The Cell
advertisement

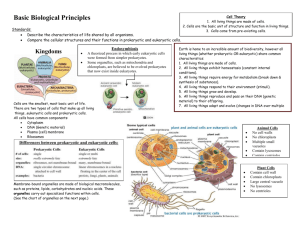
The Cell I. Cell Theory A. Three parts 1. All living things are made of cells 2. The cell is the basic unit of life 3. New cells are made by other living cells II. Two kinds of cells A. Prokaryotic 1. No membrane-bound organelles 2. Single-celled organisms B. Eukaryotic 1. Membrane-bound organelles 2. Singled-celled and multi-cellular organisms III. Eukaryotic Cell Structure A. Organelles 1. “Small organs”, structures that perform vital functions for the cell 2. Present in all eukaryotic cells a. Cell Membrane* i. Controls what goes in and out of the cell ii. Phospholipid bilayer b. Cytoplasm i. Gel-like substance that fills the cell ii. Holds many monomers for the cell to make polymers with c. Cytoskeleton i. Provides support ii. Protein fibers that criss-cross the whole cell d. Centrosome i. Produces microtubules for various processes - Microtubules are small protein fibers - Can be used for structure or for cellular division e. Nucleus* i. Stores the DNA of a cell ii. It must protect the DNA, but also make the DNA available for use - Nuclear Membrane has pores that allow only DNA and special proteins to pass through - Nucleolus is a dense area of DNA that makes ribosomes f. Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum i. Makes lipids g. Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum 3. 4. i. Is covered in ribosomes ii. These make proteins that will go to the cell membrane, or be secreted h. Ribosome* i. Tiny organelles that link amino acids together to make proteins ii. Some are suspended in the cytoplasm - They make proteins that will be used for chemical reactions i. Golgi Apparatus i. Puts the finishing touches on some proteins ii. Packages them for delivery inside the cell and outside the cell j. Vesicle i. Small membrane-bound sacs that safely transport materials in the cell k. Vacuole i. A fluid-filled membrane-bound sac that stores materials l. Mitochondrion* i. Converts molecules from food (glucose) into usable energy ii. Have their own DNA and ribosomes Plant Cells a. Central Vacuole i. Huge fluid-filled membrane-bound sac that takes up most of a plant cell ii. Adds support and rigidity to the cell b. Chloroplast* i. Converts solar energy into chemical energy c. Cell Wall i. Gives the cell it’s structure and makes the cell more rigid ii. In plant, algae, and bacteria cells Animal Cells a. Lysosome i. Contains enzymes to break down invaders, or old cell parts b. Centriole i. Specially arranged microtubules made by the centrosome ii. Help with cell division