Circulatory System Study Guide KEY 7E and 7M
advertisement

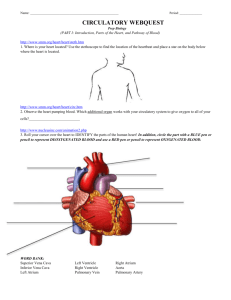
Circulatory System Study Guide 7M and 7E Vocabulary Relevant Terms Parts of The Heart – know the location of each term and how they aid in blood flow through the heart Superior vena cava Inferior vena cava rt atrium lf atrium rt ventricle lt ventricle tricuspid valve (av) bicuspid valve (av) pulmonary valve (semi lunar) aortic valve (semi lunar valve) pulmonary artery pulmonary vein aorta After Dissection chordae tendineae papillary muscles visceral pericardium myocardium interventricular sulcus apex coronary artery blood vessels veins capillaries arteries blood plasma platelets white blood cells red blood cells hemoglobin fibrin liver kidneys heart Review Question 1. What are the two big jobs of the circulatory system? 1. Carrying nutrients, water, and oxygen 2. Removing wastes from cells. 2. What are the three other jobs of the circulatory system? 1. Maintaining Body Temperature 2. Fighting Disease 3. Carrying Chemicals 3. Explain why people get red in the face after running around? Why does it happen faster when it is hot out? When someone increases their physical activity, they need more energy, so cellular respiration speeds up. The energy is released to do work and some is released as heat. When there is an increase in temperature, the capillaries move toward the surface of the skin an expand. This is so that the excess heat can easily escape the body. 4. What type of muscle is the heart made up of? Blood vessels? Describe the difference in appearance. after dissection The heart is made up of cardiac muscle and blood vessels are made up of smooth muscle. Cardiac muscle is thick and textured, where the blood vessels are smooth and stretchy. 5. Distinguish between the three types of blood vessels. Arteries - Carry blood away from the heart Veins- Carry blood to the heart Capillaries - thin blood vessel where gas exchange occurs. 6. How does blood circulate around the heart? (use the vocabulary in the top left box) See Video in circulatory system notes 7. What artery carries unoxygenated blood? Pulmonary artery - rt ventricle to the lungs 8. What vein carries oxygenated blood? Pulmonary vein - lungs to lt atria 9. Restate why veins have valves. Veins have valves to prevent blood from pooling in your feet. When the veins contract it pushes blood against gravity through the valve. (see notes for picture) 10. Explain how food, water, and oxygen pass from the blood vessels into the body? Food - broken down into small molecules in the digestive track and will enter the cells through facilitated diffusion (passive transport) or endocytosis (active transport) 11. What does blood pressure measure? Systolic vs. Diastolic? Blood pressure measures the pressure of blood on the blood vessels when the heart contracts and relaxes. Systolic = Pressure when the heart contracts Diastolic = Pressure when the heart relaxes. 12. What are some thing that affect normal blood pressure ranges? Stress and High Fat Diet 13. Compare and contrast between heart rate and blood pressure. Heart rate 1. Measurement of how many times your heart beats per minute. 2. Can be measured multiple ways. Both Both are used to determine if your health status. Blood pressure 1. Measurement of the pressure on the blood vessels. 2. two numbers 3. One way to take 14. How does exercise affect heart rate? How do you know? When you exercise you need more energy. Your heart beats faster to deliver more oxygen to your cells to release more energy from glucose. You should also know this that you breathe heavier and have a fast heart beat after you go up the stairs to the thirf floor:) 15. How much blood is in an adult? (gallons) 1 and 1/2 gallons 16. List the components of blood, and describe their importance in the human body. Components of blood Plasma Percentage and Job 55% Dissovles salts, chemicals, and food RBC 44% Carries oxygen and carbon dioxide through the blood stream. WBC Less than 1% Fights off pathogens in the body. Platelets Less than 1% Clots blood when cuts occur to the blood vessels. 17. What is the role of hemoglobin? What type of macromolecule is it? Hemoglobin is a protein that is on RBC that carries both oxygen and carbon dioxide through the circulatory system. 18. Explain what happens when you get a minor cut. WBC rush to the cut to attack invading bacteria, blood vessels contract, and platlets start to group together to clot the blood. The clot is to stop the bleeding. 19. List the four ALL the possible blood types. A + , A- , B +, B - , AB+, AB-, O+, and o20. Sketch out the four blood types. See diagrams in notes 21. Explain what blood is the universal donor. O- is the universal donor because is doesn't have any antigens on the in it. 22. Explain what blood type is the universal receiver. The universal receiver is AB+, it has A , B, and Rh antigens and will recognize all the possible blood types. Bringing all together 1. List the characteristics of life and highlight the ones we have studied so far. 1. Made up of cells 2. Reproduce 3. Are made up of a universal genetic code 4. Obtains and use materials for energy 5. Maintain a stable internal environment 6. Respond to its environment (started this) 7. Taken as a group changes over time 8. Grow and develop 2. Why do living things need oxygen? Most living things need oxygen to release energy from glucose. 3. Explain how the terms circulation, respiration, and breathing relate. Breathing is the act of exchanging gases from the respiratory system into the air. When oxygen enters the lungs it diffuses into the blood stream and circulates in the blood and is delivered to the cells. Once it is delivered to the cells it is used in respiration to release energy from glucose. 4. Write out the balanced equation for cellular respiration and explain what is going on. C6H12O6 + 6 O2 --> 6 CO2 + 6 H2O glucose reacts with oxygen and releases the energy stored in the bonds of glucose. This energy is then used to do work for the cell and heat the body. Carbon dioxide and water are released as wastes. Water is used in the body, but carbon dioxide is released back into the air. 5. List 3 examples of how the respiratory, digestive, and circulatory system maintain homeostasis in the body. Many possibilities 1. Sweating 2. Capillaries moving toward surface and inward in different temperatures. 3. Increased heart rate as the body needs more oxygen for high energy demands.