Arguing Style Test

P s y c h o m e t t r r i i c R e p o r r t t
A r r g u i i n g S t t y l l e T e s t t R e v i i s e d
Copyright Plumeus Inc. 2003 1
Description:
A 40-item test assessing the test-taker's style of arguing (constructive vs. destructive) and to what degree s/he plays by the rules of constructive problem solving in typical conflict situations.
The test is suitable for adult and late adolescent population.
Reference:
Jerabek, I. (1999). Arguing Style Test. QueenDom.com
Sample Size
: 673
Sample Description
:
The sample includes men and women, aged 6 to 100, who took the test on Queendom.com .
Number of questions
: 40
Copyright Plumeus Inc. 2003 2
1.Descriptive Statistics
Men and Women
Statistics score
N Valid
673
Missing 0
Mean
62.70
Std. Error of Mean .443
Median
63.00
Mode 64
Std. Deviation 11.503
Variance
132.329
Skewness -.057
Std. Error of Skewness
.094
Kurtosis -.468
Std. Error of Kurtosis
.188
Range 64
Minimum
31
Maximum 95
Percentiles 5
43.00
10 48.00
15
51.00
20 53.00
25
54.00
30 56.00
35
57.90
40 59.00
45
61.00
50 63.00
55 64.00
60 66.00
65 68.00
70 69.00
75 71.00
80
74.00
85 75.00
90
78.00
95 81.00
97
83.78
99 88.00
Copyright Plumeus Inc. 2003 3
Women Only
Statistics score
N Valid
260
Missing 0
Mean
62.93
Std. Error of Mean .775
Median
63.00
Mode 73
Std. Deviation
12.490
Variance 155.999
Skewness
-.209
Std. Error of Skewness .151
Kurtosis -.684
Std. Error of Kurtosis .301
Range 56
Minimum 34
Maximum 90
Percentiles 5
41.00
10 45.00
15
49.00
20 52.00
25
54.00
30 56.00
35
58.00
40 59.40
45
61.00
50 63.00
55
64.00
60 68.00
65
69.00
70 71.70
75
73.00
80 74.00
85 76.00
90
78.90
95 82.90
97
84.00
99 87.39
Copyright Plumeus Inc. 2003 4
Men Only
Statistics score
N Valid 148
Missing 0
Mean 63.99
Std. Error of Mean
.916
Median 65.00
Mode
64(a)
Std. Deviation 11.140
Variance
124.109
Skewness -.070
Std. Error of Skewness
.199
Kurtosis -.353
Std. Error of Kurtosis
.396
Range 58
Minimum
33
Maximum 91
Percentiles 5
45.00
10 48.00
15
52.00
20 53.00
25 55.25
30
57.70
35 60.15
40
62.00
45 64.00
50
65.00
55 66.00
60
67.00
65 69.00
70
71.00
75 72.00
80
74.00
85 75.00
90
78.00
95 80.00
97
87.53
99 90.02
a Multiple modes exist. The smallest value is shown
Copyright Plumeus Inc. 2003 5
2.Distributions for the Arguing Style Test
The distribution of the scores is shown in red; the normal curve is represented by the black line. The scores are displayed on the x-axis. The y-axis corresponds to the number of respondents who fall in the relevant score range.
Men and Women
Histogram
60
50
40
30
20
10
0
30 40 50 60 70
Score
80 90 100
Mean = 62.7
Std. Dev. = 11.503
N = 673
Copyright Plumeus Inc. 2003 6
Women Only
Histogram
30
25
20
15
10
5
0
30 40 50 60
Score
70 80 90
Mean = 62.93
Std. Dev. = 12.49
N = 260
Copyright Plumeus Inc. 2003 7
Men only
Histogram
25
20
15
10
5
0
30 40 50 60 70
Score
80 90 100
Mean = 63.99
Std. Dev. = 11.14
N = 148
Copyright Plumeus Inc. 2003 8
3. Reliability and Internal Consistency
Score (40 items)
Inter-Item Consistency
Cronbach's Coefficient Alpha: 0.874
Split-Half Reliability
Correlation between forms: 0.700
Spearman-Brown formula: Unequal 0.824
Guttman’s formula: 0.818
Copyright Plumeus Inc. 2003 9
62
60
58
66
64
4. Criterion and Construct Validity
1. Relationship between age and arguing style score.
Question #1: Enter your age
Significant score differences were found among groups of subjects depending on their age. As people age, their arguing style becomes less destructive and more constructive. See Annex 1 for a table showing homogeneous subsets.
F
(8,401)
= 1.678 p < 0.102
AGE AND OVERALL SCORE
68
10-15 16-18 19-24 25-29 30-34 35-39 40-49 50-59
Age Groups
60+
Copyright Plumeus Inc. 2003 10
2. Relationship between marital status and arguing style score.
Question #2: Relationship status:
OPTION VALUE="na" SELECTED>I don't want to answer
OPTION VALUE="1">Married
OPTION VALUE="2">Living with partner
OPTION VALUE="3">In a relationship, but living apart
OPTION VALUE="4">Currently not in a relationship
OPTION VALUE="5">Divorced and single
OPTION VALUE="6">Widowed and single
OPTION VALUE="7">Engaged to be married
No significant score differences were found among groups of subjects depending on their marital status.
