Pedigree Analysis I
advertisement

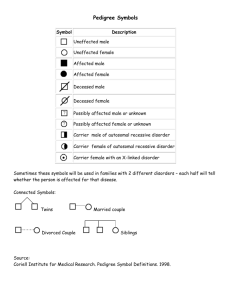
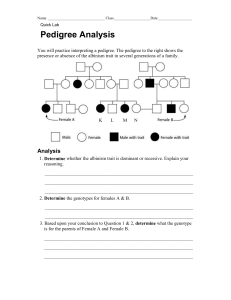
Bio/Chem/Phys 10 Genetics Name Date Period PEDIGREE ANALYSIS I INTRODUCTION Geneticists are able to study human inheritance by observing the occurrence of traits in families over several generations. A pedigree is a diagram that shows the appearance of a particular genetic trait from one generation to the next in a family tree. From a pedigree it is possible to gain understanding about dominance, sex-linkage, and other factors involved in human inheritance. In this activity you will be analyzing different pedigrees and determining the type of inheritance that the pedigree represents. A pedigree can be either autosomal (non-sex chromosome) or sex-linked. Each of those may be dominant or recessive. From the pedigree you will be able to determine the genotype and of the parents and offspring. PEDIGREE SYMBOLS AND MEANINGS Symbol Meaning Symbol Meaning Symbol unaffected male affected male unaffected female affected female Meaning marriage Symbol Meaning twins parents and children: 1 boy, 1 girl USING A PEDIGREE PEDIGREE A: Camptobrachydactyly. Camptobrachydactyly is an inherited condition in which individuals have extremely malformed hands and feet. The disorder is a dominant disorder. Use "B" to represent the dominant allele and "b" for the recessive allele. 1. List all of the possible genotypes and phenotypes for Camptobrachydactyly. Genotype Phenotype Homozygous dominant Heterozygous Homozygous recessive Bio/Chem/Phys 10 Genetics Page 1 of 5 Pedigree Analysis I February 2, 2010 GMZ Pedigree of a family with Camptobrachydactyly 1 3 2. Is person # 4 a male or female? 5 4 8 2 6 9 7 10 11 ___________________ 3. Which two people are the grandparents in the family?____________________ 4. List the numbers of the people who are affected with the disorder. _________________________ TESTING TO SEE IF THE DISORDER IS AUTOSOMAL DOMINANT PEDIGREE B: Achondroplasia. Achondroplasia is a type of dwarfism, the long bones do not develop properly, with the result that the individual is usually quite short, although the trunk and head may approach normal size. The intelligence of these persons is unaffected and they mature physically and mentally. Use "A" to represent the dominant allele and "a" for the recessive allele. Pedigree for a family affected with Achondroplasia 1 3 8 4 2 5 9 6 7 10 5. Circle the set of parents with the same phenotype and their child with a different phenotype. Bio/Chem/Phys 10 Genetics Page 2 of 5 Pedigree Analysis I February 2, 2010 GMZ When looking at pedigrees, an indicator that can help you determine if the trait is dominant or recessive is by finding parents with one phenotype with a child of a different phenotype. The parents in both cases will be heterozygous and the child will be homozygous recessive. If you find this on a pedigree you can use this information. If the disorder is dominant the parents will have the disorder and the child is normal. DOMINANT DISORDER Aa Aa Parents genotype: Aa aa Child’s genotype: aa If the disorder is recessive then the parents will be normal and the child will have the disorder. RECESSIVE DISORDER Aa Parents genotype: Aa Aa aa Child’s genotype: aa 6. From the pedigree involving Achondroplasia, determine if the disorder is dominant or recessive. 7. On the pedigree on the previous page, label all of the individuals with their genotypes. PEDIGREE C: Tay-Sachs Disease. Tay-Sachs disease is a condition involving degeneration of the nervous system, appears at about the sixth month after birth. The degeneration of the optic neurons leads to blindness, followed by loss of intellectual capabilities, progressive muscular weakness, and paralysis. It is usually lethal by the age of two or three. In this pedigree use "T" to represent the dominant allele and "t" for the recessive allele. 1 3 8 4 2 5 9 8. Is Tay Sachs Disease a dominant or recessive disorder? 6 7 10 __________________________ 9. Label each individual above with the appropriate genotype. Bio/Chem/Phys 10 Genetics Page 3 of 5 Pedigree Analysis I February 2, 2010 GMZ PEDIGREE D: Albinism. In albinism, the formation of melanin, a dark skin pigment, are blocked so that albinos have extremely light skin and hair. They also have little or no coloration in the iris of the eye, giving their eyes a pale blue or pink appearance. . In this pedigree use "A" to represent the dominant allele and "a" for the recessive allele. 1 3 2 4 8 5 7 6 10 9 10. Is albanism a dominant or recessive disorder? 11. Label each individual above with the appropriate genotype. __________________________ 12. When two carriers (heterozygous) reproduce what is the probability that one of their children will be affected? ______ Complete the punnett square to justify your answer. PEDIGREE E: Huntington's Disease. Huntington's disease is most characterized by jerky, random, and uncontrollable movements. which include slurring of speech, abnormal facial expressions, difficulties chewing and swallowing. As the disease progresses, memory deficites tend to appear. In this pedigree use "H" to represent the dominant allele and "h" for the recessive allele. 1 3 9 4 2 5 10 13. Is Huntington's a dominant or recessive disorder? 7 6 11 12 8 13 __________________________ 14. Label each individual above with the appropriate genotype. Bio/Chem/Phys 10 Genetics Page 4 of 5 Pedigree Analysis I February 2, 2010 GMZ