National Workshop on “Enabling MSME
to be Competitive through Quality Tools”
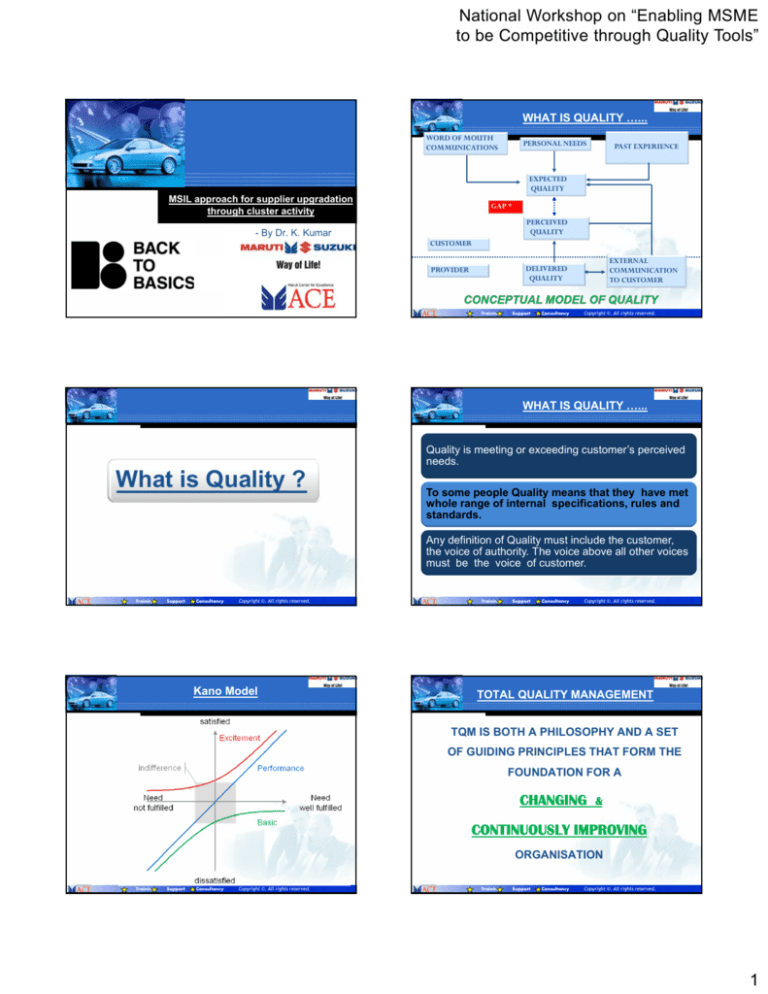
WHAT IS QUALITY …...
WORD OF MOUTH
COMMUNICATIONS
PERSONAL NEEDS
PAST EXPERIENCE
EXPECTED
QUALITY
MSIL approach for supplier upgradation
through cluster activity
GAP *
PERCEIVED
QUALITY
- By Dr. K. Kumar
CUSTOMER
EXTERNAL
COMMUNICATION
TO CUSTOMER
DELIVERED
QUALITY
PROVIDER
Training
Support
Consultancy
Copyright ©. All rights reserved.
WHAT IS QUALITY …...
Quality is meeting or exceeding customer’s perceived
needs.
What is Quality ?
To some people Quality means that they have met
whole range of internal specifications, rules and
standards.
Any definition of Quality must include the customer,
the voice of authority. The voice above all other voices
must be the voice of customer.
Training
Support
Consultancy
Copyright ©. All rights reserved.
Kano Model
Training
Support
Consultancy
Copyright ©. All rights reserved.
TOTAL QUALITY MANAGEMENT
TQM IS BOTH A PHILOSOPHY AND A SET
OF GUIDING PRINCIPLES THAT FORM THE
FOUNDATION FOR A
CHANGING
&
CONTINUOUSLY IMPROVING
ORGANISATION
6
Training
Support
Consultancy
Copyright ©. All rights reserved.
Training
Support
Consultancy
Copyright ©. All rights reserved.
