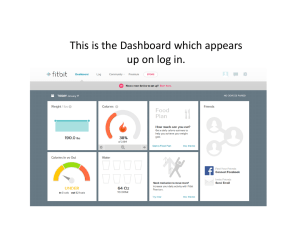
Applying Performance Dashboard in Hospitals
advertisement

International Journal of Software Engineering and Its Applications Vol. 9, No. 1 (2015), pp. 213-220 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/ijseia.2015.9.1.19 Applying Performance Dashboard in Hospitals Andre M. R. Wajong Industrial Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, Bina Nusantara University (Syahdan Campus) Jl. K.H. Syahdan No. 9 Palmerah, Jakarta Barat 11480 - Indonesia awajong@gmail.com Abstract Performance dashboard is one of the way to improve a company’s performance, a hospital in this study, due to the ease it provides for the executive entities of the hospital in measuring, supervising, and evaluating the performance of the hospital based on the Key Performance Indicator (KPI). The information requried by the executive entities in making a strategic decision involves numerous separate source of data. By implementing performance dashboard, the existing data sources will be consolidated and demonstrated in an informative visual form through an interface screen in order to allow the executives to easily comprehend and analyze those data, therefore assisting the process of strategic decision making. Currently, a lot of hospitals uses performance dashboard. By applying it, hospitals are capable of identifying the strengths and weaknesses pertaining to the them, and eventually, use such information to improve the performance. By an increase in performance, the loyalty of patients will be maintained and the hospital’s competitiveness will also increase. Keyword : performance dashboard, performance, KPI 1. Introduction 1.1. Background With the increasing number of new hospitals, the competition between hospitals are also escalating. Hospitals race to improve its services to patients with affordable prices. A satisfying service quality is the key to establishing patients’ loyalty to the hospital. A good service quality serves as a result of a good performance of the whole unit in a hospital. Each of them posess Key Performance Indicator which represents what each unit has achieved in terms of performance, and which, in turn, influences the hospital’s performance as a whole. This KPI will be analyzed by the hospital’s executives in order to determine business strategies and also the necessary steps to prevent and solve the problems which may exist in the hospital. In order to make business strategies and decision, the hospital’s executives need data and information derived from every entity in the hospital. Therefore, it requires a system which can support the management and presentation process of data and information which is efficient and effective for the hospital’s executives, that is the performance dashboard system. Performance dashboard system can integrate data from various sources from each unit in the hospital, manage those data and present it in a qualified form of information. The implementation of this system is expected to assist the executives in measuring the performance of the hospital and analyzing the strategy which will be taken to deliver good impacts to the hospital. ISSN: 1738-9984 IJSEIA Copyright ⓒ 2015 SERSC International Journal of Software Engineering and Its Applications Vol. 9, No. 1 (2015) 1.2. Research Objective The objectives of this journal are: - To attain information regarding the use of performance dashboard in hospitals - To attain information regarding the impacts of implementing performance dashboard in hospitals 2. Theoretical Background 2.1. Performance Dashboard Shadan Malik (2005) used the terminology “enterprise dashboard”, which is defined as an interface computer that presents information in the form of tables, reports, visual indicators, and alert mechanism dynamically and with relevance. Stephen Few (2006) used the terminology “information dashboard”, which is defined as a visual display of crucial information made by arranging it in such a way that the performance of an organization can be supervised in a glance and ease the user in reaching a certain purpose. Such visual display of information must be designed well in order to quicken user’s understanding of the information and its meaning. Based on the previous elaborations, it can be inferred that enterprise dashboard, information dashboard, and dashboard are means of displaying crucial information in the form of tables, reports, visual indicators, and alert mechanism which exists in performance management. Those information are designed in such a way to be visually displayed on a screen in a manner that eases the user in supervising and managing his business initiative. Shadan Malik (2005) claimed that information