Human Inheritance Patterns: Worksheet & Application
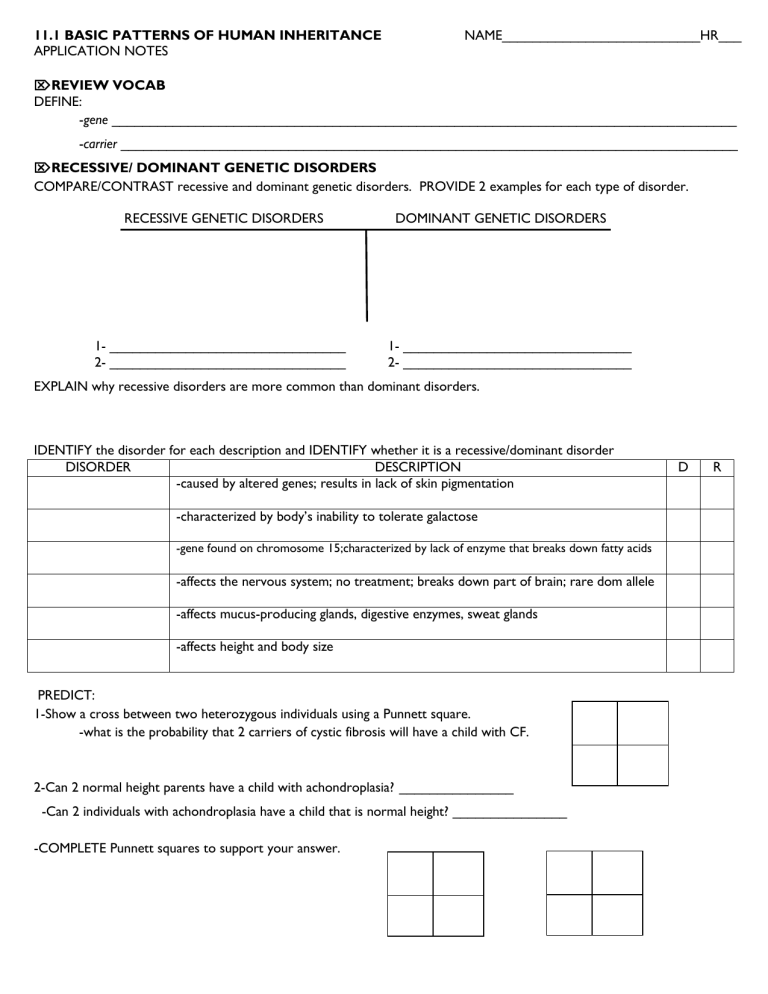
11.1 BASIC PATTERNS OF HUMAN INHERITANCE NAME__________________________HR___
APPLICATION NOTES
REVIEW VOCAB
DEFINE:
gene __________________________________________________________________________________
carrier _________________________________________________________________________________
RECESSIVE/ DOMINANT GENETIC DISORDERS
COMPARE/CONTRAST recessive and dominant genetic disorders. PROVIDE 2 examples for each type of disorder.
RECESSIVE GENETIC DISORDERS DOMINANT GENETIC DISORDERS
1- _______________________________ 1- ______________________________
2- _______________________________ 2- ______________________________
EXPLAIN why recessive disorders are more common than dominant disorders.
IDENTIFY the disorder for each description and IDENTIFY whether it is a recessive/dominant disorder
DISORDER DESCRIPTION
-caused by altered genes; results in lack of skin pigmentation
-characterized by body’s inability to tolerate galactose
-gene found on chromosome 15;characterized by lack of enzyme that breaks down fatty acids
-affects the nervous system; no treatment; breaks down part of brain; rare dom allele
D R
PREDICT:
-affects mucus-producing glands, digestive enzymes, sweat glands
-affects height and body size
1-Show a cross between two heterozygous individuals using a Punnett square.
-what is the probability that 2 carriers of cystic fibrosis will have a child with CF.
2-Can 2 normal height parents have a child with achondroplasia? _______________
-Can 2 individuals with achondroplasia have a child that is normal height? _______________
-COMPLETE Punnett squares to support your answer.
PEDIGREES
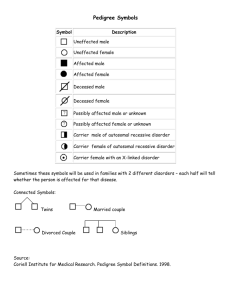
SUMMARIZE pedigree symbols by naming them then drawing the symbol in the table.
INFO DESCRIPTION SYMBOL male female affected male affected female carrier=known heterozygous parents generation represented
STEPS for INTERPRETING PEDIGREES
1-DETERMINE if the pedigree is showing AUTOSOMAL or X-LINKED disorder
-AUTOSOMAL: _____________________________________________________
-X-LINKED: ________________________________________________________
2-DETERMINE if the disorder is DOMINANT or RECESSIVE
-DOMINANT: ______________________________________________________
-RECESSIVE: _______________________________________________________
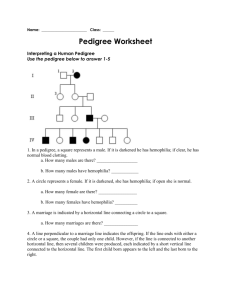
ANALYZING PEDIGREES
EVALUATE the inheritance of achondroplasia shown in the pedigree
-parent with achondroplasia
-# of children with achondroplasia
-genotype of younger son
____________________
__________
__________
ANALYZE / RESPOND to each question using the pedigree below by placing an in the correct response.
-RECALL if the trait is recessive or dominant based on the following information:
-In the pedigree, individuals I-1 and I-2 are unaffected by have affected child
RECESSIVE DOMINANT
-SPECIFIY if parents II-1 and II-2, who have an affected child, are carriers of that trait
CARRIER NOT A CARRIER
-TELL whether there is a dominant gene in the genotype of II-4
NONE
-Individual II-1is in generation 2.
A LEAST ONE
TRUE FALSE
THINK / RESPOND for each statement below, true or false
TRUE FALSE -A scientist uses a pedigree to study family history
TRUE
TRUE
TRUE
FALSE
FALSE
FALSE
-A pedigree traces the inheritance of a particular trait through only two generations
-In a pedigree, one who does not express the trait is represented by a darkened circle/square
-In a pedigree, a horizontal like between 2 symbols shows that these individuals are the parents
DIAGRAM
of the offspring.
Suppose both parents can roll their tongues but their son cannot.
DRAW a pedigree showing this trait
LABEL each symbol with the appropriate genotype