LAB: Locating An Epicenter
advertisement
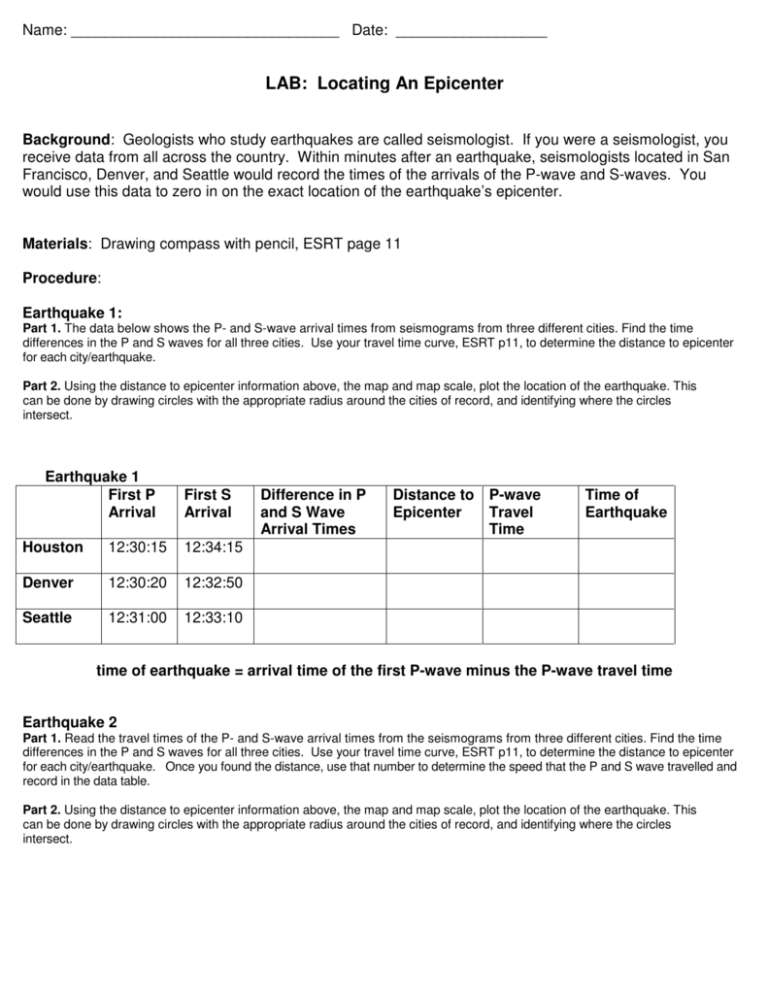
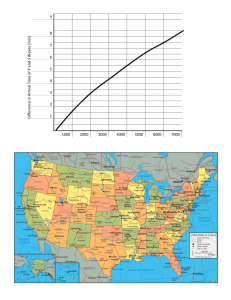
Name: ________________________________ Date: __________________ LAB: Locating An Epicenter Background: Geologists who study earthquakes are called seismologist. If you were a seismologist, you receive data from all across the country. Within minutes after an earthquake, seismologists located in San Francisco, Denver, and Seattle would record the times of the arrivals of the P-wave and S-waves. You would use this data to zero in on the exact location of the earthquake’s epicenter. Materials: Drawing compass with pencil, ESRT page 11 Procedure: Earthquake 1: Part 1. The data below shows the P- and S-wave arrival times from seismograms from three different cities. Find the time differences in the P and S waves for all three cities. Use your travel time curve, ESRT p11, to determine the distance to epicenter for each city/earthquake. Part 2. Using the distance to epicenter information above, the map and map scale, plot the location of the earthquake. This can be done by drawing circles with the appropriate radius around the cities of record, and identifying where the circles intersect. Earthquake 1 First P Arrival First S Arrival Houston 12:30:15 12:34:15 Denver 12:30:20 12:32:50 Seattle 12:31:00 12:33:10 Difference in P and S Wave Arrival Times Distance to P-wave Epicenter Travel Time Time of Earthquake time of earthquake = arrival time of the first P-wave minus the P-wave travel time Earthquake 2 Part 1. Read the travel times of the P- and S-wave arrival times from the seismograms from three different cities. Find the time differences in the P and S waves for all three cities. Use your travel time curve, ESRT p11, to determine the distance to epicenter for each city/earthquake. Once you found the distance, use that number to determine the speed that the P and S wave travelled and record in the data table. Part 2. Using the distance to epicenter information above, the map and map scale, plot the location of the earthquake. This can be done by drawing circles with the appropriate radius around the cities of record, and identifying where the circles intersect. MAP#2-AFRICA SeismicStationA S-Wave TravelTime OriginTime (TimeofEarthquake) A xxxxxxxxxx LagTime 6:31:0 0 P-Wave TravelTime 6:30:0 0 Epicenter Distance 6:29:0 0 6:28:0 0 S-Wave ArrivalTime 6:27:0 0 6:26:0 0 6:25:0 0 P-Wave ArrivalTime S-Wave TravelTime B 6:32:0 0 S P 6:24:0 0 6:23:0 0 SeismicStationB Seismic Station 6:32:0 0 6:31:0 0 P-Wave TravelTime 6:30:0 0 Epicenter Distance 6:29:0 0 Lag Time 6:28:0 0 S-Wave ArrivalTime 6:27:0 0 P-Wave ArrivalTime 6:26:0 0 6:25:0 0 Seismic Station S 6:24:0 0 6:23:0 0 P OriginTime (TimeofEarthquake) xxxxxxxxxx SeismicStationC B LagTime S-Wave TravelTime 6:32:0 0 6:31:0 0 P-Wave TravelTime 6:30:0 0 Epicenter Distance 6:29:0 0 S-Wave ArrivalTime 6:27:0 0 P-Wave ArrivalTime 6:26:0 0 6:25:0 0 6:24:0 0 6:23:0 0 Seismic Station 6:28:0 0 S P OriginTime (TimeofEarthquake) xxxxxxxxxx Answer the following questions. 1. Add a P or an S next to each word/phrase depending on if it describes a P-wave or an Swave. First to arrive ______ Shear _____ push-pull _____ primary ______ Second to arrive _____ Travels through solid, liquid and gas ________ Compression ______ secondary _______ Travels through solid only _______ Wave travels at right angles to directions its moving _______ 2. What is the difference between a focus and an epicenter? (use your notes) Refer to Earthquake 1 for questions 3 through 6. 3. What was the approximate location of the earthquake? ______________________ 4. Which city on the map is closest to the earthquake epicenter? How far, in kilometers, is this city from the epicenter? (use the scale) 5. Which city, Houston, Denver or Seattle, had the fastest P wave travel time? ___________ Which of those cities was closest to the epicenter? _______________ Fill in the statement below. The faster the P-wave travel time, the ___________________ to the epicenter. 6. List in order the 3 cities seismologists would detect the earthquake in order from first to last? 7. When you are trying to locate an epicenter, why is it necessary to know the distance from the epicenter for three recording stations? 8. What happens to the difference in arrival times between P waves and S-waves as the distance from the earthquake increases?