FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING FINAL EXAMINATION Sample Exam for
advertisement

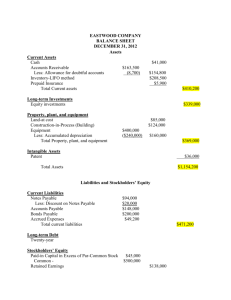
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING FINAL EXAMINATION Sample Exam for Practice Only Time: 3 hours Question 1 (40 marks) (72 minutes) Each question is worth 2 marks. 1. The journal entry to record a return of merchandise purchased on account under a periodic inventory system would credit a. Accounts payable b. Purchase returns and allowances c. Sales d. Merchandise inventory 2. Under the accrual basis of accounting a. Cash must be received before revenue is recognized. b. Net earnings are calculated by matching cash outflows against cash inflows. c. Events that change a company's financial statements are recognized in the period they occur rather than in the period in which cash is paid or received. d. The ledger accounts must be adjusted to reflect a cash basis of accounting before financial statements are prepared under generally accepted accounting principles. 3. If a company fails to record estimated bad debts expense a. Net realizable value is understated b. Expenses are understated c. Revenues are understated d. Receivables are understated 4. 5. If the amount of bad debts expense is understated at year end, a. Earnings will be understated. b. Shareholders’ Equity will be understated. c. Allowance for Doubtful Accounts will be overstated. d. Net Accounts Receivable will be overstated. Equipment was purchased on January 1 for $30,000 with an estimated salvage value of $6,000 at the end of its useful life. The current year's Amortization Expense is $3,000 calculated on the straight-line basis and the balance of the Accumulated Amortization account at the end of the year is $15,000. The remaining useful life of the equipment is a. 10 years. b. 8 years. c. 5 years. d. 3 years. 6. A company purchased equipment for $100,000. The equipment has an estimated $10,000 salvage value at the end of its estimated 5-yr useful life. If the company uses the diminishing / declining balance method of depreciation (rate = 40%), the amount of annual depreciation recorded for the second year after purchase would be a. $40,000. b. $24,000. c. $36,000. d. $21,600. 7. One thousand bonds with a face value of $1,000 each, are sold at 103. The entry to record the issue: a. Cash 1,030,000 Bonds Payable.............................................................. 1,030,000 b. Cash ...................................................................................... 1,000,000 Premium on Bonds Payable .................................................. 30,000 Bonds Payable.............................................................. 1,030,000 c. Cash ...................................................................................... 1,030,000 Premium on Bonds Payable ......................................... 30,000 Bonds Payable.............................................................. 1,000,000 d. Cash ...................................................................................... 1,030,000 Discount on Bonds Payable ......................................... 30,000 Bonds Payable.............................................................. 1,000,000 8. Following is the shareholders’ equity section of the balance sheet of Brownlow Corporation: Share capital: Common shares, 10,000 authorized, 7,000 shares issued $ 70,000 Retained earnings 120,000 Total shareholders’ equity $190,000 Entry to record Brownlow’s repurchase of 1,000 of its common shares at $11/share includes: a. a debit to Retained Earnings for $10,000 b. a debit to Common Shares for $10,000 c. a debit to Contributed Capital—Reacquisition of Shares for $11,000 d. a credit to Common Shares for $11,000 9. The Bryan Company purchased inventory on account for $350. This transaction was properly recorded. A week later, the Bryan Company discovered a defect in the inventory and returned the inventory to the supplier for credit. As the accountant, you would tell the bookkeeper to record the return of the inventory by: a) Debiting inventory and crediting accounts payable for $350 b) Debiting accounts payable and crediting inventory for $350 c) Debiting inventory and crediting cash for $350 d) Debiting cash and crediting inventory for $350 e) Debiting cash and crediting accounts payable for $350 10. The Troy Company acts as a landlord, renting office space to companies. On October 1, it rented office space and received three months' rent in advance totaling $4,500. The entire amount was used to increase rent revenue. What adjusting entry is necessary on October 31? a) Rent revenue $1,500 Unearned rent $1,500 b) Unearned rent $1,500 Rent revenue $1,500 c) Rent revenue $3,000 Unearned rent $3,000 d) Unearned rent $3,000 Rent revenue $3,000 e) No adjusting entry is necessary 11. The Brunswick Company obtained a $20,000 note payable on October 1, 20x7, which is due in 5 years. Interest, at an annual rate of 12%, will be paid once a year on September 30th. Brunswick made the appropriate journal entry on October 1, 20x7. No other journal entry has been made. What journal entry is necessary as of December 31, 20x7? a) Debit interest expense and credit note payable for $600 b) Debit interest expense and credit note payable for $2,400 c) Debit interest expense and credit interest payable for $600 d) Debit interest expense and credit interest payable for $2,400 e) Debit interest expense and credit interest receivable for $2,400 12. The Jerome Company's records were partially destroyed in a flood. The company does not know what sales have been for the year, but it does know that 60% of its sales have been on account. Furthermore, the company knows that its beginning accounts receivable balance was $45,000 and its ending accounts receivable balance at the time of the flood was $60,000. From the beginning of the year until the flood occurred, cash collections on credit sales were $255,000. What were the total sales for the year until the time of the flood? a) $270,000 b) $400,000 c) $425,000 d) $450,000 13. A buyer borrows money at 12% interest to pay an $8,000 invoice with terms 1/10, n/30 within the discount period. What is the buyer’s net savings of borrowing the money to pay the invoice within the discount period? a. $0 b. $26.67 c. $27.92 d. $53.33 14. Shannon Company acquires land for $56,000 cash. Additional costs are as follows: Removal of shed $ 300 Filling and grading 1,500 Salvage value of lumber from shed 120 Broker commission 1,130 Paving of parking lot 10,000 Closing costs 560 Shannon will record the acquisition cost of the land as a. $56,000. b. $57,690. c. $59,610. d. $59,370. 15. The following totals for the month of April were taken form the payroll register of Main Co. Salaries CPP withheld Income taxes withheld Medical insurance deductions EI withheld Union dues withheld $12,000 550 2,500 450 32 216 The journal entry to record the monthly payroll on April 30 would include a a. debit to Salaries Expense for $12,000. b. credit to Salaries Payable for $12,000. c. debit to Salaries Payable for $12,000. d. debit to Salaries Expense for $8,500. 16. On April 1, 20x6, a company issued 5-year, 9% bonds totaling $7,000,000 when the market interest rate was 8%. Interest is paid semi-annually on June 30 and December 31. Which of the following represents the amount of cash the company will receive on April 1, 20x6, when the bonds are issued? Select the answer to the nearest thousand. a) $7,000,000 b) $7,157,500 c) $7,284,000 d) $7,630,000 17. On January 1, 20x3, Ross Ltd. issued $1,000,000 of 9% 10-year bonds when the market interest rate was 10%. Ross received $937,878 cash. The bonds pay interest semiannually. On December 31, 20x3, the market interest rate changed to 10.5%. Which of the following statements is true? a) The discount on the bonds will be increased on December 31, 20x3 to reflect change in the market rate. b) Bonds payable will be reduced on December 31, 20x3 to reflect the drop in the market value of the bonds. c) The bonds payable amount will not change on December 31, 20x3 d) The amount of discount on the bonds will remain at $62,122 on December 31, 20x3 18. Allstate Inc., has 10,000 shares of $8, no par value, cumulative preferred shares and 100,000 shares of no par value common shares outstanding at December 31, 20x1. If the board of directors declares a $60,000 dividend, the a. preferred shareholders will receive 1/10th of what the common shareholders will receive. b. preferred shareholders will receive the entire $60,000. c. $60,000 will be held as restricted retained earnings and paid out at some future date. d. preferred shareholders will receive $30,000 and the common shareholders will receive $30,000 19. Which of the following items would not be considered a capital asset? 