1
National Workshop on “Enabling MSME
to be Competitive through Quality Tools”
Principle of total quality
ELEMENTS OF CUSTOMER SATISFACTION
Principle 1
• Proactively and systematically understand current and
PRODUCT DESIGN
QUALITY
CONFORMANCE
COST EFFECTIVE
COST
WORLD CLASS
QUALITY FOR
CORPORATE
SURVIVAL
PRICE EFFECTIVE
RIGHT PLACE
RIGHT TIME
DELIVERY
RIGHT AMOUNT
ASSURANCE OF QUALITY
SERVICE
FULL
CUSTOMER
SATISFACTION
/ DELIGHT
Proactively Companies must anticipate
customer’s needs.
•
IN USE
SAFETY
future customer needs (External and Internal)
• Customer complaints analysis is critical, it can only be
done after the complaint is resolved.
IN PRODUCTION
MORALE
EVERYONE CARES
10
Living Our CI Values
Principle 2
My input
My
Supplier
I Am
Responsible
for
Quality
As a
Good Customer
Requirement
And
feedback
I will
2)
3)
Agree on and
document my
requirements with
my supplier
Return defective
inputs to my supplier
promptly and
tactfully
Feed back input
quality data to my
supplier
My output
My
Customer
As a
Good Process
Owner or User
As a
Good Supplier
I Will:
1)
1)
Systematically it must be ensured that the process
used to resolve the
complaints is valid, objective
and statistically reliable.
2)
3)
Learn and apply
the tools of
quality and
teach others.
Continuously
improve my
process-reduce
defects, cycle
time and know
benchmarks
Document and
display my
process, defect
levels, and CI
projects
I Will:
1)
2)
3)
Requirement
And
feedback
Proactively and systematically measure the customer’s
perception of how well your organization and your direct
competitors satisfy these needs.
Robert Galvin, former chairman and CEO of Motorola
cited,
“Only by measuring something it can be truly known.”
In order to be useful, customer satisfaction measurements
must be both objective and reliable.
To ensure objectivity, a number of companies use a third
party to assess customer satisfaction.
Reliability means that for any situation the measurement
process will yield the same, or nearly the same result.
Understand my
customer
requirements and
agree on
and
document my
deliverables
Reduce defects
and variations in
my output
Measure my
output quality
from my
customer’s
perspective
11
Principle 3
Focus efforts on improving the processes or methods that
satisfy customer needs. Better financial results such as cost
reduction and higher profits are the outcome of process
improvements.
Total Quality approach would be to improve the process by
streamlining it, reducing errors, shortening process, cycle time
and eliminating activities that don’t affect Customer
Satisfaction.
To improve quality, reduce process variation.
Variation is present in all activities and processes. Although
they might be made or delivered according to the same design,
there will be differences in parts, products and services. In
many instances, variation is within an acceptable tolerance
band.
Principles of Quality
9
12
2
National Workshop on “Enabling MSME
to be Competitive through Quality Tools”
Principle 5
Variation
•Develop robust design for products and processes.
•Robust design are not sensitive to variations of
production processes, components, raw materials,
and customer usage.
•The traditional engineering approach is to design a
target (target value, target function, target region)
then reduce variation around the target.
•The new approach developed by Genichi Taguchi,
is to design for robust function, then adjust the
target.
13
16
Taguchi Loss Function
Principle 4
causes of process variation are
ever present and vary randomly within some
statistical distribution. Process is stable when
common causes are present.
•Special causes of variation are those outside
the common causes that are ever present. The
variation is due to specific assignable causes
that are non random occurrences. Special
causes are sporadic and not predictable.
LSL
USL
A
L = k (y – T)2
0
y
T-
L
Loss ($)
•Common
Loss ($)
L
T
Step function
T+
USL
LSL
T = Target
k = Quality Loss Function
y
T-
A stable process in control (Natural or common cause)
Upper
process
limit
Customer
Satisfaction
T
T+
Quadratic function
17
Principle 6
Variation
Mean
Lower
process
limit
Time
An unstable process out of control(Special Cause)
Upper
process
limit
Customer
Satisfaction
y = Performance Characteristic
A
0
14
L = Cost Incurred as quality
Deviates from the target
Mean
Lower
process
limit
•Use the scientific method for solving problems
and improving processes.
