MCR3U Course Outline
advertisement

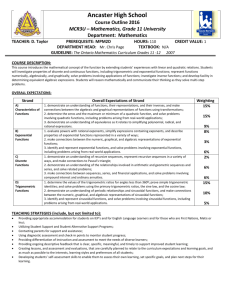
T.I.S.S. Thousand Islands Secondary School 613-342-1100 Principal: D. Lewis Course Name: Functions 11 Course Code: MCR3U Teacher: Mr. Nash Department: Mathematics Credit Value: 1 Prerequisite: Grade 10 Mathematics Date: February 6, 2012 Program Leader: Mrs. Mackellar Course Description: (Ontario Mathematics Curriculum, Grades 11 and 12: 2007 Revised) This course introduces basic features of functions by extending students’ experiences with quadratic relations. It focuses on quadratic, trigonometric, and exponential functions and their use in modeling realworld situations. Students will represent functions numerically, graphically, and algebraically; simplify expressions; solve equations; and solve problems relating to applications. Students will reason mathematically and communicate their thinking as they solve multi-step problems. Resources: Textbook: Functions 11, Thomson/Nelson Replacement Cost: $90 Additional Resources: Scientific Calculator, ruler, Technology based applications provided by teacher, additional notes provided by teacher. Consumable Cost: $0 Extra Help: The staff of TISS is committed to the success of all students. Students are strongly encouraged to seek extra help from the teacher both in and out of the classroom. Communication: Please feel free to contact me at the school, 613-342-1100, if you have any questions or concerns. My voicemail extension is 449. My email address is chris.nash@ucdsb.on.ca Page 1 Assessment & Evaluation – Ministry of Education’s Fundamental Principles: The primary purpose of assessment and evaluation is to improve student learning. To ensure that assessment, evaluation, and reporting are valid and reliable, and that they lead to the improvement of learning for all students, teachers use practices and procedures that: • are fair, transparent, and equitable for all students; • support all students, including those with special education needs, those who are learning the language of instruction (English or French), and those who are First Nation, Métis, or Inuit; • are carefully planned to relate to the curriculum expectations and learning goals and, as much as possible, to the interests, learning styles and preferences, needs, and experiences of all students; • are communicated clearly to students and parents at the beginning of the school year or course and at other appropriate points throughout the school year or course; • are ongoing, varied in nature, and administered over a period of time to provide multiple opportunities for students to demonstrate the full range of their learning; • provide ongoing descriptive feedback that is clear, specific, meaningful, and timely to support improved learning and achievement; • develop students’ self-assessment skills to enable them to assess their own learning, set specific goals, and plan next steps for their learning. Learning Skills: Teachers use their professional judgment to provide authentic and relevant opportunities to help students develop their learning skills and work habits. The student: Responsibility Organization Independent Work Collaboration Initiative Self-Regulation • Fulfils responsibilities and commitments within the learning environment. • Completes and submits class work, homework, and assignments according to agreed-upon timelines. • Takes responsibility for and manages own behaviour. The student: • Devises and follows a plan and process for completing work and tasks. • Establishes priorities and manages time to complete tasks and achieve goals. • Identifies, gathers, evaluates, and uses information, technology, and resources to complete tasks. The student: • Independently monitors, assesses, and revises plans to complete tasks and meet goals. • Uses class time appropriately to complete tasks. • Follows instructions with minimal supervision. The student: • Accepts various roles and an equitable share of work in a group. • Responds positively to the ideas, opinions, values, and traditions of others. • Builds healthy peer-to-peer relationships through personal and media-assisted interactions. • Works with others to resolve conflicts and build consensus to achieve group goals. • Shares information, resources, and expertise, and promotes critical thinking to solve problems and make decisions. The student: • Looks for and acts on new ideas and opportunities for learning. • Demonstrates the capacity for innovation and a willingness to take risks. • Demonstrates curiosity and interest in learning. • Approaches new tasks with a positive attitude. • Recognizes and advocates appropriately for the rights of self and others. The student: • Sets own individual goals and monitors progress towards achieving them. • Seeks clarification or assistance when needed. • Assesses and reflects critically on own strengths, needs, and interests. • Identifies learning opportunities, choices, and strategies to meet personal needs and achieve goals. • Perseveres and makes an effort when responding to challenges. Page 2 T.I.S.S. Thousand Islands Secondary School Course Name: Functions 11 Course Code: MCR 3U Overall Course Expectations: OVERALL EXPECTATIONS CHARACTERISTICS OF FUNCTIONS demonstrate an understanding of functions, their representations, and their inverses, and make connections between the algebraic and graphical representations of functions using transformations; determine the zeros and the maximum or minimum of a quadratic function, and solve problems involving quadratic functions, including problems arising from real-world applications; demonstrate an understanding of equivalence as it relates to simplifying polynomial, radical, and rational expressions. Chapter 1 2 ● 3 4 5 6 7 8 ● ● ● EXPONENTIAL FUNCTIONS evaluate powers with rational exponents, simplify expressions containing exponents, and describe properties of exponential functions represented in a variety of ways; make connections between the numeric, graphical, and algebraic representations of exponential functions; identify and represent exponential functions, and solve problems involving exponential functions, including problems arising from real-world applications. ● ● ● TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONS determine the values of the trigonometric ratios for angles less than 360[degree sign]; prove simple trigonometric identities; and solve problems using the primary trigonometric ratios, the sine law, and the cosine law; demonstrate an understanding of periodic relationships and sinusoidal functions, and make connections between the numeric, graphical, and algebraic representations of sinusoidal functions; identify and represent sinusoidal functions, and solve problems involving sinusoidal functions, including problems arising from real-world applications. ● ● ● DISCRETE FUNCTIONS demonstrate an understanding of recursive sequences, represent recursive sequences in a variety of ways, and make connections to Pascal's triangle; demonstrate an understanding of the relationships involved in arithmetic and geometric sequences and series, and solve related problems; make connections between sequences, series, and financial applications, and solve problems involving compound interest and ordinary annuities. 1. 2. 3. 4. Introduction to Functions Equivalent Algebraic Expressions Quadratic Functions Exponential Functions ● ● ● Chapter Topics 5. Trigonometric Ratios 6. Sinusoidal Functions 7. Discrete Functions: Sequences and Series 8. Discrete Functions: Financial Applications Page 3 Assessment & Evaluation Tools: The primary purpose of assessment and evaluation is to improve student learning. The assessments will cover the four areas of the achievement chart, namely a) Knowledge & Understanding, b) Thinking & Inquiry, c) Communication, d) Application Final Mark: Assessing, evaluating and reporting on the demonstration of learning skills and work habits is separate from the achievement of curriculum expectations and should not be considered in the determination of a student’s grade. The final grade will be determined as follows: Term work: 70% Culminating Activities: 30% - Culminating Activities in this course include: Final Exam Page 4