LIGHT-FOLLOWING ROBOT
advertisement

LIGHT-FOLLOWING
ROBOT
EGGN 383 Final Project
Jacob Dubinsky
Tyler Scott
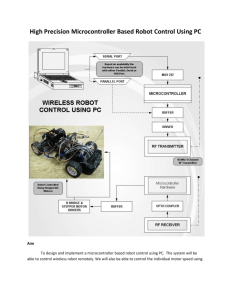
Overview
• Mobile platform that determines and drives towards the
direction of strongest light
• If an obstacle is in the way, redirects and then resumes
following the light
Hardware
• Arduino Uno
• 4 Photoresistors
• 4 10kΩ resistors
• Two wheels with attached DC Motors and Rotary
Encoders
• H-Bridge
• Proximity Sensor
• Platform
Schematic
Software Overview
• Arduino Uno – ATMega328P
• Registers instead of built in functions (digitalWrite(),
analogRead(), etc)
• Interrupts
• Analog Read
• PWM
• Subsumption Architecture
• Avoid obstacles has highest priority (lowest layer)
Interrupt Registers
Interrupt Registers
• Set INT# bit to enable interrupts on pin INT#
• Set I bit to enable global interrupts
Analog Read Registers
Analog Read Registers
PWM Registers
PWM Registers
Source (Register Slides 6-11): http://www.atmel.com/Images/doc8161.pdf
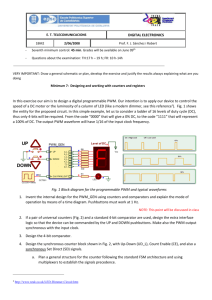
Phase-Corrected PWM
Source:
http://www.cs.washington.edu/education/courses/csep567/10wi/lectures/Lecture7.
pdf
Pseudo Code – Light Following
Initialize PWM to 1kHz on pins D5,D6,D9,D10
Initialize A/D converters on A0-A3
Input capture on D2,D3 with interrupts
Loop:
Check analog values
Determine new direction
Check the speed of wheels
Change speed of wheels with PWM
D5 = PWM D6 = 0 for left wheel forward
D9 = PWM D10 = 0 for right wheel forward
Interrupt:
Calculate speed of right wheel
Interrupt:
Calculate speed of left wheel
Pseudo Code – Obstacle Avoidance
Loop: // same loop as previous; broken up for readability
// Read proximity voltage
Vproximity = ReadAnalog(ProximityPin)
// Check if closer than 15 cm (1.75 V) to an obstacle
If(Vproximity > 1.75 V)
{
Allow vehicle to turn, do not allow it to move forward
}
else
{
Follow light // loop in last slide
}
Questions?