•This means that organizations must manage by
fact and not by assertion. Dr. W. Edwards Deming
has said
“In God we trust, but from all others we demand
data.”
•Managing by fact really means applying the
scientific process, which is described very clearly
by the Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA) Cycle
Time
18
3
National Workshop on “Enabling MSME
to be Competitive through Quality Tools”
PDCA Cycle
Objective
Data
Cont.
Inside & Outside
Company
Never pass on known or suspected bad quality
Abroad
Method
the next person in the process.
Education
Follow 3-NAI activity
Implementation
to
Do not receive
Consumer
Do not make
Checking
Do not send defects to the next process
Corrective
action
Product
19
22
Principle 7
When there are problems, and expectations haven’t been
met, look to the system. Don’t blame people.
Instead of finger pointing, management should focus on
the system. Instead of asking “Who did it?” or “Who didn’t do
it.?” Management should ask “What is wrong with the
system?”
Paradoxically the whole system is controlled by
management and not by people who work inside the system.
Emphasize prevention instead of detection. Inspection does
not add value and it doesn’t improve quality. It only helps to
ensure that what goes to the customers is okay.
Biggest Challenge
•How to Maintain the Market Share & How many varieties of products are
introduced in the Market every Year?
•To improve the Quality of the Products in terms of Quality, Cost &
Delivery.
For improving Quality what should we do?
20
Training
Principle 8
Support
Consultancy
Copyright ©. All rights reserved.
QC 7 Step Solving approach
The ultimate way to ensure quality, however, is to
design processes so that regardless of variation of
process control parameters the output is optimal or nearly
optimal. Such processes are said to be robust designs. A
related concept is the principle of Fool Proofing, or
poka - yoke in Japanese.
QC 7 steps Procedure is the basic procedure for solving
problems scientifically, rationally & effectively.
It is the fundamental Problem solving strategy which
allows to solve the problems rationally & scientifically.
If we want to achieve EFFECTIVE improvement we have
Put Quality ahead of quantity.
to know the rules of the game i.e. QC 7 Steps
It means:- Consistent Quality standards
Procedure.
The secret of our problem solving is to know the
21
Procedure & act in accordance with it.
Training
Support
Consultancy
Copyright ©. All rights reserved.
4
National Workshop on “Enabling MSME
to be Competitive through Quality Tools”
QC 7 Step Problem Solving Formula
QC 7 Step Formulae
The conventional method is based on trial & error.
Figure‐1
a.
b.
Table‐1 Cont.
Step
No.
Basic Steps
Action Item
Expose Problem
Expose Problem
•Grasp Problem
•Set Target
•Identify
gap
between existing
situation & Target
Experience, Intuition,
nerve, Inspiration
Analyze Causes
•Investigate Causes
6
Check Results
•Check results of Countermeasures
•Compare results with Target
•Identify Tangible & Intangible benefits
Implement CounterMeasure
•Plan
Countermeasures
•Implement
Countermeasure
•Institutionalize
7
Implement CounterMeasure
Standardize & Establish
Control
Standardize
•Establish new standards & revise old ones.
•Decide methods of control
Establish Control
•Familiarize relevant people with the methods.
•Educate those responsible.
•Verify that benefits are being maintained.
Conventional Problem Solving approach
Training
QC Problem Solving approach
Support
5
Consider & Implement
Countermeasures
Consider Countermeasures
•Propose the ideas for Countermeasures
•Discuss how put Countermeasures into effect.
•Check details of the Countermeasures
Implement Countermeasures
•Plan how to implement Counter Measures
•Implement Countermeasures
Copyright ©. All rights reserved.
Consultancy
Training
Support
Consultancy
Copyright ©. All rights reserved.
Procedure for Problem Solving
QC Problem Solving approach Figure‐2
In the QC Seven Step Procedure the following points are
important:
1.
Problem
arises
Identify its
Causes
Act against
the Causes
Understand the situation & set targets: This
would mean analyzing data on the existing & past
situation & then decide the target. Fig. 3 shows the
procedure to calculate the targets
Figure‐3
Symptom
Disappears
Problem
Solved
In case of QC Problem Solving approach, the problem really has been Solved; this
is true Problem Solving
Training
Support
Consultancy
Copyright ©. All rights reserved.
