1 1 Chapter 1 Earth Science Learning Outcomes Key Terms
advertisement

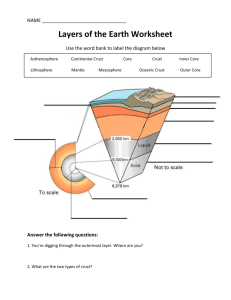
1 Chapter 1 Earth Science Learning Outcomes Define Earth science. List the sciences traditionally included in the study of earth science Summarize the early evolution of Earth and the Solar System Describe Earth's "spheres.” Briefly discuss Earth’s internal structure, including different ways to separate layers. Explain the mobile nature of the geosphere that enables Plate Tectonics to happen and why. List the principal divisions of earth’s layers and name and locate each discontinuity. Discuss Earth system science and Earth as a system. Summarize some of the relationships between people and the natural environment Describe the nature of scientific inquiry. What is science and how does it function. Define the principle characteristics of science. Key Terms: Aesthenosphere Atmosphere Biosphere Closed system Convection currents Core Crust Discontinuity Geosphere Hydrosphere Hypothesis Inner core Lithosphere Mantle Nebular hypothesis Open system Plate tectonics Non-renewable resource Renewable resource Questions: 1. The disciplines that are studied in earth science include: a. Meteorology, astrology, oceanography, and vulcanology b. Meteorology, oceanography, astronomy, geology c. Geology, geography, biology, astronomy d. Geology, oceanography, philosophy, meteorology 2. Literally translated ‘geology’ means__________________________________________ 3. Define what is means to be a “renewable” resource and give three examples of a renewable resource that you use in your every day life. 4. Define non-renewable resource and give three examples of non-renewable resources that you us in your every day life. 1 2 5. The Milky Way is one of about clusters of 28 ________________ that are called the ____________Group. 6. Our star, the sun, and the solar system around it began to form about ______________ years ago. 7. The USA has about _____% of the world population and uses about _____% of the world resources. 8. Population grows at what type of rate: a. Exponential c. Linear b. Constant d. Indirect 9. The current population of the earth is ________________ 10. The current population of the USA is: ________________ http://www.census.gov/main/www/popclock.html 11. Knowing how our planet works is necessary to our survival and well being? a. True b. False 12. List 5 environmental problems that you think are happening locally: 13. The earth is the only suitable habitat that we have and its resources are unlimited. a. True b. False 14. All science is based on the assumption that the world behaves in: a. Consistent and predicable ways that are comprehensible through careful, systematic study. b. Logical process that is universally accepted and undisputed. c. Based on concrete facts that never change d. Erratic and unpredictable ways 15. A hypothesis is a: a. Prediction based on models that are not validated by nature b. Tentative explanation that is tested to determine if it is valid 2 3 c. Observations that are well tested, have withstood serious scrutiny and repeatedly supported d. All of the above 16. Hypotheses must be testable, compared against objective observations and shared with scientific community by being published in scientific journals. a. True b. False 17. If a hypothesis survives extensive scrutiny and competing models have been eliminated through testing evidence it is elevated to a a. Paradigm c. Theory b. Law d. Model 18. In common language a Theory is often considered a guess or idea, in scientific terms it is considered: a. Well tested fact that will not change. b. Well tested, widely accepted explanation that the scientific community agrees best explains the observable facts. c. Well tested fact that eventually turns into a paradigm. d. Well tested, widely accepted explanation that the scientific community agrees best explains the observable facts, and is continually open to revision. 19. Plate tectonics and the Big bang are two examples of a. A hypothesis c. A paradigm b. A theory d. A law 20. Consider the following statement “Science is the acceptance of what works and the rejection of what does not” a. True b. False 21. What are the four major divisions in the geologic time scale or earth history in their correct order from oldest to youngest time period? a. Precambrian, Archean, Proterozoic, and Phanerozoic b. Eon, Era, Period, Epoch c. Paleozoic, Mesozoic, Cenozoic, and Quaternary d. Epoch, Period, Era, and Eon 24. The nebular hypothesis suggests that the solar system was formed from an enormous rotating cloud called the ____________ _________________ and was formed about _____________ BILLION years ago. 25. What are the two most prevalent elements in the nebular cloud? a. hydrogen and plutonium b. helium and oxygen c. hydrogen and plasma d. hydrogen and helium 26. What force helped collapse the cloud into proto-suns? 3 4 a. b. c. d. Supernova and gravity Supernova and electricity Supernova and magnetism Supernova and charm 27. What materials collided to form inner planets? a. Magma, ice, carbon dioxide, methane b. Iron, silica, ammonia and ice c. Iron, nickel, silicon, calcium and sodium d. Meteorites, iron and nickel 28. What materials are included in high percentage in outer planets? a. water, ammonia, carbon dioxide and bubble bath b. water, ammonia, carbon dioxide and magma c. water, ammonia, carbon dioxide and methane d. water, ammonia, carbon dioxide and radioactive decay. 29. What are the two types of earth’s crust? a. oceanic and continental b. basalt and mantel c. graham cracker and whole wheat d. None of the above 31. The continental crust has an average density of 2.7 g/cm3 and in some areas is known to be 4 billion years old. On the other hand, ocean crust is much younger and has a density of 3.0 g/cm3. Which of the two is more dense than the other? a. Ocean crust is more dense than continental crust b. Continent crust is more dense than ocean crust c. There is really no difference in density 32. The lithosphere, which means ‘sphere of rock’, is the cool outer rocky shell of the earth a. True b. False 33. The upper mantel is made up of what two layers according to layering by physical properties: a. Lithosphere and biosphere b. Geosphere and lithosphere c. Lithosphere and asthenosphere d. Asthenosphere and mesosphere 34. Layering by chemical composition of earth’s layers is as follows: a. Crust, asthenosphere, core b. Lithosphere, asthenosphere, mantel, outer core, inner core c. Low density rock, high-density rock, super dense iron and nickel. d. Crust, Mantel, Outer core, Inner core 35. Despite the super high temperature at the inner core, it is solid because the immense pressure that exists at the center of the planet. a. True b. False 4 5 36. The outer core is liquid even though it is made from the same materials as the inner core. The motion of the outer core is believed to be the cause of earths a. Atmosphere b. Magnetic field c. Lithosphere plate motion d. None of the above 37. The unequal distribution in the earth’s interior causes _________________________ currents that drive plate motion. 38. Temperature differences drive these currents in which hotter, ____________ dense, materials rise and cooler, _______________dense, materials sink. DRAWING Draw the earth layers with the five layers of the physical properties of the layers. Include the three discontinuities and each layer labeled. Label all parts of your drawing. 5