GAS EXCHANGE & CIRCULATION
advertisement

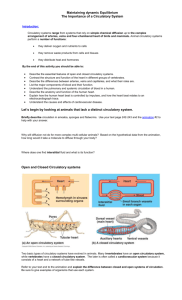
1 of 10 GAS EXCHANGE & CIRCULATION Chapter 42; Pages 867–891 CELLULAR RESPIRATION VS. RESPIRATION MOVEMENT OF GASES • Both O2 and CO2 move by ____________________________ – The movement down a __________________________________________________ – If a gas produced in one location, it diffuses away • But diffusion is usually not __________________________ or ___________________________ – Time it takes a substance to diffuse is proportional to the square of the distance • If it takes _____________ to diffuse 100µm • It will take _______________ to diffuse 1mm • It would take ________________ to diffuse 1cm! • Therefore 1 mm – the maximum ____________________________ distance for simple diffusion to supply cells with oxygen • Poses a problem if cells are ____________________________ from an O2 source – They will asphyxiate! – So animals are limited to being 2mm thin • But most animals are thicker than 2 mm! – A ____________________________ mechanism must be involved to ensure no cell is >1 mm from O2 2 of 10 REQUIREMENTS FOR GAS EXCHANGE • In order to facilitate gas exchange certain requirements must be met: • ____________________________ – gas dissolves into the water film and diffuses across cell membranes • Adequate respiratory ____________________________ to supply internal tissues • Larger animals have more ____________________________ • More cells equals a ________________________________________________________ GAS EXCHANGE • ________ large organisms still use ____________________________ – across moist surfaces – If the animal is too large for diffusion ____________________________________ they add a ____________________________ – Sites of gas exchange are highly ____________________________ – Capillaries pick-up and carry ____________________________ to the tissues in exchange for ____________________________ OPTIONS FOR GAS EXCHANGE • All animals need a way to facilitate exchange • There are two major strategies – Exchange gases over their ___________________________________________________ – Exchange gases at ____________________________ • ____________________________ • ____________________________ CUTANEOUS RESPIRATION • The diffusion of gases across the body surfaces • When does this work? – Animals dependent on water – _________________________________________________ – Animals with thin skin – ______________________________________________________ • Poriferans – sponges – Water canals everywhere – All cells are directly ________________________________________________________ 3 of 10 – Choanocytes generate a constant current • Immediate ________________________________________________________ – ____________________________ for gas exchange • Cnidarians • Some can get very large – how? – Only 2 tissue layers (just ____________________________) – The ‘bulk’ of big jellyfish is non-living jelly – ____________________________ – Gastrovascular cavity supplies O2 to the ____________________________ • Flatworms – are flat! – Not many platyhelminths get thicker than ____________________________ • Earthworm gas exchange • Live in terrestrial but ____________________________ to help keep the body surface moist (facilitates exchange) • Numerous ____________________________ just beneath the integument which ________________________________________________________ – Works the same way as our lungs! • What about more complex animals? – Not just restricted to the simpler animals – Largely dependent on the animal’s ____________________________ • Usually found in __________________________________________________ – Animals that are ____________________________ – Animals that still ____________________________ GILL BREATHING • Most large aquatic organisms rely on ________________________ – ________________________________________________________ (outgrowths) of the body surface – Thin-walled structures (____________________________) • Why not cutaneous respiration? – Many are covered with protective ____________________________ • ____________________________ – Not enough ____________________________ to supply all cells 4 of 10 • Gills can be outside the body (____________________________) or protected inside a chamber (____________________________) • Evolutionary trend in gills is towards either – An increased ____________________________ – Increased ____________________________ – Both lead to ____________________________________________________ gas exchange • Many annelids (the Polychaetes) have large and elaborate lateral appendages – ____________________________ • Multitasking structures – ____________________________ – ____________________________ • ____________________________ – 1 pair/segment • Relatively ____________________________ • Rich ____________________________ • Other polychaete worms have highly modified appendages - ____________________________ • Large feathery structures on the anterior end – A massive, highly vascularized ____________________________ • Multitasking again! – ____________________________ – ____________________________ VENTILATION • Internal gills pose a problem – How do you get water to ____________________________ – Ventilation • Fish – open their mouths & opercula to generate ____________________________ – Or they don’t ________________________________________________________ • Lobsters, crabs, shrimp – beat appendages (____________________________) to create water currents 5 of 10 COUNTERCURRENT EXCHANGE • The most efficient way to collect O2 out of water • Water moves in the ____________________________ direction as the blood – There is always a ____________________________ drawing O2 into the blood AIR BREATHING • Turn your gills inside out • Rather than outpocketings, use ____________________________ or infoldings – Forming a lung – an internal chamber • Still has to be ____________________________ with a large • But there are problems with this system – Every breath you take, ____________________________ – More surface area equals more water loss • Lungs vary in their efficiency • Frogs have small lungs – Smaller surface area for gas exchange • Why? – ____________________________ (skin) is their major gas exchange structure – Therefore they need to keep moist • Stay near water • Mucus (helps for sunburn too) OTHER VERTEBRATE LUNGS • Thousands of alveoli – ____________________________ – The site of ____________________________ – Associated with blood vessels – ____________________________ • Incredibly large surface area ____________________________ in humans – Ciliated & mucus lining 6 of 10 AIR BREATHING • Insects use an entirely different system – the ____________________________ – Open to the environment through multiple ____________________________ – The network of tracheae and tracheoles (small airways) reaches nearly __________________ • Based on simple ____________________________ with each cell having a ________________________________________________________ CIRCULATORY SYSTEMS • So you’ve exchanged your gases, now what? – You need a way to get the O2 to the tissues and cells – You need a circulatory system • Circulatory systems come in three different flavours: – ____________________________ cavity – ________________________________________________________ system – ________________________________________________________ system GASTROVASCULAR CAVITY • Think of who has a GVC? • What are their body shapes? • ____________________________ – ____________________________, but some are quite large >>2mm • Diffusion cannot get into the deeper layers • Does it need to? • ____________________________ – ____________________________, thin & flat • Diffusion is an efficient mechanism to get to all tissues • The GVC works to move gasses and nutrients OPEN CIRCULATORY SYSTEMS • The____________________________ pumps the circulatory fluid throughout the system • Vessels usually leave the heart and are ____________________________ – Fluid spills out into cavities called ____________________________ – Fluid then ____________________________ the cells providing nutrients, O2 7 of 10 • Fluid re-enters the heart through ____________________________ (_____________________) or separate vessels • The body fluid that bathes the tissues is the ____________________________ as that inside the vessels – No ____________________________ – Just ____________________________ CLOSED CIRCULATORY SYSTEMS • The____________________________ pumps the circulatory fluid throughout the entire system • The circuit is ____________________________ enclosed in a series of blood vessels • Two ____________________________ types of fluid in the body are required – The ____________________________ within the vessels – And __________________________________________ which bathes the cells in the tissues • Seen in: – Some annelids (earthworms) – Active molluscs – squid & octopi – The vertebrates EARTHWORM CIRCULATION • Advantages of a closed system – Higher ____________________________ – Greater ____________________________ – More efficient ____________________________ • ____________________________ carries blood towards the heart – anteriorly • ____________________________ carry blood towards the tissues – posteriorly • 5 pairs of auxiliary hearts (pseudohearts) come off the main dorsal heart and connect the vessels VERTEBRATE CIRCULATORY VESSELS • ____________________________ (arterioles) – Carry blood away from the heart • ____________________________ (venules) – Carry blood towards the heart • ____________________________ – Link arterioles with venules 8 of 10 • ____________________________ – Carry blood between capillary beds • All are modifications of a similar structure depending blood pressure • Arteries (arterioles) – Usually very ____________________________ made mostly of muscle and connective tissue – Necessary to resist the enormous ________________________________________________ • Veins (venules) – Relatively ____________________________ -walled vessels containing – Blood pressure is relatively ____________________________ • Capillaries – Very thin walled vessels • One cell thick – Site of ________________________________________________________ ARTERIES AND VEINS • Muscular walls of arteries are ____________________________ – Assists blood movement to the ____________________________ • Veins have ____________________________ muscle to effectively move blood – Rely upon contraction of nearby ____________________________ – Valves prevent ____________________________ since the pressure is so low – Think about when you sit still for a long time CAPILLARIES • Extremely thin-walled with only one cell layer • Huge number and total surface area to reduced ____________________________ and ____________________________ – What other benefit does this have? – More efficient ____________________________ 9 of 10 VERTEBRATE CIRCULATORY SYSTEMS • Evolution of the vertebrates lead to an increase in complexity of the circulatory system Fish • A simple ____________________________ heart – One atrium – from body – One ventricle – to body • One circulatory loop – Heart (Ventricle) – Arteries – Gill capillaries – Portal veins – Systemic capillaries – Veins – Heart (Atrium) Amphibians • A 2nd circulatory loop exists – ____________________________________________ • Heart divided into ____________________________ as a result – Two atria – One ventricle – some • Ridges in the ventricle wall prevent ____________________________ • Pulmocutaneous circuit – ‘Right’ ventricle – Arteries – Lung and skin capillaries – Veins – Left atrium • Systemic circuit – ‘Left’ ventricle – Arteries – Systemic capillaries – Veins – Right atrium 10 of 10 • Advantage is _________________________________________ to the organs because of a ____________________________ heart beat – More efficient gas exchange at tissues Reptiles • Also have a 3 chamber heart with 2 blood circuits – ___________________________ circulation • Pulmonary circuit – ____________________________ is not used as a respiratory surface • Systemic circuit • Ventricle has a __________________________________________ to minimize mixing of blood – Increased efficiency – more ____________________________ Birds and Mammals • Also have double circulation – Pulmonary circuit – Systemic circuit • A ____________________________ divides the ventricle into two – No mixing of oxygen-rich and oxygen-poor blood TAKEN TOGETHER • Gas exchange and circulation • Both O2 and CO2 move by diffusion – Down their concentration (pressure) gradients • ____________________________ – [O2] = 160 [CO2] = 0.2 • ____________________________ – [O2] = 104 [CO2] = 40 • ____________________________ – [O2] = <40 [CO2] = >45 • ____________________________ – [O2] = 40 [CO2] = 45 • ____________________________ – [O2] = 120 [CO2] = 27