Agricultural Advertising & Marketing Kristi Murdock
advertisement

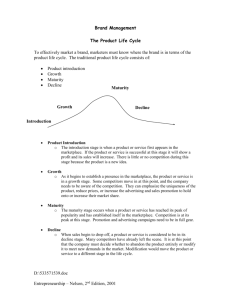
Agricultural Advertising & Marketing Kristi Murdock We’ve Learned: That MARKETING involves: “creating a product , then planning and carrying out the pricing, promotion, and placement of that product to stimulate buying exchanges in which both seller and buyer profit in some way.” We’ve learned: That people don’t buy the They buy the In other words, people buy solutions to problems; they buy to satisfy needs. We’ve learned: That in order for the buyer to benefit from a sale, the product must successfully meet the buyer’s need. And we’ve learned a little bit about identifying (and appealing to) the different needs that people have. Next on the Agenda: The LIFE of a product Important Concept: The Product Life Cycle Most products don’t “live” forever! Stage One: Introduction (the “Launch”) Stage Two: Growth (assuming launch was successful) Stage Three: Maturity (we hope this lasts a long time) Stage Four: Decline (product may lose viability unless rejuvenated) Product Life Cycle Characteristics of the Introduction Period Low sales Customers may not be aware of your product and its benefits Higher advertising costs Negative profit usually GOAL: establish a market and build demand Marketing Mix During Introduction Product : limited variations Price : generally high Promotion Goal is to build awareness and convince sellers to carry product Provide samples or trial incentives Place: Usually selective but Scattered Characteristics of the Growth Period Rapid revenue growth Sales increase Additional market segments come on board More retailers carry the product – expanded distribution Competitors enter market & price competition begins GOAL: gain customer preference and increase sales Marketing Mix During Growth Product : new product features, packaging, quality improvement Price : May be reduced to capture more customers Promotion: Increased advertising to build brand preference Place: More extensive Characteristics of the Maturity Period Most profitable Slower pace of growth Less Advertising Competitors product may be very similar GOAL: maintain market share and extend product life cycle Marketing Mix During Maturity Product: Modifications and features added to differentiate product Price : Possible reductions to compete better Promotion Emphasize differentiation Build brand loyalty Place: New distribution channels and incentives to avoid losing shelf space Characteristics of the Decline Period Sales decreasing Market is saturated Product is obsolete Unit costs may increase with declining production volume Marketing Mix During Decline Product Number of products in product line reduced Try to rejuvenate surviving products Price Prices lowered to liquidate discontinued products Prices maintained for niche markets Promotion Low expenditures Reinforce brand image for continued products Place Distribution more selective Phase out channels Period of Decline: Considering the Options Shall we maintain the product? Can we out-last competitors How can we reduce costs? What new uses (needs) can we find for the product? Shall we “Harvest” the product? Reduce market support (& associated costs) “Coast” to see how far it can get. Shall we discontinue the product? No more profit can be made . Stop production and support. Where are these products in their Life Cycle? Electric cars Hybrid cars Refrigerators Black & white television sets High Definition television sets GPS collars for pets Rabies vaccine Cotton bed sheets Haircuts Oil changes Genetic testing for breast cancer therapy Horseshoeing Home theater design Physical therapy for pets Telephone operator services Mapmaking A Fad is identified by its Life Cycle Rapid growth during introduction But no sustained growth or sales following that Examples of Fads Generally, almost anything that is a “Must Have” Christmas present item is a fad (see http://www.badfads.com/) Tickle-me Elmo Cabbage Patch dolls “Baby on board” signs Furby Rubik’s Cube Coonskin caps (circa 1950!) Bell-bottom jeans Pet rock Go-go boots Poodle skirts Any “named” haircut (pixie, mullet, Dorothy Hamill, Farrah Fawcett) How can you extend a product’s life? Market Modification Increase frequency of use by current customers Add new customers Find new uses for the product (example: baking soda) Product modification (change product’s market mix) Product – Add “bonus” features, “new & improved” Price – lower Promotion – change your advertising Place – add new distribution channels Modifying the Product Upgrade features and benefits Example: from litterbox to self cleaning litter box to litterbox over the toilet Example: from portable phone to “device that keeps track of my appointments, does math, works as an alarm clock and memo pad AND works as a portable phone” Example: “20% more at the same price!” Modifying the Price You can always lower the price, but remember: The price of your product exerts influence over the whole operation Customers’ perception of value Image of the product Under-valuing a product can be as destructive as overpricing a low value item Modifying Promotion Short term strategies Give customers incentives to buy Coupons Sales Business card drawings These produce results quickly without lasting impact Less common in services but very common in retail Change the advertising campaign Marshall Macluhan : “The Medium is the Message” Modifying the Place Add some distributors, delete some distributors Change retail outlets New displays, different department or shelf location Can change the whole concept of the product! Important Word: Commodity Q: What is a commodity? A: A product that the customer perceives to be differentiated only on price. Examples: Soybeans, corn, pork bellies, cattle (The Commodities Market) Nalgene water bottles Pet bath & blowout In general, it’s easier to make money on products that aren’t commodities! Assignment Due Tuesday, Jan 27. Select a product (hint – this will be more fun if you pick a product that has been around a while) and 1. Identify the product 2. Identify where the product is in the product life cycle – and why you think so. 3. Identify changes that you would recommend making in each of the 4Ps to increase sales of this product. 4. Give an example of current promotion of this product. 5. Identify the need(s) that the promotion targets.