Problem 13-3A
advertisement

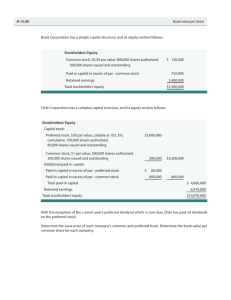
Problem 13-3A Part 1 Explanations for each of the journal entries Oct. 2 Declared a cash dividend of $2 per share of common stock. ($60,000 / 30,000 shares) Oct. 25 Paid the cash dividend on common stock. Oct. 31 Declared a 10% stock dividend when the market value is $25 per share. ($36,000/$12 par = 3,000 shares = 10% of 30,000 shares; $75,000/3,000 shares = $25 per share) Nov. 5 Distributed the common stock dividend. Dec. 1 Executed a 3-for-1 stock split. ($12 par / $4 par = 3-for-1 ratio) Dec. 31 Closed the Income Summary account to Retained Earnings. Part 2 Oct. 2 Oct. 25 Common stock ................. $360,000 $360,000 Oct. 31 Nov. 5 Dec. 1 Dec. 31 $360,000 $396,000 $396,000 $396,000 Common stock dividend distributable .. 0 0 36,000 0 0 0 Paid-in capital in excess of par................... 90,000 90,000 129,000 129,000 129,000 129,000 Retained earnings............ 260,000 260,000 185,000 185,000 185,000 395,000 Total equity ......................... $710,000 $710,000 $710,000 $710,000 $710,000 $920,000 Problem 13-5A 1. Market price = $85 per share (current stock exchange price given) 2. Computation of par values of stock Preferred: Paid-in amount / Number of shares = $50,000 / 1,000 = $50 Common: Paid-in amount / Number of shares = $80,000 / 4,000 = $20 3. Book values with no dividends in arrears Book value per preferred share = par value (when not callable) = $50 Common stock Total equity ............................................... Less equity for preferred ......................... Common stock equity .............................. $280,000 (50,000) $230,000 Number of outstanding shares ................ Book value per common share ............... 4,000 $ 57.50 ($230,000 / 4,000 shares) 4. Book values with two years’ dividends in arrears Preferred stock Preferred stock par value .......................... $ 50,000 Plus two years’ dividends in arrears* ....... 5,000 Preferred equity .......................................... $ 55,000 *2 years’ dividends = 2 x ($50,000 x 5%) = $5,000 Number of outstanding shares .................. 1,000 Book value per preferred share ................ $ 55.00 ($55,000 / 1,000 shares) Common stock Total equity ................................................. $280,000 Less equity for preferred ........................... (55,000) Common stock equity ................................ $225,000 Number of outstanding shares .................. 4,000 Book value per common share ................. $ 56.25 ($225,000/4,000 shares) Problem 13-5A (Concluded) 5. Book values with call price and two years’ dividends in arrears Preferred stock Preferred stock call price (1,000 x $55) ....... Plus two years’ dividends in arrears* .......... Preferred equity ............................................. $ 55,000 5,000 $ 60,000 *2 years’ dividends = 2 x ($50,000 x 5%) = $5,000 1,000 Number of outstanding shares..................... 60.00 ($60,000 / 1,000 sh.) Book value per preferred share ................... $ Common stock Total equity .................................................... Less equity for preferred .............................. Common stock equity ................................... $280,000 (60,000) $220,000 Number of outstanding shares ..................... Book value per common share .................... 4,000 $ 55.00 ($220,000 / 4,000 sh.) 6. Dividend allocation in total Preferred 2 years’ dividends in arrears ...........$ 5,000 Current year dividends .................... 2,500 Remainder to common ..................... . Totals .................................................$ 7,500 Common $ 0 4,000 $ 4,000 Total $ 5,000 2,500 4,000 $11,500 Dividends per share for the common stock $4,000 / 4,000 shares = $1.00 7. Equity represents the residual interest of owners in the assets of the business after subtracting claims of creditors. With few exceptions, these assets and liabilities are reported at historical cost, not market value. Therefore, the book value of common stock does not normally match its market value. Also, the book value of common stock is based on past transactions and events, whereas the market value takes into account expected future earnings, growth, dividends, and other industry and economic factors.