Kaplan Financial Dr. Thomas Wu ACCA P4 Revision Course Notes
advertisement
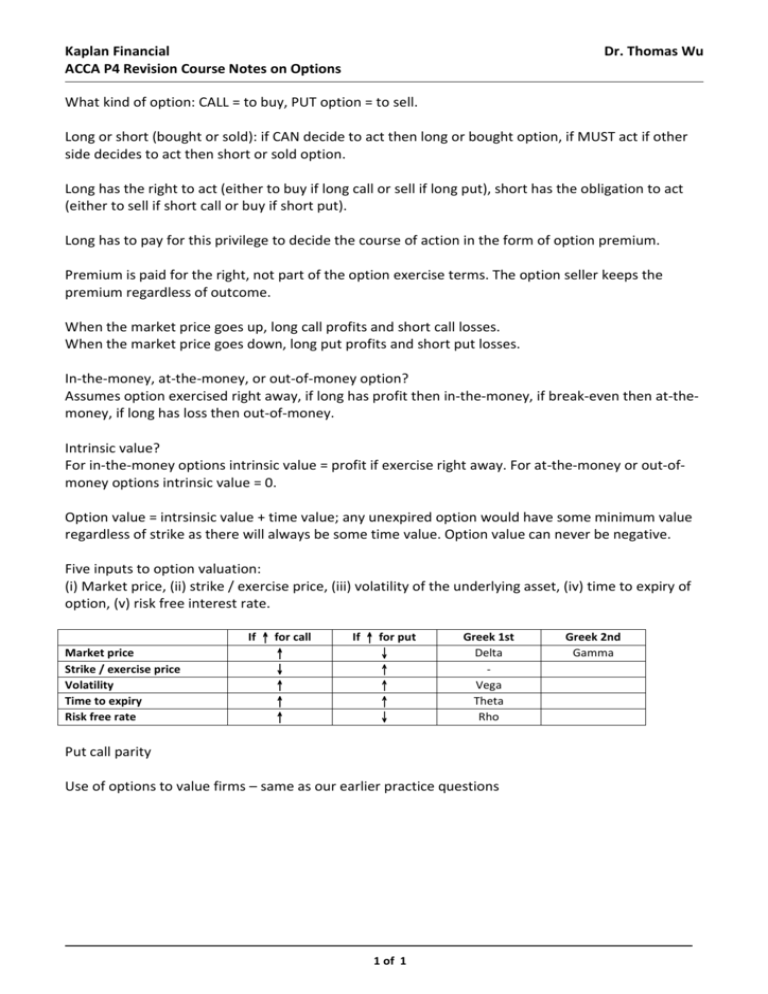
Kaplan Financial ACCA P4 Revision Course Notes on Options Dr. Thomas Wu What kind of option: CALL = to buy, PUT option = to sell. Long or short (bought or sold): if CAN decide to act then long or bought option, if MUST act if other side decides to act then short or sold option. Long has the right to act (either to buy if long call or sell if long put), short has the obligation to act (either to sell if short call or buy if short put). Long has to pay for this privilege to decide the course of action in the form of option premium. Premium is paid for the right, not part of the option exercise terms. The option seller keeps the premium regardless of outcome. When the market price goes up, long call profits and short call losses. When the market price goes down, long put profits and short put losses. In-the-money, at-the-money, or out-of-money option? Assumes option exercised right away, if long has profit then in-the-money, if break-even then at-themoney, if long has loss then out-of-money. Intrinsic value? For in-the-money options intrinsic value = profit if exercise right away. For at-the-money or out-ofmoney options intrinsic value = 0. Option value = intrsinsic value + time value; any unexpired option would have some minimum value regardless of strike as there will always be some time value. Option value can never be negative. Five inputs to option valuation: (i) Market price, (ii) strike / exercise price, (iii) volatility of the underlying asset, (iv) time to expiry of option, (v) risk free interest rate. If Market price Strike / exercise price Volatility Time to expiry Risk free rate ↑ for call ↑ ↓ ↑ ↑ ↑ If ↑ for put ↓ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↓ Greek 1st Delta Vega Theta Rho Put call parity Use of options to value firms – same as our earlier practice questions 1 of 1 Greek 2nd Gamma