dashboard which exists in a big organization is akin to that of airplanes. Dashboard for every airplanes display a set of KPI (Key Performance Indicators) which holds the information on the condition of airplanes internally, as well as externally. Numerous airplane manufacturers design the display of airplane’s dashboard, but one thing to be certain of is that they must display a set of KPI to the pilot to ensure the success of the flight. The similarity which exists in flying an airplane and running an organization is the existing need of various information to make a strategic decision which will lead to a successful attainment of a predetermined goal. 2.1.1. Characteristic of Enterprise Dashboard: Shadan Malik (2005) identified several basic characteristics for a company’s dashboard by the acronym S-M-A-R-T (Synergetic, Monictor, Accurate, Responsive, Timely) and I-M-P-A-C-T (Interactive, More data history, Personalized, Analytical, Collaborative, Trackability). SMART consists of several basic elements which needs to exist in a dashboard, namely: - Synergetic It must be ergonomic and visual to ensure its utilization to be done effectively by user in order to synergize information regarding different aspects in a single screen display - Monitor It must display the critical KPI which is required in effective decision making done by dashboard users. - Accurate The presented information must be completely accurate to gain full trust from the dashboard user. Supporting data for the dashboard must be tested and validated appropriately. 214 Copyright ⓒ 2015 SERSC International Journal of Software Engineering and Its Applications Vol. 9, No. 1 (2015) - Responsive It must respond to the predetermined limitation by having “user alert” added to the visual presentation in other dashboard (for example: voice alarm, email) to attract user’s attention shall a critical problem occurs. - Timely It must present the most updated information to guarantee effective decision making. Information must be real-time and right on time of occurence. Beside the aforementioned basic elements, enterprise dashboard also needs to have these additional elements, which goes by the acronym IMPACT, namely: - Interactive It must enable the user to trace and acquire details, root of the problem, et cetera. - More data history Dashboard must enable the user to asses the timely trend for a given KPI. For example, right now, market segmentation may experience an increase (positive trend), yet last year, it decreases (negative trend). - Personalized Performance dashboard must be specified for each user according to the responsibility, right, and limitation of data. - Analytical It must enable the user to conduct analysis. - Collaborative Dashboard must facilitate user to exchange information regarding special observation on each user’s dashboard. In other words, dashboard serves as a communication platform for managerial tasks and obedience control. - Track ability It must enable each user to adjust the metric which he desires to track. From hereon, enterprise dashboard and dashboard will be referred to as performance dashboard. 2.2. Key Performance Indicator Mahdi Seifi (2010) claimed that Key Performance Indicator (KPI) is a quantitive form and the measurement of criticial success factors (CSFs). Hur Wonchang (2009) suggests that Key Performance Indicator (KPI) is an indicator which represents how goods or services or finances are allocated to produce certain goods or services, as well as how fast and efficient an organization can deliver goods and services to the customer. 3. Research Method 3.1. Literature Study This part of the study involves the search for referrences and other sources which can be utilized as a basis in producing this journal, it involves definitions of performance dashboard, its application in hospitals, the impacts of its implementation in hospitals, as well as other relevant referrences. Copyright ⓒ 2015 SERSC 215 International Journal of Software Engineering and Its Applications Vol. 9, No. 1 (2015) 3.2. Analysis This part of the study involves the analysis on the problem posed in this journal. The analysis is conducted based on the literature that the researcher has collected. Therefore, the result which will be derived from this journal will be in accordance to the objectives of this journal. 