JDBC Programming I
advertisement

JDBC Programming I
Unit Objectives
After completing this unit, you should be able to:
Code connection-related statements within a JDBC
application
Code the necessary import statements for JDBC interfaces
Embed INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE and simple SELECT
statements in JDBC applications
Write code to check for Warning and Exception
conditions and understand the SQLCA
Utilize parameter markers in JDBC application programs
Process data that allows NULL values
Understand database access security when using JDBC
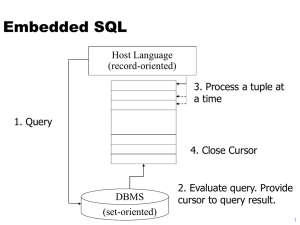
What Is JDBC?
Java API for executing SQL
A set of classes and interfaces written in Java
A vendor-neutral dynamic SQL interface
Uses only dynamic SQL
JDBC Programming
1. Import appropriate Java packages and classes
2. Load appropriate JDBC driver
3. Connect to the database, specifying the location
with a URL and using the db2 subprotocol
4. Pass SQL statements to the database
5. Receive results
6. Close the connection
Import Classes and Load Driver
import java.sql.*; 1
import java.io.*;
import java.lang.*;
class MyJDBC {
static {
2
try { Class.forName("COM.ibm.db2.jdbc.app.DB2Driver");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
Connect to Database
public static void main (String argv[]){
try {
1
Connection con = null;
2
String url = "jdbc:db2:sample";
if (argv.length == 0)
3
{ con = DriverManager.getConnection(url); }
else if (argv.length == 2)
{
String userid = argv[0];
String passwd = argv[1];
4
con = DriverManager.getConnection(url,userid,passwd);
}
else
{ throw new Exception
("\n Usage: java MyJDBC[,username,password]\n");}
SELECT Statement
1 Statement stmt = con.createStatement();
2 ResultSet rs
= stmt.executeQuery
("SELECT EMPNO, LASTNAME " +
" FROM TEMPL "
+
" WHERE SALARY > 40000 " );
3 while ( rs.next() ) {
4
System.out.println("empno = " + rs.getString(1) +
"lastname = " + rs.getString(2) );
}
5 rs.close();
6 stmt.close();
7 con.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
8
}
e.printStackTrace();
UPDATE Statement
1 Statement updStmt = con.createStatement();
2 int numRows = updStmt.executeUpdate
("UPDATE TEMPL " +
" SET LASTNAME = 'Stohl' " +
" WHERE EMPNO = '000110' ");
System.out.println("Number of rows updated " + numRows);
Using Parameter Markers - UPDATE
1 PreparedStatement pUpd = con.prepareStatement
("UPDATE TEMPL " +
" SET SALARY = ? " +
" WHERE EMPNO = ? ");
2 pUpd.setString(1,argv[1]);
3 pUpd.setString(2,argv[2]);
4 int numRows = pUpd.executeUpdate();
System.out.println("Number of rows updated " + numRows);
5 pUpd.close();
Insert Statement
1 String sql = null;
sql = "INSERT INTO TEMPL (EMPNO, LASTNAME, SALARY)"
2
+ "VALUES ('000110', 'Roth', 50000)",
3 stmt = con.createStatement();
4 insertCount = stmt.executeUpdate( sql );
Delete Statement
1
String eno = "000110";
2
String mysql = null;
3
mysql = "DELETE FROM TEMPL WHERE EMPNO = ?";
4
psstmt = con.prepareStatement (mysql);
5
pstmt.setString (1, eno);
6
deleteCount = psstmt.executeUpdate();
Declaring Host
Variables Language Definitions
GRAPHIC
CHAR
FLOAT
C
DB2
REFERENCE
LIBRARY
FORTRAN
Java
VARCHAR
DECIMAL
COBOL
INTEGER
Declaring Host Variables - Java Program
Host variables follow normal Java variable syntax
Host variable names are treated by DB2 as global
to the source module in which they are defined
Declaration Considerations for Java
CREATE TABLE SIMPLE
(TITLE CHAR (20) NOT NULL,
NUMBER SMALLINT NOT NULL )
private static String title;
private static short number;
sql = "SELECT TITLE FROM SIMPLE "
+ "WHERE NUMBER = ?";
pstmt = con.prepareStatement(sql);
pstmt.setString (1, number);
ResultSet prs = pstmt.executeQuery();
While (prs.next())
{ title = prs.getString(1);}
DCLGEN
Generate table declaration db2dclgn (DCLGEN)
Creates Structures for host
variables
Languages supported
C, Java, COBOL, FORTRAN
db2dclgn -D sample -T employee -L Java
Processing Null Values
In all but Java, use Indicator variables
In Java, compare the value of the host variable
with Java null
Java example:
sql = "SELECT MGRNO FROM EMP";
........