1. A 747 owned by Air Canada. 2. A new car in the lot of a Ford dealership. 3. The patent on the "11 secret herbs and spices" owned by Kentucky Fried Chicken. 4. The land on which the John Deere manufacturing plant is located. 5. A coal mine owned by a mining company. a) 2 b) 1 and 4 c) 2 and 3 d) 4 and 5 e) 1, 3 and 5 20. The Laughton Company acquired land to be used for the construction of a new office building. The following items were associated with the acquisition of the land: Land Survey Legal Fees Title Search Realtor Commissions Amount paid to the former owner of the land Demolition of the existing building on the land $ 2,000 10,000 5,000 35,000 350,000 50,000 For what dollar amount will The Laughton Company debit the land account and debit various expense accounts, respectively? Various Land Expenses a) $350,000 $102,000 b) 385,000 67,000 c) 402,000 50,000 d) 437,000 15,000 e) 452,000 0 Question 2 (17 marks) (31 minutes) The following are the Balance Sheet and Income Statement for Fuzzy Wines Ltd. for 20x5: Fuzzy Wines Ltd. Balance Sheet as at August 31, 20x5 20x5 Current Assets: Cash $ 80 Term deposits 0 Accounts receivable 520 Inventories 340 940 Noncurrent assets Plant and equip. 1,450 Accumulated Dep. (475) 975 $1,915 20x5 Current Liabilities: $ 175 Demand loan $ 140 150 Accounts payable 425 350 565 250 Noncurrent liabilities 925 Long-term notes 225 790 925 Shareholders' equity (350) Paid-in capital 700 575 Retained earnings 425 1,125 $1,500 $1,915 Fuzzy Wines Ltd. Income Statement for the year ended August 31, 20x5 Revenue Cost of goods sold Interest expense Other expenses Income before income taxes Income tax expense Net income 20x4 20x4 $ 100 200 300 400 700 500 300 800 $1,500 $3,000 1,200 25 1,350 425 190 $ 235 Additional information 1. The term deposits and demand loan are considered to be cash and cash equivalents. 2. One noncurrent asset was sold for $15 during the year. The cost of the asset was $100, the accumulated depreciation on the asset was $75. The gain or loss on the asset sold is included in Other expenses on the statement of income. Required (a) Prepare a statement of cash flow for the year ended August 31, 20x5 using the indirect method. (b) Prepare the Cash Flow from Operations section using the direct method. Question 3 (7 marks) (13 minutes) The Kara Corporation issued, $5,000,000 of 15 year bonds on December 31, 20x5. Coupon payment dates are on June 30 and December 31. The bonds pay a coupon of 6.2% and were issued to yield 5.8%. Required (a) (b) Write the journal entry to record the issue of the bonds on December 31, 20x5. Write the journal entry to record the June 30 and December 31 coupon payments in 20x6. Question 4 (8 marks) (14 minutes) A friend of yours is just starting a yard grooming service and has purchased a group of lawnmowers for $20,000. The friend expects the mowers to last 5 yrs and to have negligible resale value at that point. The friend's business plan projects cutting 5,000 lawns over the five years, with per year projections of 500, 1,000, 1,200, 1,800 and 500 lawns over the five years. Required (a) (b) (c) (d) Calculate the accumulated depreciation balance at the end of the 2nd yr with the following: 1. Straight-line 2. Diminishing balance / declining balance (25% rate) 3. Units-of-production Based on your calculations, which depreciation basis would produce the highest retained earnings at the end of the second year? Your friend has never heard of the units-of-production basis. Explain why companies use it and comment on whether it would make sense for your friend's