Arguing style remains similar regardless of relationship status. See Annex 1 for a table showing homogeneous subsets.
F
(6,375)
= 1.105 p < 0.359
RELATIONSHIP STUTUS AND OVERALL SCORE
65
60
55
50
Ma rrie d
Liv ing
Wi th
Pa rtne r
In A
R elat io ns hi p,
Cu rre ntl
Bu t Li y N ot In A ving
Ap
Di vo rce d a
R elati on shi nd
S ingl e p
W ido w ed A ar t
En nd
Si ng le ga ge d T o B e Ma r
Relashionship Status
Copyright Plumeus Inc. 2003 11
3 Relationship between length of the current romance and arguing style score.
Question #3: How long have you been in your current relationship?
OPTION VALUE="na" SELECTED>I don't want to answer
OPTION VALUE="1">Less than a year
OPTION VALUE="2">1-2 years
OPTION VALUE="3">3-5 years
OPTION VALUE="4">5-7 years
OPTION VALUE="5">7-10 years
OPTION VALUE="6">10-15 years
OPTION VALUE="7">15-20 years
OPTION VALUE="8">20+ years
No significant score differences were found among groups of subjects depending on the length of their current relationship. The arguing style remains similar regardless of whether people have been engaged for a short or long period of time. See Annex 1 for a table showing homogeneous subsets.
F
(7,324)
= 1.782 p < 0.090
LENGTH OF CURRENT RELATIONSHIP AND OVERALL SCORE
70
62.5
60
57.5
55
67.5
65
Less than 1-2 years 3-5 years 5-7 years 7-10 a year years
10-15 years
15-20 years
20+ years
Length Of Current Relationship
Copyright Plumeus Inc. 2003 12
4. Relationship between level of satisfaction in a current romance and arguing style score.
Question #4: How satisfied are you with your current relationship?
OPTION VALUE="na" SELECTED>I don't want to answer
OPTION VALUE="1">I am 100% satisfied with my relationship with my partner
OPTION VALUE="2">I am quite content with my relationship with my partner
OPTION VALUE="3">I am neither happy nor unhappy
OPTION VALUE="4">I am rather unhappy in the relationship
OPTION VALUE="5">Our relationship is terrible
Significant score differences were found among groups of subjects depending on their level of satisfaction in a current relationship. Those who claim to be unhappy have a more destructive arguing style than those who are not. The effects are robust. See Annex 1 for a table showing homogeneous subsets.
F
(4,327)
=22.975 p < 0.000
SATISFACTION AND OVERALL SCORE
70
65
60
55
100% Satisfied Quite Content Neither Happy nor Unhappy
Rather Unhappy
Satisfaction
Terribly
Unhappy
5. Relationship between fighting and arguing style score.
Copyright Plumeus Inc. 2003 13
Question #5:
Do you consider fighting with your partner to be a serious problem in your current relationship?
OPTION VALUE="na" SELECTED>I don't want to answer
OPTION VALUE="1">Yes
OPTION VALUE="2">Somewhat
OPTION VALUE="3">No
Significant score differences were found among groups of subjects depending on their attitude towards fighting in their current relationship. The arguing style of people who are unhappy about fighting is less destructive than those who are not.. The effects are robust. See Annex 1 for a table showing homogeneous subsets.
F
(2,336)
=52.534 p < 0.000
FIGHTING AND OVERALL SCORE
65
60
55
Yes Somewhat
Fighting
No
Copyright Plumeus Inc. 2003 14
62
60
58
56
6. Relationship between stability, commitment and arguing style score.
Question #6:
Do you consider your relationship to be stable and long-term?
OPTION VALUE="na" SELECTED>I don't want to answer
OPTION VALUE="1">Yes
OPTION VALUE="2">No
OPTION VALUE="3">Not sure
Significant score differences were found among groups of subjects depending on the stability and degree of commitment in their current relationship. The arguing style of people who are in a stable and long term relationship is more constructive than the arguing style of those who express doubts. The effects are robust. See Annex 1 for a table showing homogeneous subsets.
F
(2,329)
=20.593 p < 0.000
STABILITY AND COMMITMENT AND OVERALL SCORE
68
66
64
Yes No
Stability and Commitment
Not Sure
Copyright Plumeus Inc. 2003 15
5. Gender differences
Significant gender differences were detected: t
1) Men scored significantly higher than women in the general score:
(335)
=-0.883 p < 0.378 Mean difference: -1.060
Group Statistics for Gender Differences
Score
Gender
Woman
Man
N
260
148
Mean
62.93
63.99
Std. Deviation
12.490
11.140
Independent Samples Test for Gender Differences
Std. Error
Mean
.775
.916
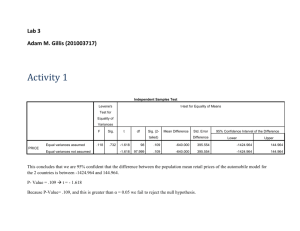
Score Equal variances assumed
Equal variances not assumed t
-.856 df
406 t-test for Equality of Means
Sig.
