application guide
advertisement

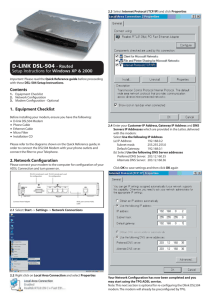
APPLICATION GUIDE AG082311 SITRANS RD500 GPRS Connectivity Objective: How to set up a GPRS connection using static and dynamic IP addressing. Equipment: SITRANS RD500 Internal GPRS modem and antenna PC with Ethernet card Internet Explorer 6.0 or higher While every effort was made to verify the following information, no warranty of accuracy or usability is expressed or implied. Overview GPRS (General Packet Radio Service) is a global standard telecommunications for data transfer. Although initially GPRS was used in the public domain with cell phones, smart phones and mobile computing, GPRS is now widely used for industrial applications for remote telemetry. These applications are generally know as M2M solutions. GPRS Manufacturing Data center The M2M solutions allow two-way communication between industrial equipment in the field (SITRANS RD500) and a host system. The host system could be a server, SCADA system or other communication device. In general, the equipment in the field will report alarm and data log information to the host system. In some applications, it is necessary for the host system to contact the device in the field and request information or configure the device when you turn it on. If your connection to the cell network is lost or your phone is off, your IP address is lost until you turn on Siemens Canada Limited Siemens Milltronics Process Instruments 1954 Technology Drive, P.O. Box 4225 Peterborough, Ontario K9J 7B1 / Canada Tel.: (705) 745-2431 Fax: (705) 741-0466 www.siemens.com/sensorsystems APPLICATION GUIDE your phone. At this point you are reassigned a new IP address. The dynamic IP address service allows the cell carrier to re-use IP addresses and not have to worry what IP address is being used by the device in the field. The disadvantage of dynamic IP is that you never know what your IP address is going to be so you can never get back to your device from the host system (unless a service such as Dyndns is used). Public Static IP With a static IP service, the cell carrier permanently assigns an IP address to your account. When the device in the field logs onto the network, the same IP address always is assigned to the device. The Static IP address allows the host system to contact the device in the field because the IP address is known and allows for full two-way communication. Third party management of IP addresses In some countries, the cell providers do not offer a public static IP service. Alternatively they lease a pool of IP addresses to data management partners who manage the static IP addresses for the end user and cell carrier. The cell carrier partners will deliver the SIM cards and assign IP address and APN login to the end users. APN For initial connection to the cell network whether it be dynamic or static IP an APN (Access Point) is required. An APN is like logging into your computer, it represents login credentials to allow access to the cell network. The APN information is provided by the cell provider. Custom APN A Custom APN or private IP will allow a private connection from the cell carrier to the host. In essence, the IP address of the device in the field is not publicly available. The APN is essentially a VPN (Virtual Private Network) from the cell carrier to the host system. Custom APNs are more expensive but deployment on a large scale would most likely warrant the extra cost with the added security benefit. DNS support DNS stands for Domain Name System (or Service or Server). Basically, the DNS is a network of DNS servers that sit on the Internet and have a database of domain names and their associated IP addresses. When you enter a Web site, for example URL http://www.siemens.com into your web browser, a domain name server on the Internet will look up that domain name and resolve the IP address. That IP address is then used to contact that domain. When using DNS service in the RD500 you simply enter the IP address of your DNS server into the “DNS server name” in the network page. The RD500’s FTP and email client allows the user to enter a domain name. This enables the RD500 to send the datalog files to a host whose IP address is not static. The FTP server or email client’s domain name is resolved by the DNS server specified in the SITRANS RD500 GPRS Connectivity AG082311 2 of 7 APPLICATION GUIDE DNS server field on the network page. The destination IP address will be resolved by the DNS server. That IP address will be populated next to the domain name in the FTP or email pages. Service and feature overview Cell plan Dynamic Public Static IP Custom APN RD500 services Web Browser FTP Server FTP Sync SMS