business. If the 25% diminishing / declining balance method is used, accumulated depreciation will be $15,254 at the end of the fifth year. Suppose that on the first day of the sixth year, all the lawnmowers are sold as junk for $1,000 cash in total. Calculate the gain/loss on sale that would be recorded that day. Question 5 (10 marks) (18 minutes) On January 1, 20x0, Calvin Corporation had 60,000 shares of no par value common shares issued and outstanding for a total book value of $720,000. During the year, the following transactions occurred: Mar. 1 Issued 40,000 shares of common shares for $600,000. Mar 20 Repurchased and cancelled 5,000 shares at $12.50 each. June 1 Declared a cash dividend of $2.00 per share to shareholders of record on June 15. June 30 Paid the $2.00 cash dividend. Jul 2 Issued 20,000 shares of common stock for $360,000 Aug 1 A 2:1 stock split was announced. Sep 15 Repurchased and cancelled 2,000 shares at $11 each. Dec. 15 Declared cash dividend on outstanding shares of $1.10/share to shareholders of record on Dec 31. Required Prepare journal entries to record the above transactions. Question 6 (18 marks) (32 minutes) The following are the income statements and balance sheets for The Chappaqua Company at and for the years ended December 31,20x3, 20x2, and 20x1: Sales (all credit sales) Cost of Goods Sold Gross Profit Operating Expenses Operating Income Interest expense Income before Income Taxes Income Tax Expense Net Income Current Assets Cash Accounts receivable Inventory Prepaid rent Long-term assets Capital assets Accumulated depreciation Current liabilities Long-term liabilities Shareholders equity Common stock Retained earnings 20x3 $803.0 531.0 272.0 161.0 111.0 4.8 106.2 42.5 $ 63.7 20x2 $711.0 476.0 235.0 136.0 99.0 5.2 93.8 38.0 $ 55.8 $ 18 90 60 10 178 $ 19 72 50 12 153 160 (103) 57 158 (90) 68 20x1 $670.0 448.0 222.0 132.0 90.0 5.0 85.0 31.0 $ 54.0 $14 61 40 7 122 140 (75) 65 $235 $221 $187 $ 87 33 120 $ 45 46 91 $ 46 45 91 40 75 115 $235 40 90 130 $221 40 61 101 $187 Required For the years 20x3 and 20x2, calculate the following ratios: (a) Return on Equity (b) Return on Assets (c) Profit Margin (d) Current Ratio (e) Quick Ratio (f) Average collection period (g) Inventory turnover (h) Times interest earned (i) Debt-to-Equity (j) Asset Turover SOLUTION Question 1 1. b 2. c 3. b 4. d 5. d Depreciable base = 30,000 - 6,000 = 24,000 Total useful life = 24,000 / 3 = 8 years Years to date - 15,000 / 3 = 5 Years remaining = 8 - 5 = 3 6. b $100,000 x 0.6 x 0.4 = $24,000 7. c 8. b The journal entry to record the repurchase would be as follows: Dr. Common shares Dr. Retained earnings Cr. Cash 10,000 1,000 9. b 10. c 11. c 12. d Cash collections of $255,000 + 15,000 increase in AR = $270,000 credit sales Total sales = $270,000 / 0.60 = $450,000 13. c Savings = $8,000 x 1% Interest: 7,920* x 12% x 20/365 Amount 'borrowed' of $8,000 x 0.99 (on day 10, we effectively 'borrow' $7,920 to pay invoice and save $80. We calculate interest for 20 days only since the full $8,000 would be payable on the 30th day anyways.) 14. d $56,000 + 300 + 1,500 - 120 + 1,130 + 560 = $59,370 11,000 $80.00 52.07 $27,92 15. a The journal entry would be as follows: Dr. Salaries expense Cr. CPP Payable Cr. Income taxes payable Cr. Medical insurance payable Cr. EI payable Cr. Union dues payable Cr. Cash 16. c 17. c 18. b 19. a 20. e N = 10, I = 4, PMT = 315,000, FV = 7,000,000 CPT PV = 7,283,881 All are charged to land. 12,000 550 2,500 450 32 216 8,252 Question 2 (a) Fuzzy Wines Ltd. Statement of Cash Flow For the year ended August 31, 20x5 Cash flow from operations Net income Adjust for noncash items Depreciation ($125 Increase in Acc Dep + 75 Acc Dep on Asset Sold) Loss on sale of plant and equipment ($25 Net Book Value - 15 Proceeds) Adjust for changes in non-cash working capital items Increase in accounts receivable Increase in inventory Increase in accounts payable Cash flow from investing Purchases of plant and equipment ($525 Increase in Plant & Equip + 100 Cost of Plant & Equip Sold) Proceeds on sale of plant and equipment sold Cash flow from financing Repayment of long-term notes