Baseline
117642
Entitlement
86013
Difference
31629
70% of Diff.
22140
Target @70% of
Entitlement
95502
Training
QC 7 Step Problem Solving Formula
Support
Consultancy
Copyright ©. All rights reserved.
Procedure for Problem Solving
Table‐1
Step
No.
2.
Basic Steps
Analysis of the causes : Late Dr. Kaoru Ishikawa,
Action Item
the father of Japanese Quality Control, wanted it to
1
Select Topic
•Identify Problem
•Decide Topic
2
Understand the
situation & Select
Target.
Understanding Situation
•Collect Data
•Decide characteristic to attack
•Decide Target
3
Plan Activities.
•Decide what to do
•Decide Schedule, division of responsibility etc.
4
Analyze Causes
•Check present values of Characteristic
•List Possible Causes
•Analyze Causes
•Decide items to tackle.
Training
Support
Consultancy
be renamed as “analyze the process”. But ultimately
Copyright ©. All rights reserved.
in JUSE 7 step procedure analyze the causes was
retained & is widely used.
3.
Countermeasures: After the analysis of the Causes,
the team proceeds to take the countermeasures to
prevent the occurrence of the defects.
Cont…
Training
Support
Consultancy
Copyright ©. All rights reserved.
5
National Workshop on “Enabling MSME
to be Competitive through Quality Tools”
Procedure for Problem Solving
Basic 7 QC Tools
Checksheet
Run Chart
Pareto Chart
4. Standardize & Establish the Control : In the Past
this step was known as “Apply the Brakes” i.e.
prevent any back sliding & establish the permanent
Countermeasure. Failing to check the effect of
Control Chart
Countermeasure is like omitting the touch up after
Histogram
Painting. This would need establishing the new
standards or revising the old standards. Familiarize
Scatter Plot
Fishbone Diagram
people with the new standards & verify that the
benefits are being maintained.
Training
Support
Consultancy
Copyright ©. All rights reserved.
Training
Figure‐4
Consultancy
Copyright ©. All rights reserved.
Why-Why Analysis
Procedure for Problem Solving
5. Target Control: While fixing the targets & the time
limits for the achievements following key points are
important.
What control Characteristic are to be taken up for
study.
By When the study will be completed.
By How much such as reduce the defect at the
Quality gate by 30%.
Support
Originally developed by Sakichi Toyoda.
Later
used
within
Toyota
Motor
Corporation during the evolution of their
manufacturing methodologies.
The architect of the Toyota Production
System, Taiichi Ohno, described the 5
whys method as "the basis of Toyota's
scientific approach by repeating why five
Taiichi Ohno
times, the nature of the problem as well as
its solution becomes clear
Training
Support
Consultancy
Copyright ©. All rights reserved.
Training
Support
Consultancy
Copyright ©. All rights reserved.
Problem Solving: 5 Whys
TOOLS & TECHNIQUES
USED FOR PROBLEM
SOLVING
AT
MACE
This method of
problem
solving
simply
involves
asking “Why” a
number of times
(typically five times
is enough) until the
root cause of a
problem
is
determined .
36
Training
Support
Consultancy
Copyright ©. All rights reserved.
Training
Support
Consultancy
Copyright ©. All rights reserved.
6
National Workshop on “Enabling MSME
to be Competitive through Quality Tools”
Shainin Techniques for Problem
Solving
Why -Why Analysis at Toyota
Why 2?
Why 3?
Why 4?
Why 5?
Why there is a puddle of oil on the Shop Floor?
• Because Machine is Leaking Oil
Product Process Search
Why the Machine is Leaking oil?
• Because Gasket has deteriorated
Why Gasket has deteriorated?
• Because we bought the Gasket made of inferior
Material.
Why did we buy a Gasket of Inferior Material?
Because we got a Fair deal on those Gaskets
Support
Snorkel Position
Disassembly/Asse
mbly
X-BOB
X-WOW
Parameter Range
0to 1/2"
Initial
113
86
Bag no.
