Heating Curve Key.notebook - School District of Clayton

Heating Curve Key.notebook
Melting Ice Lab Name_______________________
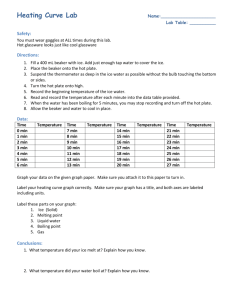
Purpose: To examine the Temperature vs. Time graph when adding heat to ice.
Materials: large beaker, tap water, temperature probe, hot plate, magnetic stir bar, ice
Pre Lab: In the space provided, draw what you think the temperature vs. time graph will look like for the heating of ice.
Procedure:
1. Fill a large beaker up to the 500mL mark with ice.
2. Fill the beaker up to the 500mL mark with tap water to the top of the ice.
3. Turn the hot plate to high.
4. On the computer, go to the Finder window and click on Applications Logger Pro
Experiments Chemistry with Vernier 02 Freeze Melt Water
5. Stir the beaker with the temperature probe until a constant temperature is reached.
6. Once a constant temperature is reached, place the beaker on the hot plate.
7. Push the data collection button on the logger pro
8. Stir the ice water until all ice has melted.
9. Once the ice has melted, use a stir bar in the beaker.
10. Run the logger pro for 15 minutes or until the water has reached a steady boil for 34 minutes.
11. Print Graph for all members of the group.
Questions:
1.
Did your prediction match your actual graph? Why or why not?
2.
Label the following points on your graph: melting point, boiling point.
3.
What is happening to the temperature at the melting point and boiling point. Why?
4.
At the boiling point, is there still a heat transfer? Why or why not?
5.
Explain what is happening at the melting point and boiling point.
March 10, 2014
Heating Curve Key.notebook
March 10, 2014
Sidenote: C for plastic is 1.67, Aluminum is 0.87, wood is 2.4, air is 1 J/ g o C
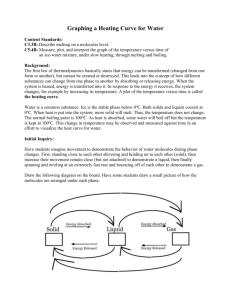
Heating Curves
Heating Curve Key.notebook
How do you find Q at a phase change?
March 10, 2014
Heating Curve Key.notebook
March 10, 2014
Heating Curve Key.notebook
March 10, 2014
How much heat is required to heat up 50g of ice from 20
o
C to gas at 150
o
C. C(ice)=2.06 J/g
o
C,
C(water)=4.18 J/g
o