Algorithms, Flowcharts, Pseudocode: A Beginner's Guide
advertisement
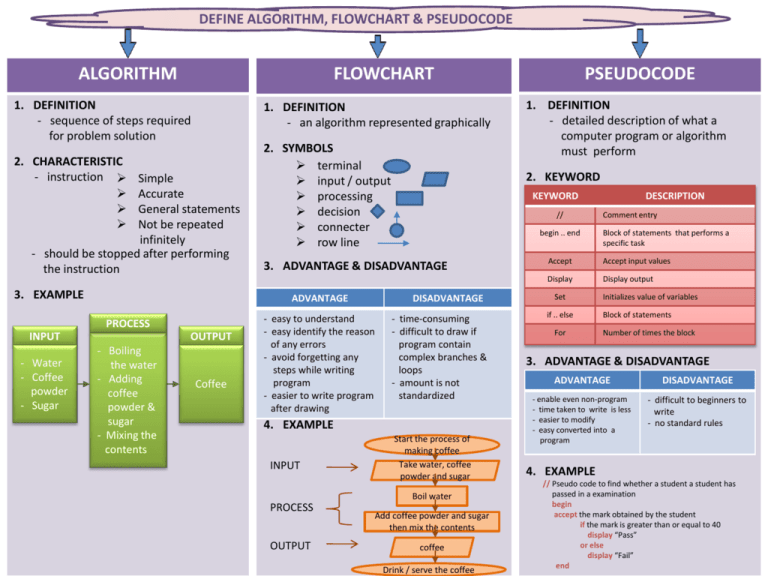
DEFINE ALGORITHM, FLOWCHART & PSEUDOCODE ALGORITHM FLOWCHART 1. DEFINITION - sequence of steps required for problem solution 1. DEFINITION - an algorithm represented graphically 2. CHARACTERISTIC - instruction Simple Accurate General statements Not be repeated infinitely - should be stopped after performing the instruction 3. EXAMPLE INPUT OUTPUT - Boiling the water - Adding coffee powder & sugar - Mixing the contents Coffee KEYWORD // begin .. end DISADVANTAGE - easy to understand - easy identify the reason of any errors - avoid forgetting any steps while writing program - easier to write program after drawing - time-consuming - difficult to draw if program contain complex branches & loops - amount is not standardized 4. EXAMPLE INPUT Start the process of making coffee Take water, coffee powder and sugar Boil water PROCESS OUTPUT 1. DEFINITION - detailed description of what a computer program or algorithm must perform 2. KEYWORD 3. ADVANTAGE & DISADVANTAGE ADVANTAGE PROCESS - Water - Coffee powder - Sugar 2. SYMBOLS terminal input / output processing decision connecter row line PSEUDOCODE Add coffee powder and sugar then mix the contents coffee Drink / serve the coffee DESCRIPTION Comment entry Block of statements that performs a specific task Accept Accept input values Display Display output Set if .. else For Initializes value of variables Block of statements Number of times the block 3. ADVANTAGE & DISADVANTAGE ADVANTAGE DISADVANTAGE - enable even non-program - time taken to write is less - easier to modify - easy converted into a program - difficult to beginners to write - no standard rules 4. EXAMPLE // Pseudo code to find whether a student a student has passed in a examination begin accept the mark obtained by the student if the mark is greater than or equal to 40 display “Pass” or else display “Fail” end
![저기요[jeo-gi-yo] - WordPress.com](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/005572742_1-676dcc06fe6d6aaa8f3ba5da35df9fe7-300x300.png)