1
2
3
1/2 B
1/2 B
1/2 B
Ist
115
84
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
1/2 B
1/2 B
1/4 B
1/4 B
1/4 B
0G
0G
0G
12
13
14
0G
0G
0G
15
16
End Counts
0G
0G
8+ 8 = 16
Support
Range
4
2
D( Diff of Medians
= ( 113 -85 ) = 28
d ( Avg. of
Ranges )
= ( 4+2 )/2 = 3
219
217
C
212
210
-40
-30
-20
-10
0
Sequence
Support
Consultancy
Copyright ©. All rights reserved.
Attributes for World Class
Dorian Shainin
Copyright ©. All rights reserved.
Consultancy
85
-50
Training
S.NO.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
Training
85
113
223
20
Shainin Techniques for Problem
Solving
Dorian Shainin (September 26, 1914 –
January 7, 2000) was an influential
American quality consultant, aeronautics
engineer, author
Known for his contributions in the fields
of industrial problem solving, product
reliability, and quality engineering,
particularly the creation and
development of the “Red X” concept
111
225
B
10
Copyright ©. All rights reserved.
Consultancy
IInd
Median
B Vs C
Component Search
Why we purchased the Material at Fair Price when the
Quality of the Gasket was not Good ?
a) Because the Purchasing agent gets evaluated on
short term Cost Savings
Training
Modified Component Search
Process Parameter
Temp
Why 1?
ITEM
Safety :
5 S – Score
Quality :
Supply to Customer
Customer Line Stops
Inventory Turns:
Change over time
OEE (Overall Equipment Efficiency)
VA to Employee cost
VSM : Value stream mapping
Cost
Absenteeism (Unauthorized)
Direct to Indirect manpower
Kaizens / employee
New Product Development
Training Hours / Emp / Year
Training
Support
Consultancy
TARGET
Zero Accidents
90% min.
3.4 ppm
2 hourly basis
Zero
Min 50
< 10 min.
85 - 90 %
5
25%
50% less
0%
60 : 40
24/emp/year
At 50% less time and
Cost
> 5 % of working hrs
Copyright ©. All rights reserved.
Shainin Techniques for Problem
Solving
Component Search
Disassembly/Asse
mbly
X-BOB
X-WOW
Initial
113
86
Paired Comparison
S.No.
Surface Finish
Status Of the
Pump
1
65
Bad
Ist
115
84
2
64
Bad
IInd
111
85
3
61
Bad
Median
113
85
4
58
Bad
4
2
Range
D( Diff of Medians
d ( Avg. of
Ranges )
5
51
Bad
= ( 113 -85 ) = 28
6
48
Bad
= ( 4+2 )/2 = 3
7
47
Bad
8
45
Bad
Component Search
-50
-40
9
32
Good
10
32
Good
11
28
Good
12
24
Good
13
22
Good
14
22
Good
15
21
Good
16
19
Good
CLUSTER APPROACH
AT
MACE
-30
Temp
-20
-10
0
Sequence
10
20
Training
Support
Consultancy
Copyright ©. All rights reserved.
Training
Support
Consultancy
Copyright ©. All rights reserved.
7
National Workshop on “Enabling MSME
to be Competitive through Quality Tools”
•TPM Cluster
•Certified Quality Engineer
•Six Sigma Black Belts.
•Benchmarking Visits.
•Horizontal Deployment of Cluster Activity
through Tier-2.
MODEL
F
R
WORLD CLASS
•Complete 5-S
•Up-gradation through advance Quality Tools
•Hoshin-Kanri (MFO).
•Autonomous Maintenance; OEE
•Yield Improvement
•Implementation of 8 Pillars Check sheet
•Training on advance tools like DOE, DMAIC &
OEE
Phase 3
•TEI through SSQC activities.
•Single Piece Flow using Model Line; identifying
Lean Manufacturing Projects (MPS) based on
Customer Requirements.
•Inventory Turns Ratio Management
•Energy Consumption Management
•Cost of Poor Quality
•Initial Supply Control
•Value added per employee cost (VAPCO)
•Training on SSQC, MPS, EMS, QMS, NPD.
•Capturing Customer Voice
•1-S,2-S and Visualization
•Customer Concern (QCD) through why-why
Analysis.
•Red Bin Analysis using basic QC Tools
•Daily Work Management for Target Monitoring.
