Finance Problem Set: WACC, EBIT, Capital Structure

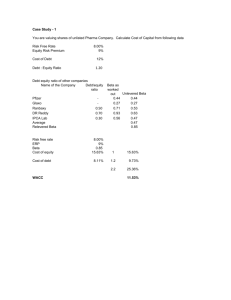
1. Nina Corp. uses no debt. The weighted average cost of capital is 11 percent. If the current market value of the equity is $43 million and there are no taxes, what is EBIT?
EBIT = $4.73
2. In the previous question, suppose the corporate tax rate is 35 percent. What is EBIT in this case? What is the WACC? Explain.
WACC = 11%; EBIT = $7.277
3. Weston Industries has a debt–equity ratio of 1.5. Its WACC is 12 percent, and its cost of debt is 9 percent. The corporate tax rate is 35 percent. a. What is Weston’s cost of equity capital? b. What is Weston’s unlevered cost of equity capital? c. What would the cost of equity be if the debt–equity ratio were 2? What if it were 1.0?
What if it were zero? a. Re = 21.225% b. Ru=15.19% c. D/E = 2, Re = 23.24%; D/E = 1, Re = 19.2135%; D/E = 0, Re = 15.19%
4. Shadow Corp. has no debt but can borrow at 7 percent. The firm’s WACC is currently 11 percent, and the tax rate is 35 percent. a. What is Shadow’s cost of equity? b. If the firm converts to 25 percent debt, what will its cost of equity be? c. If the firm converts to 50 percent debt, what will its cost of equity be? 4. What is
Shadow’s WACC in part (b)? In part (c)? a. Re = 11% b. Re = 11.87%, WACC = 10.04% c. Re = 13.6%, WACC = 9.075%
5. Alpha Corporation and Beta Corporation are identical in every way except their capital structures. Alpha Corporation, an all-equity firm, has 10,000 shares of stock outstanding, currently worth $20 per share. Beta Corporation uses leverage in its capital structure. The market value of Beta’s debt is $50,000, and its cost of debt is 12 percent. Each firm is expected to have earnings before interest of $55,000 in perpetuity. Neither firm pays taxes. Assume that every investor can borrow at 12 percent per year. a. What is the value of Alpha Corporation? b. What is the value of Beta Corporation? c. What is the market value of Beta Corporation’s equity? d. How much will it cost to purchase 20 percent of each firm’s equity?
e. Assuming each firm meets its earnings estimates, what will be the dollar return to each position in part (d) over the next year? f. Construct an investment strategy in which an investor purchases 20 percent of Alpha’s equity and replicates both the cost and dollar return of purchasing 20 percent of Beta’s equity. g. Is Alpha’s equity more or less risky than Beta’s equity? Explain. a. Vu = 200,000 b. V
L
= 200,000 c. V
E
= 150,000 d. Alpha, 40,000; Beta, 30,000 e. Alpha, Return = 11,000; Beta, Return = 9,800 f. Homemade Leverage g. Beta’s Equity is riskier (use Debt)
6. HappyCo has an 8% debt cost of capital and a 15% equity cost of capital. HappyCo’s debt has a market value of $500 million in perpetual bonds with a coupon rate of 10%. Currently there are
10 million shares outstanding, each valued at $50. If there are no taxes (and no other market imperfection either), the risk free rate is 4% and the expected return on the market portfolio is
12%, calculate the following quantities.
(a) β
D
and β
E
.
(b) r
A
and β
A
.
(c) The weighted average cost of capital (WACC).
(a) β
D
= 0.5 and β
E
= 1.375.
(b) r
A
= 11.5% and β
A
= 0.9375.
(c) The weighted average cost of capital (WACC) = Ra = 11.5%.
7. Archimedes Levers is financed by a mixture of debt and equity. You have the following information about its cost of capital: r
E
= r
D
=12% r
A
=
β
E
=1.5 r f
=10% r
β
Can you fill in the blanks?
D m
=
= 18%
β
A
=
D/V = 0.5
r
E
= 22%
β
E
=1.5 r f
=10% r
D
=12%
β
D
= 0.25
r m
= 18%
r
A
= 17%
β
A
= 0.875
D/V = 0.5
8. The El Paso Corporation (EP) is a natural gas firm with a market debt-equity ratio of 2.
Suppose its current debt cost is 6%, and its equity cost is 12%. Suppose also that if EP issues equity and uses the proceeds to repay its debt and reduce its debt-equity ratio to 1, it will lower its debt cost to 5.5%. With perfect capital market (i.e., no taxes of any kind), what effect will this transaction have on EP’s equity cost and weighted average cost of capital? (Use M&M theory)
WACC constant = 8%; Re decrease to 10.5%
9. Global Pistons (GP) has common stock with a market value of $200 million and debt with a value of $100 million. Investors expect a 15% return on the stock and a 6% return on the debt.
Assume perfect capital markets (i.e., no taxes of any kind. Use M&M theory).
(a) Suppose that GP issues $100 million of new stock to buy back the debt. What is the expect return of the stock after this transaction?
(b) Suppose instead that GP issues $50 million of new debt to repurchase the stock.
(i) If the risk of the debt does not change, what is the expected return of the stock after this transaction?
(ii) If the risk of the debt increases, would the expected return of the stock be higher or lower than in part (i)?
(a). Expected return on GP’s Equity = 12%
(b).
(i). 18%
(ii). lower
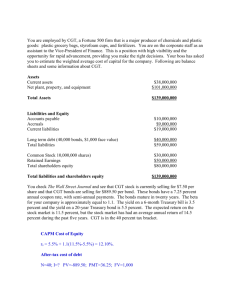
10. You are given the following information for Lorelei Motorwerke:
Long-Term Debt Outstanding:
Current Yield to Maturity (r
D
):
Number of Shares of Common Stock:
$300,000
8%
10,000
Price per Share:
Book Value per Share:
$50
$25
Expected Rate of Return on Stock (r
E
): 15%
(a) Calculate Lorelei’s weighted-average cost of capital (assuming that the firm pays no taxes).
(b) How would r
E and the weighted-average cost of capital change if Lorelei’s stock price falls to
$25 due to declining profits? Business risk is unchanged.
(a). WACC = 12.375%
(b). Re = 17.625%, WACC unchanged.