(2-tailed)
Mean
Difference
Std. Error
Difference
.392
-1.060
1.238
95% Confidence
Interval of the
Difference
Lower
-3.492
Upper
1.373
-.883 335.212
.378
-1.060
1.199 -3.419 1.300
Copyright Plumeus Inc. 2003 16
6.Correlations
Correlations
Score
Age
Length Of Current
Relationship
Pearson Correlation
Sig. (2-tailed)
N
Pearson Correlation
Sig. (2-tailed)
N
Pearson Correlation
Sig. (2-tailed)
N
Score
673
.141(**)
1
.004
411
.017
.762
332
Age
.141(**)
.004
411
1
411
.599(**)
.000
328
Length Of
Current
Relationship Satisfaction
.017
.762
-.463(**)
.000
332
.599(**)
.000
328
1
332
.035
.531
326
.046
.411
332 319
Satisfaction Pearson Correlation
Sig. (2-tailed)
N
-.463(**)
.000
332
** Correlation is significant at the 0.01 level (2-tailed).
.035
.531
326
.046
.411
319
1
332
Copyright Plumeus Inc. 2003 17
ANNEX 1 -Homogeneous Subsets
The following table presents the homogeneous subset for arguing style score and the age groups.
Score
Tukey HSD
Subset for alpha =
.05
Age Groups
10-15
25-29
N
5
1
59.00
16-18
35-39
30-34
19-24
40-49
60+
50-59
Sig.
71
17
35
65
80
84
11
42
60.42
60.47
61.43
62.46
63.81
64.99
65.73
67.10
.454
Means for groups in homogeneous subsets are displayed. a Uses Harmonic Mean Sample Size = 19.737. b The group sizes are unequal. The harmonic mean of the group sizes is used. Type I error levels are not guaranteed.
The following table presents the homogeneous subset for arguing style score and relationship status.
Score
Tukey HSD
Subset for alpha = .05
Relationship Status
Widowed And Single
Engaged To Be Married
Currently Not In A
Relationship
Married
Divorced and Single
Living With Partner
In A Relationship, But
Living Apart
N
3
10
75
127
16
61
90
1
49.00
60.00
62.32
63.09
Sig.
.052
Means for groups in homogeneous subsets are displayed. a Uses Harmonic Mean Sample Size = 12.855.
2
60.00
62.32
63.09
63.50
64.10
64.51
.965
Copyright Plumeus Inc. 2003 18
b The group sizes are unequal. The harmonic mean of the group sizes is used. Type I error levels are not guaranteed.
The following table presents the homogeneous subset for arguing style score and relationship length.
Score
Tukey HSD
Subset for alpha =
.05
Length Of Current
Relationship
5-7 years
7-10 years
10-15 years
1-2 years
3-5 years
Less than a year
20+ years
15-20 years
Sig.
N
37
21
40
58
61
59
41
15
1
59.65
61.24
61.58
61.97
65.13
65.24
65.78
68.20
.081
Means for groups in homogeneous subsets are displayed. a Uses Harmonic Mean Sample Size = 33.156. b The group sizes are unequal. The harmonic mean of the group sizes is used. Type I error levels are not guaranteed.
The following table presents the homogeneous subset for arguing style score and relationship satisfaction.
Score
Tukey HSD
Subset for alpha = .05
Satisfaction
Terribly Unhappy
Rather Unhappy
Neither Happy nor
Unhappy
N
18
46
63
1
52.89
53.85
2
60.59
3
Quite Content
100% Satisfied
Sig.
141
64
.994
65.48
.224
65.48
70.81
.153
Means for groups in homogeneous subsets are displayed. a Uses Harmonic Mean Sample Size = 43.146. b The group sizes are unequal. The harmonic mean of the group sizes is used. Type I error levels are not guaranteed.
Copyright Plumeus Inc. 2003 19
The following table presents the homogeneous subset for arguing style score and attitude toward fighting.
Score
Tukey HSD
Subset for alpha = .05
Fighting
Yes
Somewhat
No
Sig.
N
60
67
212
1
53.48
1.000
2
57.72
1.000
3
67.79
1.000
Means for groups in homogeneous subsets are displayed. a Uses Harmonic Mean Sample Size = 82.624. b The group sizes are unequal. The harmonic mean of the group sizes is used. Type I error levels are not guaranteed.
The following table presents the homogeneous subset for arguing style score, stability, and commitment in a relationship.
Score
Tukey HSD
Subset for alpha = .05
Stability and Commitment
No
Not Sure
N
37
1
56.24
2
Yes
Sig.
82
213
58.52
66.21
.483
1.000
Means for groups in homogeneous subsets are displayed. a Uses Harmonic Mean Sample Size = 68.311. b The group sizes are unequal. The harmonic mean of the group sizes is used. Type I error levels are not guaranteed.
Copyright Plumeus Inc. 2003 20