laws affecting human resource management - CUPA-HR
advertisement

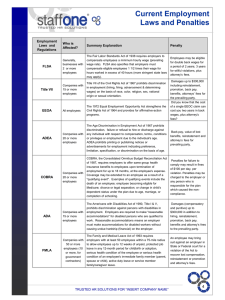
LAWS AFFECTING HIGHER EDCUATION HR MANAGEMENT Recent laws, Supreme Court decisions, an executive orders affecting human resources management LAW, COURT DECISION, OR EXECUTIVE ORDER EFFECT ON HUMAN RESOURCES MANAGEMENT Equal Pay Act, 1963 Prohibits discrimination on the basis of sex in wage payments for jobs that require equal skill, effort, and responsibilities under similar working conditions in the same establishment. Civil Rights Act, 1964 Title VII prohibits employment or membership discrimination by employers, employment agencies, and unions, based on race, color, religion, sex, or national origin; act creates the Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (EEOC). Executive Order 11246 (1965) As amended by Executive Order 11375, prohibits discrimination based on race, color, religion, sex or national origin in government contracts; also requires federal contractors to develop affirmative action plans to raise the level of minority and female employment in their firms. Age Discrimination in Employment Act (ADEA), 1967 Prohibits discrimination against persons aged forty to sixty-five in such matters as hiring, job retention, compensation and other terms, conditions, and privileges of employment. Occupational Safety and Health Act (OSH Act), 1970 Authorizes the secretary of labor to establish mandatory safety and health standards. Griggs v. Duke Power Company (1971) U.S. Supreme Court rules that the employer unlawfully discriminated against blacks by requiring a high school education or successful completion of an intelligence test as a condition of employment in certain jobs. Equal Employment Opportunity Act, 1972 Amendments to the Civil Rights Act permit the EEOC to bring enforcement actions in the federal courts. Vocational Rehabilitation Act, 1973 Requires federal contractors to take affirmative action to employ and promote qualified handicapped persons. Employee Retirement Income Security Act 1974 Prescribes eligibility rules, vesting standards, and an (ERISA), insurance program for private pension plans. Vietnam Era Veterans’ Readjustment Assistance Protects the employment rights of all disabled veterans Act, 1974 and sets forth obligations of employers to military reservists and National Guard members called to active duty. Amendments to Age Discrimination in Employment Extends protection until age seventy for most workers and Act (1978) and without upper limit in federal employment. Pregnancy Discrimination Act, 1978 Requires employers to give pregnant workers the same group health insurance or disability benefits given other workers and makes it illegal to fire or refuse to employ a woman because of pregnancy. LAW, COURT DECISION, OR EXECUTIVE ORDER EFFECT ON HUMAN RESOURCES MANAGEMENT Steelworkers v. Weber (1979) Supreme Court endorses right of employers and unions to jointly adopt quotas to eliminate racial imbalance in a work force through affirmative action. Washington County v. Gunther (1981) In case involving female guards alleging sex discrimination in pay, Supreme Court holds that such suits were not barred under Title VII of the Civil Rights Act merely because the plaintiffs were performing work similar to but not identical with that performed by male guards. Newport News Shipbuilding and Drydock Co. v. EEOC (1983) Supreme Court rules that employers must treat male and female employees equally in providing health insurance for their spouses. Arizona v. Norris (1983) Supreme Court rules that employer-sponsored retirement plans may no longer pay women smaller benefits than men, despite studies showing different life expectancies for the sexes. NLRB v. Bildisco & Bildisco (1984) Supreme Court rules that employers filing for reorganization in federal bankruptcy court may temporarily terminate or alter collective bargaining agreements even before the judge has heard the case. Firefighters Local Union No. 1784 v. Stotts et al. (1984) Supreme Court rules that courts may not interfere with seniority systems to protect newly hired black employees from layoffs. Retirement Equity Act, 1984 Broadens conditions under which spouses receive retirement benefits and further amends ERISA through such provisions as allowing pension plan members to take maternity or paternity leave of up to one year without loss of service credit for the period. Immigration Reform and Control Act, 1986 Makes it illegal for employers to hire illegal immigrants; requires proof of legal authorization to work from all employees hired after November 6, 1986; imposes record-keeping requirements on employers; and provides for stiff fines for hiring undocumented workers and for paperwork violations. Amendments to Age Discrimination in Employment Act, 1986 Bars most mandatory retirement programs. Amendments to Public contracts (Walsh-Healey Act), 1986 Removes requirement of overtime payments beyond eight hours in one day in government contract work, thus encouraging compressed workweek schedules. Johnson v. Transportation Agency (1987) Supreme Court rules that employers may implement affirmative action plans to correct sex discrimination. Worker Adjustment and Retraining Notification Act (Plant Closings Bill), 1988 Requires businesses with a hundred or more employees to give at least sixty days’ notice when closing a facility or operating unit or making significant reductions in a work force or in working hours. Each employee and state and local government agencies must be notified. LAW, COURT DECISION, OR EXECUTIVE ORDER EFFECT ON HUMAN RESOURCES MANAGEMENT Employee Polygraph Protection Act, 1988 Bars most private employers from using polygraph tests in screening applicants and from testing current employees unless there is a reasonable suspicion of theft. Drug-Free Workplace Act, 1988 Requires employers with federal contracts to establish policies and procedures to create a drug-free workplace and to make a good-faith effort to maintain a drug-free workplace. Older Workers Benefits Protection Act, 1990 Requires that waivers of ADEA rights be “knowing and voluntary” and codifies the “equal benefit or equal cost” principle. Immigration Act, 1990 Authorizes larger numbers of immigrants to enter the United States on the basis of unique expertise, training, and experience. Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA), 1990 Makes it illegal to discriminate in human resources practices against individuals with known physical or mental limitations who can perform the essential functions of the job, and requires employers to make “reasonable accommodation” for disabled applicants and employees. UAW v. Johnson Controls (1991) Supreme Court rules that employers may not bar women of childbearing age from certain jobs because of potential risk to fetuses. Civil Rights Act, 1991 Allows compensatory and punitive damage in cases involving intentional discrimination based on sex, religion, or disability previously available to racial and ethnic minorities. Either party to a case can demand a jury trial. Prohibits “race-norming” or other discriminatory adjustment of test scores or cutoff points on the basis of race, color, religion, sex, or national origin. Codifies the concepts of “business necessity” and “job related” stated in Griggs v. Duke Power Co. Includes the Glass Ceiling Act of 1991. Glass Ceiling Act, 1991 Establishes a Glass Ceiling Commission to study and make recommendations concerning elimination of artificial barriers to the advancement of women and minorities and concerning increasing opportunities and developmental experiences of women and minorities in management; establishes a national award for “diversity and excellence in American executive management.” Family and Medical Leave Act, 1993 Requires larger employers to give workers unpaid leave up to 12 weeks for family or medical emergencies. Ohio Civil Service Law, 1912 For a more complete list of laws that impact higher education HR management, visit the following web site: http://counsel.cua.edu/mainpage/index.htm. Human Resources Management, Third Edition/Wendell French, pp.56 - 59.