4. Results and Discussion 4.1. Benefits of Using Performance Dashboard Rasmussen, N. H., Bansal, M., & Chen, C. Y. (2009), suggests several benefits which can be attained from using performance dashboard, namely: - Improve the performance of decision making: o o o o Ease in identifying and correcting negative trends Ease in making decision supported by collected data Ease in measuring efficiency and inefficiency of the organization Ease in analyzing information which is derived from visually displayed performance measurement o Ease in defining organizational strategy and goal - Benefits from workers efficiency: o Increase in productivity o Saves time by eliminating numerous needs for reports o Decrease the need to create and manage various statistical reports o Easy to use - Motivating workers: o o User will be able to produce reports in detail by displaying new trends More time can be allocated to analyze data and efficiently make use of time to find, compile, and format data o Well-designed dashboards are more attractive in comparison to conventional designs, like tabulation reports o Dashboard serves as means to share strategies, tactics, and operational data which can motivate workers to understand them objectively and to be involved in the right decision making 4.2. Types of Performance Dashboard Rasmussen, N.H., Bansal, M., & Chen, C. Y. (2009), suggests 3 types of performance dashboard, namely: - Strategic dashboard By utilizing strategic dashboard, an organization will be able to monitor the steps which have been undertaken to reach a certain strategic object. This type of dashboard is rather brief, uses a lot of tables, lacks updates, and contains global, external, trend, and growth measurement. Strategic dashboard is based on balance scorecard method by David Norton and Robert Kaplan which is a method to determine and reach organizational goal. 216 Copyright ⓒ 2015 SERSC International Journal of Software Engineering and Its Applications Vol. 9, No. 1 (2015) - Tactical Dashboard Tactical dashboard is used to monitor advancement and relationship of trends as a result of a strategic initiation. Tactical dashboard is ideally established using a technology which allows detailed data tracking and detailed segregation of data, therefore easing the process of problem analysis - Operational Dashboard Operational dashboard is used to monitor business processes, business activities and various complex issues. This dashboard provides daily or weekly reports and tables which illustrates the current status/condition of the business process. Managers can easily discover issues and determine the necessary steps to solve problems or to attain benefit from existing opportunities. This type of dashboard is mostly used in the department level and not the executive level. Senior executives mostly use tactical or strategic dashboard. From the previous elaboration regarding benefit and characteristics of performance dashboard, it can be inferred that it can be categorized into 3 groups, namely tactical strategic and operational dashboard. The users of each type may differ, ranging from the executives to the operational level of an organization, or in this particular study, a hospital. By differentiating types of dashboards from the user, it will ease the user in analyzing data according to his needs. Data which is displayed in an accurate and easily comprehensible form of information can be used to measure the performance of each unit, analyze the current and future trends, as a tool to solve existing problems, as means to motivate workers based on the grades they attained in KPI personally or based on unit, also as means to grant rewards to best-performing worker or unit in order to induce competitiveness. The better the performance of the hospital, the patients’ satisfaction level will also increase. Therefore, patients’ loyalty will increase and it will entail maximum profit gain. It will yield good impacts for the hospital in such a competitive era. The visual presentation of data by tables and reports will also relieve the executive entities of the hospital in monitoring, measuring, and evaluating the performance of the hospital, as well as the process of strategic decision making, such as the right marketing strategy for a hospital. 4.3. Application of Performance Dashboard in Hospitals Numerous hospitals in the world, including Indonesia, has implemented performance dashboard to monitor, measure, and evaluate their service performance. This analysis is based on several previous researches, articles and related journals regarding the implementation of performance dashboard and its impacts to the hospital’s performance, namely: - Sungkar, I. I., et al.,’s research, Performance Dashboard in Moslem Hospitals [4] the application of performance dashboard: performance dashboard in Moslem hospital Harapan Anda Tegal is used for performance measurement which is classified into 5 perspectives, which are financial, customers, service process quality, environment, and human resource development. Impact: qualified information are