Nervous Reflex Lab
advertisement

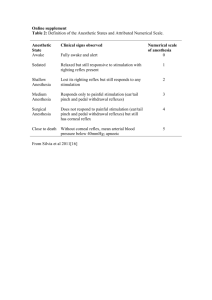
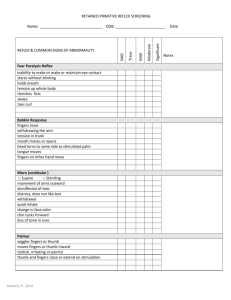
Lynn Schuster Chiles High School Name________________________ Period _______________________ TITLE: PURPOSE: MATERIALS: PROCEDURE: Nervous Reflex Lab to understand that the entire nervous system can be considered a system of innumerable reflex arcs mallet, cotton swab, feather, 3x5 index card, textbook, ruler, light, cotton ball Complete the following activities and answer the corresponding questions in each section. Possible abnormal spinal reflex results include: hyperflexia (exaggerated response), which results from damaged or diseased motor areas in the CNS; and hypoflexia (inhibited response), which results from degeneration of nerve pathways, voluntary motor control, and other factors. DATA: Patellar Relfex (aka. knee-jerk reflex) This reflex is mediated by a two-neuron arc centered in the spinal cord. 1. Subject should sit on the edge of a table or chair so that his leg hangs freely. The observer should locate the patella and the tendon below it. Then tendon should then be struck sharply with the flat end of the mallet. If done properly, this should produce the patellar reflex. The tap stretches a quadriceps muscle in the anterior thigh, stimulating stretch receptors located in the muscle. In response to the increased stretch, which normally would only occur when the muscle load has suddenly increased, the muscle contracts and extends the lower leg. Describe your results: _______________________________________________________________ 2. Repeat the above procedure but have the subject interlock his fingers and attempt to pull them apart as vigorously as possible just as the blow is struck. What effect does this muscular tension have on the reflex action? _______________________________________________________________ Explain how clenching your fists during a fight or athletic contest may affect your reflex responses: _____________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ Biceps Reflex This is a spinal reflex that involves nerves C5 and C6. Have the subject sit with the elbow flexed at about 90 degrees and palm facing downward. Put your thumb on the biceps brachii tendon at the inside angle of the elbow and press gently. Tap your thumb with a reflex mallet. Describe your response: _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ Lynn Schuster Chiles High School Achilles Reflex This is a spinal reflex that results in plantar flexion of the foot. Have the subject kneel on a chair, facing away from you, with the toes pointing toward the floor. Tap the middle of the Achilles (calcaneal) tendon with a reflex mallet. Describe your response: __________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ Triceps Reflex This is a stretch reflex. Have the subject sit in a chair, with an arm across the abdomen. Supporting the subject’s arm with the elbow flexed at a 90 degree angle, sharply tap the posterior surface of the upper arm just proximal to the olecranon fossa (see page 155 in your text). Describe your response: _______________________________________________________________ How might you explain this response? ________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ Uvular Reflex 1. Ask your subject to open his mouth widely. 2. Touch the uvula lightly with the cotton swab. What is the reaction? _______________________________________________________________ How does this reflex aid in swallowing? ______________________________ _______________________________________________________________ Cilio-spinal Reflex Gently pinch the skin at the nape of the subject's neck. Note the reaction of the pupils of his eyes: ___________________________________________________________ Sneezing Reflex 1. Stimulate the lining of the nose with a few strands of thread or a feather. Be careful that these items are not inhaled. Describe the results: _____________________________________________________________ 2. Try to inhibit this reflex by having the subject press on the upper lip just below the nose. Describe the results you obtain: ______________________________ ________________________________________________________________ Pupillary Reflex This is a reflex which is mediated by the brainstem, involving cranial nerves and autonomic reflex centers. Lynn Schuster Chiles High School 1. Have the subject close both of his eyes for ninety seconds. Hold a 3x5 index card along the bridge of his nose so that the right eye is shielded from the left. 2. Shine a bright light into his left eye as soon as he opens their eyes. Normally, the light receptors in the eye receive the bright light and trigger a reflexive response by the muscles in the iris. Note the effect it has on the pupil of the left eye: _____________________________________________________________ What is the advantage of such a response? ______________________________ _________________________________________________________________ 3. The right pupil may also exhibit a reflexive response, even though the light is not shown on it. This is an example of a consensual reflex in which one side of the body responds to a stimulus applied to a corresponding organ on the other side. Describe your results: _______________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ Corneal Reflex This is a reflex mediated by the brain which involves the fifth cranial nerve. Have the subject stand facing at a 90 degree angle to you. While the subject stares straight ahead, quickly move a clean, sterile cotton ball toward the surface of one eye. Do NOT actually touch the eye! What is the reaction? ___________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ What survival advantage does this reflex have? _________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ Accomodation Reflex 1. Examine the pupils of the subjects eyes. 2. Have the subject read a page in a textbook. 3. Ask the subject to glance up to look at a distant object. Describe what happens to the subject's pupils: _________________________________________________ Reaction Time 1. Reaction time is defined as the interval between the application of a stimulus and the beginning of a response. Have the subject rest his forearm on the edge of a table with his arm with his hand projecting over the edge. His thumb and index finger should be separated by about 1 ½ inches. 2. The observer should suspend a ruler above the hand of the subject, with the lower edge of the ruler even with the upper margin of the thumb and finger. Make certain that the ruler is suspended with the one inch measurement at the bottom. 3. The observer should drop the ruler without warning and measure the distance at Lynn Schuster Chiles High School 4. 5. which the subject caught the ruler. Record your results: ____________________ Why is it so difficult to catch the card? __________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ Repeat the above step 10 times. Record your results each time: 1. __________________ 6. ______________________ 2. __________________ 7. ______________________ 3. __________________ 8. ______________________ 4. __________________ 9. ______________________ 5. __________________ 10. ______________________ Do you feel that repeated trials decreased your reaction time? ______________ Why do you feel that this occurred? __________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ CONCLUSION: