liquid is to add _______________________. 3. When a solid is melted into a _______________________, the liquid weighs _________________________________as the original solid. Vocabulary: Freeze: To change from a ______________________to a solid by__________________________. Melt: To change from a ______________________ to a ____________________ by heating. LESSON 8: Evaporation: Changing from Liquid to Gas Notes: 1. Water vapor is a ___________________. 2. Matter can change between ___________________________________. 3. Even if matter is not ___________________________, it still exists 4. When water ______________________________, it goes into the air as an invisible __________________. Vocabulary: Evaporation: The process of a __________________________ changing into an invisible ______________________. Variable: Any factor in an _________________________________ that can be _______________________________. Water Vapor: The state of water when it is an ___________________________ gas. LESSON 9: Condensation: Changing from Gas to Liquid Notes: 1. __________________________can change between states. 2. Temperature affects the change of __________________________from one state to another. 3. Even if matter is not visible, it still ____________________________. 4. When a gas is ___________________________, it can turn into a liquid. 5. Water formed on the outside of a glass comes from _____________________. Vocabulary: Condensation: The change of a gas into a _______________________ when the gas is _____________________________. LESSON 10: Evaporation Investigations: Setting Up Notes: 1. One way to answer a question is to design a simple _______________________. 2. Data is information gathered by counting, measuring, or other types of ____________________________________. Vocabulary: Data: A ________________________ of what happened during an investigation. Experiment: A well-organized activity designed to test whether _____________________________________________. Fair Test: An experiment that compares something by changing one _________________________ while keeping all other variables ________________________________. Results: Data from the experiment __________________________ so that it is easier to _____________________________. Surface Area: The part of a liquid that is exposed to the _________________. LESSON 11: Evaporation Investigations: Drawing Conclusions Notes: 1. One way to answer a question is to design a simple ________________________. Vocabulary: Variable: Any factor in an experiment that can be ______________________. Matter Changing State: From Solid to Liquid to Gas and Back Again (BrainPop Video to be shown after Lesson 11) Notes: 1. _____________, ______________, and _________________ are the three states of matter. 2. Changes in the state of matter are ___________________ changes. 3. When you ______________ ice, water molecules are given ____________ energy and ice ________________. 4. Gas molecules have _____________ energy than liquid molecules. 5. When heated enough, a liquid becomes a ___________________. LESSON 12: Mixing and Separating Solids Notes: 1.When you mix materials together, the results weigh _______________________ as the ________________ of the parts. 2. A mixture can be separated by the __________________________ of the different materials in it. Examples of ________________________ could be size, color, shape, or magnetism. Vocabulary: Magnetism: A property that allows some objects to be attracted by a ______________________. Mixture: A combination of two or more _____________________________. Recycle: To ________________________ items from trash or garbage. Separate: To _______________________ something from a mixture. Sort: To separate objects into groups with ________________________ properties. LESSON 13: Mixing and Separating Solutions Notes: 1. When you mix materials together, the result ___________________ the same as the sum of the parts. 2. A mixture can often be separated by the ______________________ of the different materials in it. 3. A ____________________________ often cannot easily be separated by the ____________________________ of the different materials in it. Vocabulary: Dissolve: To mix one material, such as a solid, with another material, such as a liquid, until they create a _____________. Solution: A mixture in which one material, such as a liquid, combines with another material so that you can’t tell __________________________________ from other. LESSON 14: Whatzit?! Notes: 1. Materials can be described in terms of their ________________________ (Color, Shape, Size, Magnetism). 2. Sometimes when you mix materials together, you get a new material with ____________________________ properties. LESSON 15: Chemical Changes Notes: 1. Sometimes when you mix materials together, you get a _______________ material with different ____________________________. 2. Two examples of physical change are _____________________________ and _____________________________________. 3. Two examples of chemical change are _____________________________ and _____________________________________. Vocabulary: Chemical Change: A change to materials that results in forming a new _______________________ with new ____________________________. Physical Change: A change to the __________________, ____________________, or state of a material, through which the material _______________________________kind of matter. Property Changes: You’re Made of Solids, Liquids, and Gases (BrainPop Video to be shown after Lesson 15) Notes: 1. A change in the shape, size, form, or state of ________________ is a _______________________ change. 2. A chemical change happens when substances that make up an object have been ______________________ into another ____________________.