Cladograms & Dichotomous Keys: Biology Worksheet
advertisement

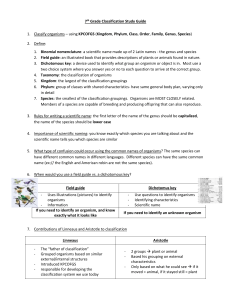
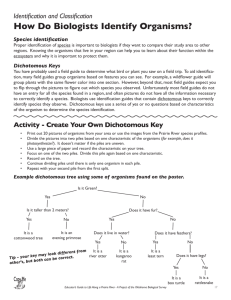
Branching Diagrams (Cladograms) and Dichotomous Keys I. Branching Diagrams A. branching diagram (or cladogram) = a branching, treelike diagram that shows the relationship between certain species of organisms based on specific characteristics and their evolutionary history from a common ancestor. 1. A branching diagram is used to show the characteristics that are shared by organisms as well as which characteristics cause organisms to separate (or branch) from each other on the evolutionary tree to become new species. 2. Example: a. The line pointing to the right shows the evolution of certain characteristics through time. 1. Each characteristic is shared by those organisms to the right of it. 2. Organisms that do not have that characteristic branch off of the main line. a. In the example, the fern, pine tree, and hibiscus all have tissues that transport materials (the moss does not), but only the pine tree and hibiscus produce seeds. II. Dichotomous Keys (also called Identification or Taxonomic Keys) A. Dichotomous keys list specific traits of an organism to identify exactly which organism it is. 1. Most keys are arranged in steps, offering 2 descriptive statements at each step. a. Once you decide which statement best describes the organism you are observing, you will be directed to a new step to make another dichotomous (either/or) choice. 1. Example: Step 1—The leaf is needlelike…………go to Step 2 The leaf is broad and flat……. go to Step 3 b. If you continue to work your way through the statements (WITHOUT SKIPPING STEPS), you will eventually be told what the organism is. 1. Example: Step 11— Needles grouped in threes……. loblolly pine (Pinus taeda) Needles grouped in fives………white pine (Pinus monticola) 2. If you keep tract of the traits listed at each step, you will get a fairly complete description of your organism in addition to identifying it and finding out its name. 3. Sometimes it is necessary to use a key backwards if you want to find out a specific trait for one of the organisms listed in the key. (This method will be discussed in class).