Respiration
advertisement

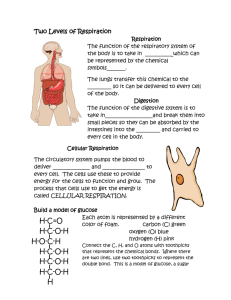
Respiration Plants Oxygen diffuses into the leaf via stomata. It enters the air spaces in the leaf and then dissolves in the moisture covering the cell surfaces and then passes through the membrane into the cell in solution. Respiration This is the oxidation of food to produce energy. Oxygen + Glucose 6O2 + C6H12O6 Carbon dioxide 6CO2 + water + energy + 6H2O + 38 ATP Not all the energy is released at once. Some is stored as A.T.P. This reaction occurs in the mitochondria of cells – without this, the cell would die as it would have no source of energy. Do not confuse respiration with breathing. Experiment to demonstrate respiration in living organisms suction: - speeds the end result - draws air through the system sodium hydroxide - to absorb all of the CO2 limewater: to check that all the CO2 is absorbed living organism limewater: to indicate CO2 and therefore, respiration Explanation Air is drawn through the system. It is first taken through the sodium hydroxide, which absorbs the CO2 from it. The next beaker contains limewater, which would turn cloudy if CO2 is present. The air is then passed through a beaker with the living organism in it. The air from this is then taken to the next beaker containing limewater. If CO2 is present, it would turn cloudy and therefore respiration has taken place. There are two forms of respiration: (a) (b) aerobic anaerobic (a) Aerobic: (with oxygen (O2)) (without oxygen) Oxygen + Glucose O2 + C6H12O6 Carbon dioxide CO2 + water + energy + H2 O + 38 ATP The oxygen comes from the air, which is breathed in. In the case of fish, the oxygen is dissolved in the water. (b) Anaerobic: 1. Animals Glucose Lactic acid + energy (only 2 A.T.P.) This occurs in muscle cells which are actively working and which have a shortage of oxygen. It also occurs in some bacteria (e.g. the making of yogurt). When glucose is broken down without oxygen, lactic acid is produced in the process shown above: anaerobic respiration. Although the energy, which is released, is little, the energy released is rapid. The lactic acid, which is produced, is toxic and so anaerobic respiration cannot be used for a long period of time. As the lactic acid levels increase, a person would feel exhausted. The person would then need to rest to repay the oxygen debt. The lactic acid is oxidised and is no longer harmful. 100 metre sprint A well trained athlete does not breathe during the race – only before and after the race. This is because the race is sufficiently short – all the energy can be gained by the anaerobic process. The reason for this is: it is a rapid release energy is not wasted in the movement of the rib cage and diaphragm At the end of the race, the person would pant so that they can take in oxygen to oxidise the lactic acid and repay the oxygen debt. However, the anaerobic process is inefficient: - only 2 A.T.P. is produced in comparison to 38 A.T.P. in aerobic respiration. the lactic acid is toxic and causes fatigue, cramps and stitches. Experiment to demonstrate the build up of lactic acid 1. 2. 3. (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) 2. Raise one hand above the head and let one hand hang down your side Clench and unclench both fists continuously Proceed for as long as possible and then let both arms rest on the table Which arm tires first? The arm above the head Describe the feeling in that arm. Pain! Describe the feeling in the other arm Pain is not as bad Describe what happens at rest. The pain stops / fades away Explain The blood flown to the arm held up above the head slower and so less oxygen reaches it. Therefore, anaerobic respiration must occur for muscle contraction to take place. Therefore, there is a build up of lactic acid. This is then oxidised when the arm is placed to rest on the table. Plants Glucose Alcohol Example of alcohol produced: Example of CO2 produced: + Carbon dioxide + energy brewing bakery Yeast can respire both aerobically and anaerobically. This can be proved by an experiment, where yeast is placed in an excess amount of glucose (so that this is not the limiting factor) and then sealed so that no oxygen can get in. A tube letting gas out would later (when the O2 is no longer there) go into limewater to test for carbon dioxide. An indicator shows whether there is any O2 present. At the start of the experiment, there is O2 present, but then the indicator colour changes as the O2 is used in aerobic respiration. When the tube is put into the limewater, the limewater turns cloudy – CO2 is produced in the anaerobic respiration. Summary Anerobic respiration without oxygen intermediate – lactic acid – not completely broken down less energy produced – only 2 A.T.P. per molecule of glucose fast reaction limited – alcohol and lactic acid are toxic less efficient Aerobic respiration with oxygen complete breakdown of glucose more energy released – 38 A.T.P. per molecule of glucose slow reaction no limit as long as oxygen is present more efficient