Leadership in Management
advertisement

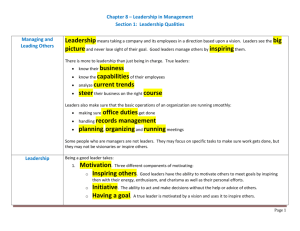
Chapter 8 Leadership in Management Objectives Describe the difference between a manager and a leader. Name the qualities needed to be a leader. Identify the three styles of leadership. Illustrate the advantages of working in teams. Chapter 8-1 The Future of Leadership Leadership in Business Taking a company and it’s employees in a direction based upon a vision. Big picture Never lose sight of their goal. 4 Leadership Qualities Motivation Confidence Communication Integrity MOTIVATION Initiative - desire to take action/get things done. Inspire others Creating goals Having a vision CONFIDENCE Self-Confidence How will I reach the goal? Decisive Ability to make mistakes and learn from them COMMUNICATION A leader must be good at HUMAN RELATIONS HR - the ability to communicate with people Explanation of goals Gestures, draw pictures, or tell stories to communicate their ideas. Listening skills INTEGRITY Most highly valued quality in a leader. Holding to principles like honesty, loyalty, and fairness. What is the difference between initiative and integrity? Developing Leadership Skills Books, videos, courses, degrees Mentor Join a club or organization Volunteer for projects or activities that give you an opportunity to lead. Chapter 8-2 Leadership Styles Introduction Different leaders have different styles. Some rule with strict discipline and watch your every move. Some are easy going and leave you along to do your work. Types of Leadership Autocratic Democratic Free-Rein AUTOCRATIC LEADERSHIP Self-ruling Running everything yourself and answering to no one. You make EVERY decision You expect orders to be obeyed Assume people don't like to work, that they avoid responsibility, and have to be constantly monitored. Lead through fear and intimidation DEMOCRATIC LEADERSHIP Managers and employees work together to make decisions New ideas are encouraged Assumes people aren't lazy and want to work Gives employees more responsibilities FREE-REIN LEADERSHIP Requires the leader to set goals for your managers and employees and then leave them alone to get the job done. Shows the most trust and confidence 'hands-off leadership' Giving managers and employees the power to run things and make decisions - Delegating Chapter 8-3 Leadership in Teams SELF-MANAGED TEAMS Work groups that supervise themselves. Started in Japan Role of the manager is being replaced by the team leader Leader is a team player Leader doesn't answer to upper level management Team usually works on one single project THE ORGANIZATION OF SELF-MANAGED TEAMS Recognized in two ways: 1. Each team member has a special skill or 2. The team selects one team leader. 1. Special Skills Different departments pulled together for a team Worked on their own but expected to produce results 2. Appointing a Team Leader Appointed by top manager or selected by team Encourages and fosters creativity and opportunity Idea Behind Self-Managed Teams They're more goal oriented Faster and more efficient Team members have a chance to learn each other's jobs and obtain new skills. It simplifies the decision-making process Team members learn to participate and cooperate with each other Self-managed teams learn to solve their own problems.