COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING COLLEGE REQUIREMENTS UNIT
advertisement

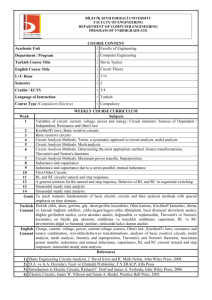
COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING COLLEGE REQUIREMENTS UNIT ELEC 201 Electric Circuits Term Instructor Information To be filled by the course instructor. TA Information To be filled by the course instructor. Class/Laboratory Schedule To be filled by the course instructor. Coordinator Information Coordinator Name: Dr. Mohammed Al-Hitmi Office: G215 Tel: 485-2706 E-mail: m.a.alhitmi@qu.edu.qa Course Information Catalog Description: Basic Concepts: Voltage, current, power, and energy. Independent and dependent voltage and current sources. DC Circuits Analysis: Ohms law, Kirchhoff’s current and voltage laws. Series and parallel DC circuits analysis, nodal analysis, and mesh analysis. Superposition, source transformation, and maximum power transfer theorems, Thevenin’s and Norton’s theorems. Capacitance and Inductance: series and parallel connections of capacitors and inductors. AC Circuits Analysis: Sinusoidal sources, rms value, phasor representation, complex impedances. Kirchhoff’s laws in the phasor domain, parallel and series AC circuits. Experiments will be conducted to support the course including the use of computer software for circuit analysis. Credits: 3. Contact Hours: 2 Lecture hours and 3 Lab hours. Prerequisites by Course: (MATH 102 Concurrent) and (PHYS 193 Concurrent) Prerequisites by Topics: Linear Algebra Calculus Complex numbers Electricity and magnetism. Textbook(s): Alexander and Sadiku “Fundamentals of Electric Circuits” Third Edition McGraw Hill. References: Nilsson and Riedel “Electric Circuits” Seventh edition Prentice Hall. Course Objective: The course objective is to: 1. Introduce fundamental concepts of electric circuits. 2. Provide students with basic electric circuits analysis techniques. 3. Emphasize practical engineering-based applications. Course Outcomes: At the end of this course, the students are expected to be able to 1. Define concepts of electric current, voltage, power, Kirchhoff’s current and voltage laws. 2. Use Ohm’s Law in series and parallel connections. 3. Use Thevenin’s theorem and Maximum power transfer and superposition theorems for circuit analysis. 4. Apply nodal and mesh analysis to solve DC circuits. 5. Apply superposition and source transformation methods to solve DC circuits. 6. Be familiar with inductors and capacitors properties. 7. Be familiar with the concept of phasors. 8. Solve series/parallel AC circuits. 9. Be familiar with essential EE instruments such as Digital Multimeters, and be able to conduct dc circuit experiments. 10. Be able to analyze electric circuit using simulation software. Relationship of Course Outcomes to "a" to "k" ABET Outcomes: Course Outcome 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 ABET Outcome a a a a a a a a 9 10 b k Topics Covered: Topics Electric current, voltage, power, and voltage and current sources Kirchhoff’s current law and Kirchhoff’s voltage law Ohm’s law and series/parallel connections of resistors Series/parallel DC circuit analysis Nodal analysis Mesh analysis Superposition theorem Thevenin’s Theorem and Norton’s theorem Source transformation and maximum power transfer theorem Capacitance and capacitors series/parallel connections Inductance and inductors series/parallel connections Sinusoidal sources and phasor representation Phasor relationships for circuit elements Series/parallel AC circuit analysis Weeks 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 Method of Instruction To be filled by the course instructor. Assessment Methods and Grading Policy Required Assessment Methods: Exams and Course Work (e.g. HW/Quizzes/Project/Lab Work). The detailed weights to be determined by the instructor. e.g. Homeworks: Quizzes Lab Work Midterm Exam Final Exam : 10% : 10% : 10% : 30% : 40% ABET Contribution of Course to Professional Component Math & Basic Science : Engineering : 3 cr Engineering Design : General Education :- Computer/Software Usage Multisim 9. Laboratory Projects Laboratory work includes experiments on ohm's law, nodal analysis, superposition theorem, thevenin theorem, maximum power transfer theorem, …etc. Course Ground Rules To be filled by the course instructor. Declaration This syllabus and contents are subject to changes in the event of extenuating circumstances. The instructor (with approval of the Head of the College of Engineering Requirements Unit) reserves the right to make changes as necessary. If changes are necessitated during the term of the course, the students will be notified by email communication and posting the notification on the online teaching tool Blackboard. It is student’s responsibility to check on announcements made while they were absent. May 15, 2008 CRU