Email Last Log report Alarms Overview Reports Device originated Host originated communication communication Yes DYNDNS req. Yes Yes Yes Yes Dynamic IP Yes with DNS support Yes with DNS support Yes Yes Yes with DNS support Yes Yes Yes Static IP Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Application In this application we are going to set up a static IP address for the SITRANS RD500 using the internal modem option. If we wanted to set up a dynamic IP address instead of a static IP, we would simply replace the SIM card for the one with a dynamic IP. Some external modems are also supported: please see catalog for external modem options. SITRANS RD500 GPRS Connectivity AG082311 3 of 7 APPLICATION GUIDE Modem Setup 1 2 Remove the GPRS internal modem from its packaging, being careful not to damage the modem. Insert the SIM card into the holder making sure the contacts face down and the cut edge of the SIM card lines up with the board layout. SIM 3 4 Remove the front expansion slot cover as shown in figure 2 Insert the modem into the expansion slot. Ensure modem is seated correctly and the two locking dials are in the locked position. Configuring the SITRANS RD500 This application guide assumes you are already familiar with connecting direct to the RD500 via a crossover Ethernet cable. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Open your web browser and enter the IP address for the SITRANS RD500: default 192.168.2.100 with the login and password; default login is ‘admin; and default password is ‘rd500’. From the main overview page, click on the “Configuration” tab. In the configuration screen select the “Network” tab. Once in the network page, set the options as below with the exception of your own APN, which is provided by your cell carrier. Make sure the connection type is set to “on demand” and set the frequency to your correct regional setting. Refresh your web browser and look at the “modem status” at the bottom of the page. If your modem is connected correctly and the SIM card is inserted you will see the current signal strength, e.g. “IDLE 17” Be sure to set your connection type to “internal” if using the internal GPRS modem or “external” if using an external GPRS modem. SITRANS RD500 GPRS Connectivity AG082311 4 of 7 APPLICATION GUIDE Note: Signal strength ranges from 0 to 99: a value of 99 indicates that the antenna is not connected or the internal modem is not seated correctly. A typical signal strength for reliable communication should be >15. See catalog for antenna options that may help improve your signal strength. For Multitech external modem model #: MTCBA-E the following init string settings should be used: For SMS support, add the following in the additional init box: SITRANS RD500 GPRS Connectivity AG082311 5 of 7 APPLICATION GUIDE 8 Change the connection mode from “on demand” to “permanent” and refresh the page a number of times and you will see the modem status has changed to “UP: 204.187.55.55” for example. The value after UP: is the IP address of the modem. You are now on the Cell network and ready to use the SITRANS RD500, test your connection by entering your public IP address into your web browser to connect to the SITRANS RD500 vai GPRS. On demand If the RD500 is set to “On demand” when using GPRS, the RD500 will allow FTP sync (datalogs sent to the FTP sever on a timed basis), reports, email alarms and SMS messages to be sent. In the “On demand” mode the RD500 will not be accessible from remote web browsers or FTP clients. In the “On demand” mode the RD500 is registered on the network but no data transfer will occur until the RD500 sends an FTP sync, email, alarm or report. Once an email, FTP, report or alarm is sent, the RD500 will hang up and return to “On demand” mode after the “Connection timeout” value is reached. SITRANS RD500 GPRS Connectivity AG082311 6 of 7 APPLICATION GUIDE Permanent Mode In permanent mode, the RD500 will register the cell modem onto the GPRS network by sending the APN information from the network page. The cell modem will be registered onto the network and a permanent connection will be established. A status and IP address will be shown in the “modem status” in the RD500’s network page. In the permanent connection mode, the RD500 will allow FTP sync, email, alarms and reports to be sent. The IP address can also be entered into the web browser to allow access to the RD500’s web server. Note: Not all cell providers will report the public IP address directly to the RD500 because the IP address is being mapped internally by the cell provider. In this case, contact your cell carrier for your static IP address information. SITRANS RD500 GPRS Connectivity AG082311 7 of 7