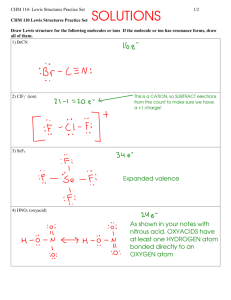
[SO2]2[O2] [SO3]2 524.4K• 462.9K• 8.314 J mol•K • ln125.4 61.5K
advertisement
![[SO2]2[O2] [SO3]2 524.4K• 462.9K• 8.314 J mol•K • ln125.4 61.5K](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/008432217_1-f6f0ddc631a0ec89f84a5e786b3339ef-768x994.png)
Department of Chemistry CHM 1220/1225 Exam IV A Answers 1. a. Concentration/amount of reactant: Increase increases rate according to the rate law Physical state of reactants: Smaller particle size, faster reaction Gases faster than aqueous or liquids which are faster than solids Presence of a catalyst: Speeds up reaction by providing a pathway with a lower Ea – b. 2. a. € b. € b. + – Use one: pH, [H ], pOH, [OH ] Acidic pH <7 + –7 [H ] > 1 x 10 M pOH >7 – –7 [OH ] < 1 x 10 M nd st Neutral =7 –7 = 1 x 10 M =7 –7 = 1 x 10 M – a. 2 order in ClO2; 1 order in OH ; 3 order overall 2 – b . Rate = k[ClO2] [OH ] 2 2 c. k1 = 1.2 x 10 /(M •s) 6. a. b. 7. x = 0.0166; [N2] = [C2H2] = 2.2 M ; [HCN] = 3.3 x 10 M 2 Basic >7 –7 < 1 x 10 M <7 –7 > 1 x 10 M rd 5. 8. 2 Kc = 6 x 10 (666); Qc = 7 x 10 ; Kc < Qc; So, the reactions proceeds reverse (to the left) –2 The equilibrium mixture is primarily reactants (Kc < 10 ) –2 a. b. € Vertical axis: potential energy Horizontal axis: reaction progress Reactants on left; products on right Difference from reactants to transition state: 25 kJ/mol Products are lower than reactants by 15 kJ/mol Ea(reverse) = 40 kJ/mol A catalyst speeds up a reaction by lowering the activation energy by providing a different reaction pathway. (It can either be a surface for the reaction or be used and produced during the reaction.) [SO2 ]2 [O2 ] 3. a. Kc = ; Kc = [O2 ] [SO3 ]2 1 –4 Kc = b. = 3.27 x 10 2 (55.3) 4. a. HCl, HBr, € HI, HClO4, H2SO4, HNO3; LiOH, NaOH, KOH, Ca(OH)2, Sr(OH)2, Ba(OH)2 € € −1 Δ[I− ] Δ[I3 ] = 3 Δt Δt Ea = 524.4K • 462.9K • 8.314 61.5K 0.693 4 t1 = = 2.75 x 10 s k 2 J • ln125.4 5 mol • K = 1.59 x 10 J/mol CHM 1220/1225 Exam IV A Answers 9. [H3O+] [OH–] 1.67 x 10 0.0600 M –13 M Page 2 of 2 pH pOH 12.778 1.222 10. a. b. c. d. e. f. g. h. i. j. The reaction shifts forward The reaction shifts forward No effect (this is a solid) No effect (same amount of gas on each side) The reaction shifts forward H2Se Binary acid same group; Se is larger so the H–X bond is weaker HClO Oxyacid, same #O; Cl has a higher electronegativity, so the H–O bond is more polar HCl Binary acid same period; Cl has a higher electronegativity, so the H–X bond is weaker – + H2PO4– Same X, sam #O’s; H2PO4 is less negative and can more easily lose the H ion H2SeO4 Oxyacid, same X; More O’s, so H–O bond is more polar Extra Credit: – 11. a. H2PO4 b. The figure below illustrates the reaction of boron trifluoride with ammonia. Label the Lewis acid and the Lewis base. Lewis acid BF3 Lewis base NH3