Chapter 3.2
advertisement

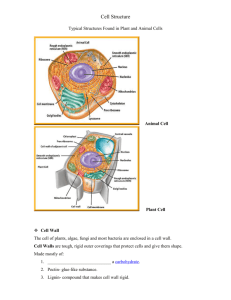
CHAPTER 3.2 Cell Organelles EUKARYOTIC CELLS • Highly organized • Surrounded by a protective membrane • Contain membrane-bound organelles that have specific functions • The internal structure is anchored to maintain its framework CYTOSKELETON • A network of proteins that can change to meet the needs of the cell. • Made of 3 types of fibers: 1. Microtubules: long hollow tubes that give the cell its shape and act as “tracks” so organelles can move 2. Intermediate filaments: give the cell strength 3. Microfilaments: tiny threads that enable cells to move and divide CYTOSKELETON PROTEIN MAKERS • Nucleus: Stores DNA (blueprints for protein) • Ribosomes: Link amino acids to form proteins • Endoplasmic reticulum (ER): protein & lipid production • Golgi apparatus: process, sort & deliver proteins • Vesicles: isolate and transport specific molecules, including proteins PROTEIN MAKERS NUCLEUS • Stores DNA • Nuclear envelope – double membrane of the nucleus • Nucleolus – special region where ribosomes are made NUCLEUS ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM (ER) • Interconnected network of folded membranes that produce proteins and lipids • Lumen: interior of the ER • Rough ER: Studded with ribosomes, proteins are made on the surface and modified in the lumen. • Smooth ER: No ribosomes, it makes lipids and breaks down drugs & alcohol. ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM (ER) RIBOSOMES • Tiny organelles that link amino acids together to form proteins • Made of proteins and RNA • Exist on the ER and freely in the cytoplasm RIBOSOMES GOLGI APPARATUS • Closely layered stacks of membrane-enclosed spaces that process, sort, and deliver proteins • Proteins processed here are: 1. Stored 2. Transported to other organelles 3. Secreted outside the cell GOLGI APPARATUS VESICLES • Temporary membrane-bound sacs that transport materials through the cell as needed. VESICLES MITOCHONDRIA • Bean-shaped organelle that provide energy for the cell • UNIQUE – they contain their own DNA and ribosomes! • What can be inferred from this????? MITOCHONDRIA LYSOSOMES • Membrane-bound organelles that contain enzymes • Defend cells from bacteria and viruses • Break-down damaged cell parts • More common in animal cells LYSOSOMES CENTRIOLES • Cylinder-shaped organelles made of microtubules arranged in a circle. • Help build spindle fibers to divide DNA during cell division • Produce and organize microtubules to form cilia and flagella. CENTRIOLES VACUOLES • Fluid-filled sac used for storage of materials needed by the cell. • CENTRAL VACUOLE • Unique to plant cells • Strengthens a plant cell and helps support the entire plant. VACUOLES CELL WALL • Rigid layer that gives protection, support and shape to plant, algae, fungi & bacterial cells • NOT present in animal cells • In plants – made of cellulose, a polysaccharide CELL WALL CHLOROPLASTS • Organelles that contain chlorophyll and carry out photosynthesis • Chlorophyll: a light-absorbing molecule that gives plants their green color • Like mitochondria: • Have their own ribosomes and DNA CHLOROPLASTS