05-10. HW-all-Ch10
advertisement

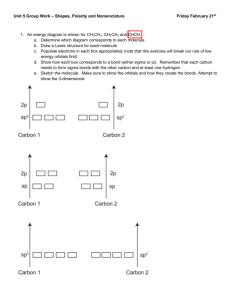
Chemistry 400 Chapter 10 Homework Problems: VSEPR, Shapes, Valence Bonding and Molecular Orbital Theories 1. Lewis Structure A. CO2 B. NO3– C. NH2Cl D. SO42– E. BrCN A. CHCl3 B. H2CO C. NH2Cl D. PO43– E. SeF5– Hybridization on central atom e– geometry Molecular geometry Approx. Bond angles Polar or non-polar (don't worry about ions) Number of σ bonds Number of π bonds Total lone pairs in the entire molecule Number of nonbonding electron pairs on the central atom 2. Lewis Structure Hybridization e– geometry Molecular geometry Approx. Bond angles Polar or non-polar (don't worry about ions) Number of σ bonds Number of π bonds Total lone pairs in the entire molecule Number of nonbonding electron pairs on the central atom 43 3. Draw the orbital overlap diagram for CH2CH2. Your diagram should include the type of each atomic orbital (s, p, d, sp2, etc.,) and whether the overlap forms a sigma or pi orbital. 4. Draw the orbital overlap diagram for CH4. Your diagram should include the type of each atomic orbital (s, p, d, sp2, etc.,) and whether the overlap forms a sigma or pi orbital. 5. Draw the orbital overlap diagram for CH3CHO. Your diagram should include the type of each atomic orbital (s, p, d, sp2, etc.,) and whether the overlap forms a sigma or pi orbital. 6. Draw the Lewis structure and orbital overlap diagram for the NO molecule. 7. Draw the Lewis structure and orbital overlap diagram for the CO molecule. Then create a version of the orbital overlap diagram that is ACTUALLY three dimensional. 8. Draw the Lewis structure and orbital overlap diagram for the CO2 molecule. Then create a version of the orbital overlap diagram that is ACTUALLY three dimensional. 9. Draw one possible structure for C4H7NO. This structure should have all neutral carbons with 4 bonds, all neutral nitrogens with three bonds and all neutral oxygens with two bonds. ("Neutral" means FC=0.) 10. Draw one possible structure for C5H6O. This structure should have all neutral carbons with 4 bonds, all neutral nitrogens with three bonds and all neutral oxygens with two bonds. ("Neutral" means FC=0.) 11. Draw one possible structure for C5H9N. This structure should have all neutral carbons with 4 bonds, all neutral nitrogens with three bonds and all neutral oxygens with two bonds. ("Neutral" means FC=0.) 12. Draw one possible structure for C6H11NO. This structure should have all neutral carbons with 4 bonds, all neutral nitrogens with three bonds and all neutral oxygens with two bonds. ("Neutral" means FC=0.) For each of the following covalent molecules, answer the questions about the molecule. In each case, answering the questions will be aided by determining the electron arrangements and shapes of the molecules in question. 13. Consider the molecule BrF5 A. What is/are the bond angles in the molecule? C. Are the bonds in the molecule polar? B. What is the molecular geometry around the bromine atom? D. Is the overall molecule polar? 14. Consider the molecule SF6 A. What is the electron geometry around sulfur? B. What is the hybridization on the sulfur atom? C. Are the bonds in the molecule polar? D. Is the overall molecule polar? 15. Consider the molecule CH2F2 A. What is the molecular geometry? B. What is the hybridization on the carbon atom? C. Is the overall molecule polar? D. Sketch the molecule (indicating any dipoles). 16. Consider the molecule PF5 A. What are the bond angles in the molecule? B. What is the molecular geometry around the phosphorus atom? C. Are the bonds in the molecule polar? D. Is the overall molecule polar? 17. Consider the ion ClF6+ A. What is the electron geometry around chlorine? B. What is the hybridization on the sulfur atom? C. Are the bonds in the molecule polar? D. Sketch the molecule (indicating any dipoles). 18. Consider the ion NH3Cl+ A. What is the molecular geometry? B. What is the hybridization on the nitrogen atom? C. Is the overall ion polar? D. Sketch the ion (indicating any dipoles). 19. Consider the ion SO42– A. What are the bond angles in the molecule? B. What is the molecular geometry around the sulfur atom? C. Are the bonds in the molecule polar? D. Sketch the ion ((indicating any dipoles). 20. Consider the molecule NH3 44 A. What is the electron geometry around nitrogen? B. What is the hybridization on the nitrogen atom? 21. The molecular orbital energy diagram for the valence orbitals of the NO molecule and the NO– ion is shown to the right. Use this diagram to answer the following questions. A. Fill in all of the electrons for the NO molecule. B. What is the bond order in NO? C. What is the bond order in NO–? D. Is NO– diamagnetic, or is it paramagnetic? How can you tell? E. Which has the larger bond distance, NO or NO–? C. What is the molecular geometry? D. Are the bonds in the molecule polar? N atom Energy 2p 2s 45 NO O atom 2p 2s 22. The molecular orbital energy diagram for the valence orbitals of the CN molecule and the CN– ion is shown to the right. Use this diagram to answer the following questions. A. Fill in all of the electrons for the CN molecule. B. What is the bond order in CN? C. What is the bond order in CN–? D. Is CN– diamagnetic, or is it paramagnetic? How can you tell? E. Which has the larger bond distance, CN or CN–? C atom Energy CN 2p 2s N atom 2p 2s 23. A d orbital and a p orbital can combine to form molecular orbitals in several different ways. Draw a sketch of the overlap between these two atomic orbitals that would produce each of the following molecular orbitals. A. a pi bonding MO B. a sigma bonding MO 24. Two p orbitals can combine to form molecular orbitals in several different ways. Draw a sketch of the overlap between these two atomic orbitals that would produce each of the following molecular orbitals. A. a pi bonding MO B. a sigma antibonding MO 25. For each of the following molecules, make a list of the molecules that are (i) polar, (ii) nonpolar and (iii) ionic. A. H2O B. CH4 C. CH3CH2OH D. CH3Cl E. Na2SO4 F. HCl G. C6H6 H. CH3COCH3 I. CCl4 26. For each of the following molecules, make a list of the molecules that are (i) polar, (ii) nonpolar and (iii) ionic. A. NH3 B. H2O C. CH3CH2CH3 D. NH4Cl E. Na2SO4 F. CH3Cl G. C6H6OH H. CH3COOH I. LiNO3 46 27. Consider the molecule: 4 8 1 5 2 7 3 6 What are the approximate bond angles in the structure? ∠1= ∠2= ∠3= ∠4= What are the hybridizations of the indicated atoms? Atom 5: Atom 6: Atom 7: Atom 8: 47