•Monthly Performance Review at Gemba &
Collaborative Learning
•5 New Kaizen/month/vendor.
•Training on 5S, VUD, 7 QC tools, CAPA
Phase 4
PHASE 2
CLUSTER MEETING IN PROGRESS
PHASE 1
Training
undergo a common training session and get hand held
experience.
Individual attention is given to all cluster members & all
queries during the session are answered.
Training
Support
Consultancy
Consultancy
Copyright ©. All rights reserved.
EXACTNESS
Concept of Cluster
A group of 5 to 10 vendors ( non-competing) get together to
Support
The first step in the improvement journey is Exactness. This
involves three parameters:
Exactness of Process: The vendor must ensure that the
process is being followed exactly as per the standards, as
per written down instructions. To achieve this the vendor
must employ check points in Daily Work management.
Copyright ©. All rights reserved.
Training
Advantages of Cluster
Support
Consultancy
Copyright ©. All rights reserved.
EXACTNESS
Exactness of Measurement:
This image cannot currently be display ed.
Lower Cost.
Group discussions & sharing of ideas.
Competitiveness.
Learning from one another.
Exposure to best practices.
Learning in a team.
Exposure to benchmarking.
Improved motivation.
Training
Support
Consultancy
Copyright ©. All rights reserved.
Any process is as good as its measurement. The vendor
must ensure that there is a control plan for all the
instruments & measuring gauges; periodic calibrations
are carried out as per the plan & all instruments /gauges
are kept in good working condition.
Training
Support
Consultancy
Copyright ©. All rights reserved.
8
National Workshop on “Enabling MSME
to be Competitive through Quality Tools”
Practical Problem Solving Process
TEAM ORIENTED PROBLEM SOLVING [ TOPS ]
Kaizen Competition at CII – Confederation of Indian
Industries
1. Initial Problem Perception
(Large , Vague, Complicated Problem)
2. Clarify the Problem
Grasp the
Situation
3. The “ Real “ Problem
Basic Cause and Effect
Investigation
4. POC
Direct Cause
Cause
Cause
Cause
Cause
Why ?
Why ?
5 Why ?Investigation
Of Root Cause
Funnel
Approach
Why ?
Why ?
Why ?
Root Cause
5. Countermeasure
6. Evaluate
Training
Support
Consultancy
7. Standardize
Copyright ©. All rights reserved.
Training
Manufacturing activities .
Every Year a competition amongst the Tier – 2 vendors is
held at MSIL where each vendors make a presentation
about the QC & Lean Manufacturing activities [ MPS ].
In order to motivate the vendors, awards are given through
MSIL, the parent organization .
We also encourage our Tier – 2 vendors to participate in
National Competitions to understand the best practices.
Training
Support
Consultancy
Copyright ©. All rights reserved.
Support
Consultancy
Copyright ©. All rights reserved.
Copyright ©. All rights reserved.
Total no. of Tier 2 clusters
Total no. of Tier 2 vendors covered
:
:
19
150
Measure
2004 - 05
2010 - 11
2011 – 12
Improvement
Rejection
ppm
10933
2695
1617
85 %
No. of defects
per month
432
263
159
63 %
Training
Support
Consultancy
Copyright ©. All rights reserved.
MPS for Tier-2 vendors
Implementation status
TEAM ORIENTED PROBLEM SOLVING [ TOPS ]
Quality Circle Competition in progress
Training
Consultancy
Result of Cluster approach
initiated by MACE
TEAM ORIENTED PROBLEM SOLVING
[ TOPS ]
We encourage Tier – 2 vendors in Quality Circle & Lean
Support
Training
Support
Consultancy
Copyright ©. All rights reserved.
9
National Workshop on “Enabling MSME
to be Competitive through Quality Tools”
QC Activity for Tier-2 vendors
MACE Quality Circle Convention
QC Projects completed in 2011-12 till Oct’11
As a part of Quality month celebration,Tier-2 Quality circle competition was
organized at MACE on 26th Nov’11.
Each of the cluster member held the competition at their end to select the best QC
Circle at their end for Competition in MACE.
A Total of 12 Quality Circles from 12 Tier-2 Clusters participated in this
competition.