Issue of common stock Payment of dividends ($235 Net Income - $125 Increase in Retained Earnings) (b) $235 200 10 (170) (90) 225 410 (625) 15 (610) (175) 200 (110) (85) Decrease in cash Cash and cash equivalents, beginning of year ($175 + 150 - 100) (285) 225 Cash and cash equivalents, end of year ($80 - 140) ($60) Cash flow from operations (direct) Cash collected from customers ($3,000 Sales - 170 Increase in A/R) Cash paid to suppliers ($1,200 COGS + 90 Increase in Inventories - 225 Increase in AP) Cash paid for interest Cash paid for other expenses ($1,350 - 200 Depreciation expense - 10 Loss on Sale of P&E) Cash paid for income taxes 2,830 (1,065) (25) (1,140) (190) $410 Question 3 (a) Proceeds received on bond issue: N = 30 I = 5.8 / 2 = 2.9 PMT = $5,000,000 x 6.2% / 2 = $155,000 FV = $5,000,000 CPT PV = $5,198,562 Dec 31, 20x5 (b) Jun 30, 20x6 Dec 31, 20x6 Cash Bonds Payable Premium on Bonds Payable Interest expense ($5,198,562 x 2.9%) Premium on Bonds payable Cash Interest expense ($5,198,562 - 4,242) $5,194,320 x 2.9% Premium on Bonds payable Cash $5,198,562 $5,000,000 198,562 150,758 4,242 155,000 150,635 4,365 155,000 Question 4 (a) 1. Depreciation expense per year = $20,000 / 5 = $4,000 Accumulated depreciation at end of 2nd year = (4,000 x 2) = $8,000 2. Depreciation expense in year 1 = $20,000 x 25% = $5,000 Depreciation expense in year 2 = $20,000 - 5,000 = 15,000 x 25% = $3,750 Accumulated depreciation at end of 2nd year = $5,000 + 3,750 = $8,750 3. Depreciation expense in year 1 = $20,000 / 5,000 x 500 = $2,000 Depreciation expense in year 2 = $20,000 / 5,000 x 1,000 = $4,000 Accumulated depreciation at end of 2nd year = $2,000 + 4,000 = $6,000 (b) Units of production has the lowest accumulated depreciation and will cause retained earnings to be the highest. (c) Units of production should be used when the revenue generated by the asset is based on units of production. If your friend charges his customers a fee everytime their lawn is cut, then the unit of production method will provide the best matching of depreciation expense to revenues. (d) Net book value: $20,00 - 15,224 Less proceeds Loss on disposal $4,746 1,000 $3,746 Question 5 Mar 1 Mar 20 Cash Common Stock Common Stock (5,000 x $13.20*) Contributed Surplus Cash (5,000 x $12.50) $600,000 $600,000 66,000 3,500 62,500 * ($720,000 + 600,000) / (60,000 + 40,000) = $1,320,000 / 100,000 = $13.20 Jun 1 Jun 30 Jul 2 Retained Earnings Dividends Payable 100,000 - 5,000 = 95,000 shares x $2.00 190,000 Dividends payable Cash 190,000 Cash Common Stock 360,000 Aug 1 No entry - common shares outstanding becomes: 60,000 + 40,000 - 5,000 + 20,000 = 115,000 x 2 = 230,000 Sep 15 Common Stock (2,000 x $7.0174*) Contributed Surplus Retained Earnings Cash (2,000 x $11) 190,000 190,000 360,000 14,035 3,500 4,465 22,000 * ($1,320,000 - 66,000 + 360,000) / 230,000 = $1,614,000 / 230,000 = $7.0174 Dec 15 Retained Earnings Dividends Payable 230,000 - 2,000 = 228,000 shares x 1.10 250,800 280,800 Question 6 (a) Return on equity = Net Income / Average S/E 20x3 $63.7 / [(115 + 130) / 2) = 63.7 / 122.5 = 52% 20x2 $55.8 / [(130 + 101) / 2) = 55.8 / 115.5 = 48% (b) Return on Assets = Net Income before taxes / Average Assets $106.2 / [(235 + 221) / 2) = 106.2 / 228 = 47% $93.8 / [(221 + 187) / 2] = 93.8 / 204 = 46% (c) Profit margin = Net Income / Sales $63.7 / 803 = 7.9% $55.8 / 711 = 7.9% (d) Current ratio = CA / CL $178 / 120 = 1.5 $153 / 91 = 1.7 (e) Quick ratio = Quick Assets / CL $108 / 87 = 1.24 $91 / 91 = 1.0 (f) Average collection period = Average AR / Average Daily Credit Sale [(90 + 72) / 2] / (803 / 365) = 81 / 2.2 = 37 days [(72 + 61) / 2] / (711 / 365) = 66.5 / 1.9479 =34 days (g) Inventory turnover = COGS / Average Inventory $531 / [(60+ 50) / 2] = 531 / 55 = 9.65 times $476 / [(50 + 40) / 2] = 476 / 45 = 10.6 times (h) Times interest earned = Operating Income / Interest Expense $111 / 4.8 = 23 times $99 / 5.2 = 19 times (i) Debt-to-equity = Debt / Equity $120 / 115 = 1.04 $91 / 130 = 0.70 (j) Asset Turnover = Sales / Average Total Assets $803 / [(235 + 221) / 2] = 803 / 228 = 3.5 $711 / [(221 + 187) / 2] = 711 / 204 = 3.5