provided and is presented communicatively by using colors found in traffic-lights in order to ease the user, in this case the executive entities of the hospital, in making decision or taking strategic actions. - Arifin, Z.’s research, Performance Dashboard Software Design of GovernmentOwned General Hospital’s Workers Performance Evaluation using The Malcolm Balridge National Quality Agard Method (MBNQA) [1]. The implementation of performance dashboard: implementing Malcolm Bridge process to establish a performance dashboard software which deals with up to 7 different measurement category (Leadership, Strategic Planning, Customer and Market, Knowledge Copyright ⓒ 2015 SERSC 217 International Journal of Software Engineering and Its Applications Vol. 9, No. 1 (2015) Management, Human Resource, Process Management, and Organizational Performance Results). Impact: by calculating 7 measurement categories based on Malcolm Balridge and visually presenting it on a performance dashboard ease the hospital in monitoring and evaluating its performance, evaluating the balance of workload, and the number of human resources in order to equally distribute the task and support the improvement of hospital’s performance. Aside from that, it can also calculate the strengths and weaknesses existing inside the hospital so an appropriate strategy can be conducted upon its finding. - Zeng, J., et al.,’s research, Using Dashboard for Lean Revenue Cycle Management [5]. Theuse of performance dashboard: by presenting 3 information category involving DFNB (Discharge Not Final Billed), inhouse and billed in a hospital using the Value Stream Mapping (VSM) method. This performance dashboard displays information in the form of tables and detailed reports regarding the daily numbers of those 3 categories. Impact: an increase in for the DNFB category, therefore increasing the income of the hospital. Aside from that, there’s an accountable transparancy from the hospital which enables it to control its financial issues transparently, thus easing the effort to monitor and calculate the hospital’s income and expenditure 5. Conclusion • • • • Performance dashboard has been used by numerous hospitals around the globe, including Indonesia. Methods of measurement used in the implementaion of performance dashboard differs in each hospital. The recent development of information technology results into a varied and useful implementation of performance dashboard in hospital, due to its ability to allow hospital’s executive entities to measure, monitor, and evaluate the performance of hospital, as well as in making strategic business decision for the hospital. The use of performance dashboard brings positive impacts. The performance of hospital increases because performance dashboard can be utilized as a tool determine a certain decision done by the hospital’s executive entities and it can also increase staffs’ performance in conducting their job. With the increase of the hospital’s service quality, the patients’ loyalty also escalates and it is followed by the hospital’s increase of income and competitiveness. References [1] Z. Arifin, “Rancang Bangun Perangkat Lunak Performance Dashboard Evaluasi Kinerja Karyawan Rumah Sakit Umum Pemerintah dengan Metode”, The Malcom Baldrige National Quality Award (MBNQA). Jurnal Informatika Mulawarman, vol. 6, (2011), pp. 108-118. [2] S. Malik, “Enterprise Dashboards: Design and Best Practices for IT. Hoboken”, John Wiley & Sons, Inc., (2005). [3] N. H. Rasmussen, M. Bansal and C. Y. Chen, “Business Dashboards: A Visual Catalog for Design and Deployment”, Hoboken: John Wiley & Sons, Inc., (2009). [4] I. I. Sungkar and I. W. Mustafid, “Performance Dashboard pada Rumah Sakit Islam”, Jurnal Sistem Informasi Bisnis, (2011). [5] J. Zeng and J. Zhang, “Using Dashboard for Lean Revenue Cycle Management”, iBUsiness, (2013), pp. 100-103. [6] M. Seifi, “Importance of KPI in BI Systems, Case Study: Iranian”, Seventh International Conference on Information Technology, Sharif University of Technology, Tehran, Iran, (2010). [7] W. Hur, “Developing Enterprise Dashboard”, Asian Journal of Information Technology, Medwell Journals, vol. 8, no. 2, (2009), pp. 55-60. [8] S. Few, “Information Dashboard Design”, O'reilly, ISBN: 0-596-10016-7, (2006). 218 Copyright ⓒ 2015 SERSC International Journal of Software Engineering and Its Applications Vol. 9, No. 1 (2015) Author Andre M.R. Wajong Education -. MBA in Management Information Systems, University Of Dallas, Apr 1090 -. Engineer in Industrial Engineering, Bandung Institute of Technology, Des 1990 Copyright ⓒ 2015 SERSC 219 International Journal of Software Engineering and Its Applications Vol. 9, No. 1 (2015) 220 Copyright ⓒ 2015 SERSC