The results of competition were as follow:
Winner
Training
Support
Consultancy
Copyright ©. All rights reserved.
: Superfine
: Lumax Cluster
1st runner up : Aar Aar Industries
: Pricol Cluster
2nd runner up :
: Subros Cluster
NRB Bearing
Training
Support
Consultancy
Copyright ©. All rights reserved.
MACE Kaizen Meet
MACE conducted Kaizen Meet for MSIL Vendors. Total of 200 Tier-1 & 400 Tier-2
vendors participated in this competition.
The results were as follow:
Tier-1
AWARD
VENDOR NAME
Winner
M/s KML Seat-1
Mr. Prateek Mandal
1st Runner Up
M/s Bright Autoplast
Mr. Himnashu Sharma
2nd Runner Up
M/s Tenneco
Mr. Sagar Vashisht
Tier-2
AWARD
VENDOR NAME
Winner
M/s Premier Pin
COUNSELLOR
CLUSTER
COUNSELLOR
Minda Cluster Mr. Amit
Chauhan
Mr. O.P.Uttareja
1st Runner Up M/s Bhamra Fabricators Subros
Cluster
Sona Cluster Mr. R.P.Bhatti
2nd Runner Up M/s Lakhani
Training
Support
Consultancy
Copyright ©. All rights reserved.
M/S Bhambra Fabricator receiving the Best Kaizen Award in T-2 Category
Training
Support
Consultancy
Copyright ©. All rights reserved.
Lumax T-2- Superfine receiving the winner Award of Quality Circle Competition
Training
Support
Consultancy
Copyright ©. All rights reserved.
M/S Precision Pin, Tier-2 of Minda receiving the Zero ppm Certificate
Training
Support
Consultancy
Copyright ©. All rights reserved.
10
National Workshop on “Enabling MSME
to be Competitive through Quality Tools”
M/S Subros receiving the Trophy for Best VSA Score in 2011-12
Training
Support
Copyright ©. All rights reserved.
Consultancy
Training
Support
Consultancy
Copyright ©. All rights reserved.
CII conducts annual Cluster summit in month of September in which various
clusters working with CII, ACMA & MACE are invited to participate by giving
their Kaizens & Case Studies on Problem Solving using 7 QC tools, Why-Why
analysis & Six Sigma.
In year 2011-12, 47 vendors of MSIL participated in this event where the best
Kaizen & the Case studies were adjudged by the Jury consisting of eminent
people from the industry.
A total of 285 Kaizens & 120 Case studies were received by CII for evaluation.
We are happy to inform that the following awards out of the total awards were
bagged by MSIL’s Tier-1 & 2 vendors:
Training
Support
Copyright ©. All rights reserved.
Consultancy
CII Cluster Championship Award Winners
Stream
MSME
Manufacturing
Excellence
Cost
Competitiveness
Energy Efficiency
Total Employee
Involvement
Vox Populi
Name of Company
Award
Auto Décor Pvt. Ltd.
1st
Horizon Industrial Products
Pvt. Ltd.
Shivai Enterprises Pvt. Ltd.
2nd
Bhambra Fabricators
1st
3rd
USV Ltd.
1st
Promed Export Pvt. Ltd.
2nd
Eastman Cast & Forge Ltd.
1st
Rakheja Engineers Pvt. Ltd.
2nd
Large
Award
Godrej & Boyce Mfg. Co. Ltd.
Mohali
Minda Industries Limited
1st
Sona Koyo Stering Systems
Ltd.
Godrej & Boyce Mfg. Co. Ltd.
Shirwal
Mahindra & Mahindra
Godrej & Boyce Mfg. Co. Ltd.
Shirwal
Mahindra & Mahindra
Tata Motors Ltd.
Godrej & Boyce Mfg. Co. Ltd.
Mohali
2nd
3rd
1st
1st
1st
2nd
3rd
1st
Godrej & Boyce. Mohali for Manufacturing Excellence
CII Kaizen Award Winners
Award
1st Award
2nd Award
3rd Award
Company
Suman Auto Parts Ltd.
Raunaq Automotive Components Ltd.
Krishna Maruti Limited
MSIL Vendors. The Case studies were based on completed MPS Projects.
11









