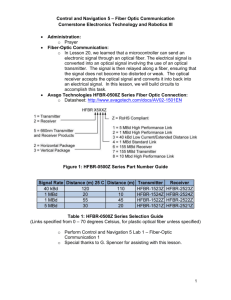
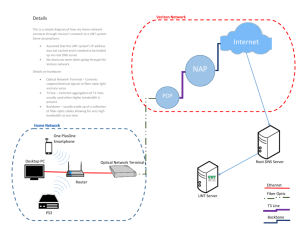
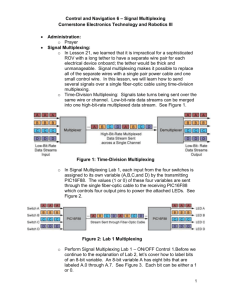
EE160 - University of California, Riverside
advertisement

EE160: Fiber-Optic Communication Systems University of California, Riverside Bourns College of Engineering, University of California, Riverside EE160: Fiber-Optic Communication Systems Spring 2005 Class Lecture: Lab: TuTh F 12:40-2:00 pm SPTH 1222 Time TBD BRNHL B140-C Staff Instructor: Ilya Lyubomirsky ilyubomi@ee.ucr.edu Office: Bourns A211 (x2 7701) Hours: W 4:00-5:30 pm TA: Cheng-Chung Chien cchien@ee.ucr.edu Office: Bourns B140 (x2 7828) Hours: during lab hours Website All homework assignments, and solutions will be posted on the class website: http://www.ee.ucr.edu/courses/ee160.html Prerequisites EE115 and EE116 (or with permission of instructor) Topics • • • • • Electromagnetic Wave Propagation, Fiber Modes, Multimode and Chromatic Dispersion Semiconductor Laser, External Modulator Semiconductor Photodetector, P-I-N and APD Receivers, Noise, Receiver Sensitivity Erbium Doped Fiber Amplifier, ASE Noise, Optically Pre-Amplified Receiver Fiber-Optic System Design Issues Homework There will be four bi-weekly homework assignments covering the above topics. The homework is due two weeks after it is handed out. No late homework will be accepted. Studying in groups is encouraged but homework must be completed independently reflecting a student's individual effort. 1 EE160: Fiber-Optic Communication Systems University of California, Riverside Laboratory There will be four bi-weekly labs covering: fiber optics, DFB laser, erbium doped fiber amplifier, and high-speed optical receiver. Each lab will be approximately 3 hours long. The lab report is due to the TA two weeks after each lab (except for Lab 4, it is due on last day of class). Exams Midterm: 05/03/2005 Final: 06/09/2005, 8 - 11 am All exams are open book. Make-up exams are possible only with documentation of illness or personal emergency. Grading Homework: Laboratory: Midterm: Final: 25% 25% 25% 25% Letter grade (4 units) is required. Any complaints regarding exam grades must be made directly to the instructor within two business days after the graded exams are returned; complaints regarding lab report or homework grades must be made directly to the TA within two business days after the graded papers are returned. A letter must be attached to your re-grading request stating clearly which question to re-grade, and reasons why you deserve more points. The instructor and/or TA will re-grade the requested questions truly. Note that if you deserve lower points than you have already been given, some points will be deducted from your grand total. It is recommended that you be very sure of your request for re-grading. Academic dishonesty will not be tolerated. This includes copying another student’s homework, allowing another student to copy your homework, cheating on exams, and altering graded papers. In accordance with UCR policy, every incident of academic dishonesty must be reported to the college dean. Text Book • Govind P. Agrawal, “Fiber-Optic Communication Systems”, 3rd Ed., Wiley-Interscience, 2002. 2 EE160: Fiber-Optic Communication Systems University of California, Riverside Spring 2005 Class Schedule Date Topic Text Assignment 3/29 3/31 Intro. Electromagnetic Waves, and Optical Comm. Total Internal Reflection, Dielectric Slab Waveguide Notes, Ch. 1 Notes Read Ch. 1-2 4/5 4/7 Single Mode Propagation in Step-Index Fiber Optical Fiber Loss and Dispersion 2.1-2.2 2.3, 2.5 Hw-1 4/12 4/14 4/15 Dispersion-Induced System Limitations Optical Processes in Semiconductors Lab 1 Intro. Fiber Optics 2.4 3.1 4/19 4/21 Semiconductor LED and Laser Semiconductor Laser Linewidth, Power, Chirp 3.2-3.3 3.4-3.5 4/26 4/28 4/29 External Optical Modulators Optical Amplifier, Erbium Doped Fiber Amp Lab 2 DFB Laser Notes, 3.6 6.1, 6.4 5/3 5/5 Midterm Photon Detection Basics 5/10 5/12 5/13 P-I-N and APD Receivers Thermal Noise and Shot Noise Lab 3 EDFA 4.2-4.3 4.4 5/17 5/19 ASE Noise from Optical Amplifiers BER and Receiver Sensitivity 6.4-6.5 4.5, 6.5 5/24 5/26 5/27 Shot Noise, and ASE Noise “Quantum Limits” Receiver Degradations Lab 4 Receiver Sensitivity Notes, 4.5 4.6 5/31 6/2 Fiber-Optic System Design Issues Review Notes, 5.1-5.4 6/9 Final 4.1 3 Read Ch. 3 Hw-2 Read Ch. 6 Hw-3, Read Ch. 4 Hw-4 Read Ch. 5 EE160: Fiber-Optic Communication Systems University of California, Riverside Course Learning Objectives The following list gives some specific learning objectives for this course, identified by the instructor as important concepts and/or skills to learn. 1. Understand and be able to explain the physical principle for how an optical fiber guides light. 2. Be able to estimate the limitations on transmission speed and/or distance caused by fiber dispersion. 3. Understand and be able to explain the advantages, and limiting characteristics of semiconductor lasers as used in fiber-optic communications. 4. Understand and be able to explain the operating principles of semiconductor photodetectors, and the main noise sources that corrupt the detection process. 5. Be able to estimate the receiver sensitivity for P-I-N, APD, and optically pre-amplified receivers. 6. Understand and be able to explain the operating principle, advantages, and limitations of erbium doped fiber amplifiers. 7. Learn how to use basic fiber-optic test equipment for measuring optical power, optical signal spectrum, and receiver sensitivity. 8. Design fiber-optic communication links limited by loss and/or fiber dispersion. 4