String mgrno = rs.getString(1);
if (mgrno == null)
{ System.out.println ("\n MGRNO is null \n");}
Example of Using the wasNull() Method
Statement stmt = con.createStatement();
ResultSet rs = stmt.executeQuery
("SELECT EMPNO, LASTNAME, EDLEVEL " +
" FROM EMP
" );
while ( rs.next() ) {
String eno = rs.getString(1);
String lname = rs.getString(2);
short edlvl = rs.getShort(3);
if ( rs.wasNull() )
{ System.out.println ("\n Edlevel is null for EMPNO
System.out.println (eno);
}
// end if
else
{ System.out.println ("\n Edlevel is:
\n");
System.out.println ( edlvl );
System.out.println ("\n For EMPNO =
System.out.println (eno);
}
// end else
\n");
\n");
Passing NULL Value - Java Program
sql = "UPDATE TEMPL SET PHONENO = ? "
+ "WHERE EMPNO = '000110' ";
stmt = con.prepareStatement(sql);
if (some condition)
{ stmt.setString (1, null); }
else
{ stmt.setString (1, newphone); }
updateCount = stmt.executeUpdate();
Example of Using the setNull() Method
sql = "UPDATE EMP SET EDLEVEL = ?
"
+ " WHERE EMPNO = '0000110' ";
pstmt = con.prepareStatement( sql );
if ( some condition )
{
pstmt.setNull (1, java.sql.Types.SMALLINT);
else
{
pstmt.setShort( 1, 16 );
}
updateCount = pstmt.executeUpdate();
}
Determining Success of SQL Statements
DB2 provides information to the program on the
success or failure of the SQL statement
Java programs throw an SQLException
Other host languages check the SQLCA
SQLCODE and SQLSTATE can be checked to
determine precise error
SQLCA - SQL Communication Area
Program
S
Q
L
C
A
Information / SQLCODE
Executable SQL
DB2
SQLCA Codes
CONDITION
INTEGER CHAR(1)
SQLCODE SQLWARNO REQUEST STATUS
<0
ERROR
WARNING
NOTFOUND
SUCCESS
>0 &
<> 100
FAILED
OR 'W'
(MORE)
DATA NOT FOUND
SQLSTATE = "02000"
+100
0
SATISFIED WITH
SPECIAL CONDITION
AND
''
SUCCESS
SQLCODE and SQLSTATE
SQLCODE
detailed
possibly platform dependent
numeric
SQLSTATE
first two characters - general
all five characters - more information
not as detailed as SQLCODE,
but not as platform dependent
SQLCA SQLERRD Third Element
PROGRAM:
SQLCA
SQLCODE
SQLWARN0
SQLERRD[2]
NUMBER
OF ROWS
AFFECTED
INSERT
UPDATE
DELETE
R
EQ
T
S
E
U
DB2
Error Processing
try {
1
2
3
4
5
sql = "DELETE FROM TEMPL WHERE EMPNO = 999";
psstmt = con.prepareStatement(sql);
deleteCount = psstmt.execute Update();
if (( SQLWarn = psstmt.getWarnings()) !=null)
{
System.out.println ("\n Warning received on a DELETE \n");}
} // end try
catch (SQLException x)
{ if (x.getSQLState().equals("42818"))
{ System.out.println ("\n Operand data types not compatible \n");
} // end if
else { System.out.println ("\n Error deleting from TEMPL \n");
System.out.println ("\n Value of SQLCODE is: \n");
SQLCode = x.getErrorCode();
System.out.println (SQLCode);
} // end else
} // end catch
JDBC and Security
JDBC
DELETE FROM
TEMPL WHERE
ID = '123'
USERA
GRANT DELETE ON TABLE
TEMPL TO USER USERA
Unit Summary
Since completing this unit, you should be able to:
Code connection-related statements within a JDBC
application
Code the necessary import statements for JDBC interfaces
Embed INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE and simple SELECT
statements in JDBC applications
Write code to check for Warning and Exception
conditions and understand th SQLCA
Utilize parameter markers in JDBC application programs
Process data that allows NULL values
Understand database access security when using JDBC