Study Guide: Economics Test 1 **Make sure you understand and
advertisement
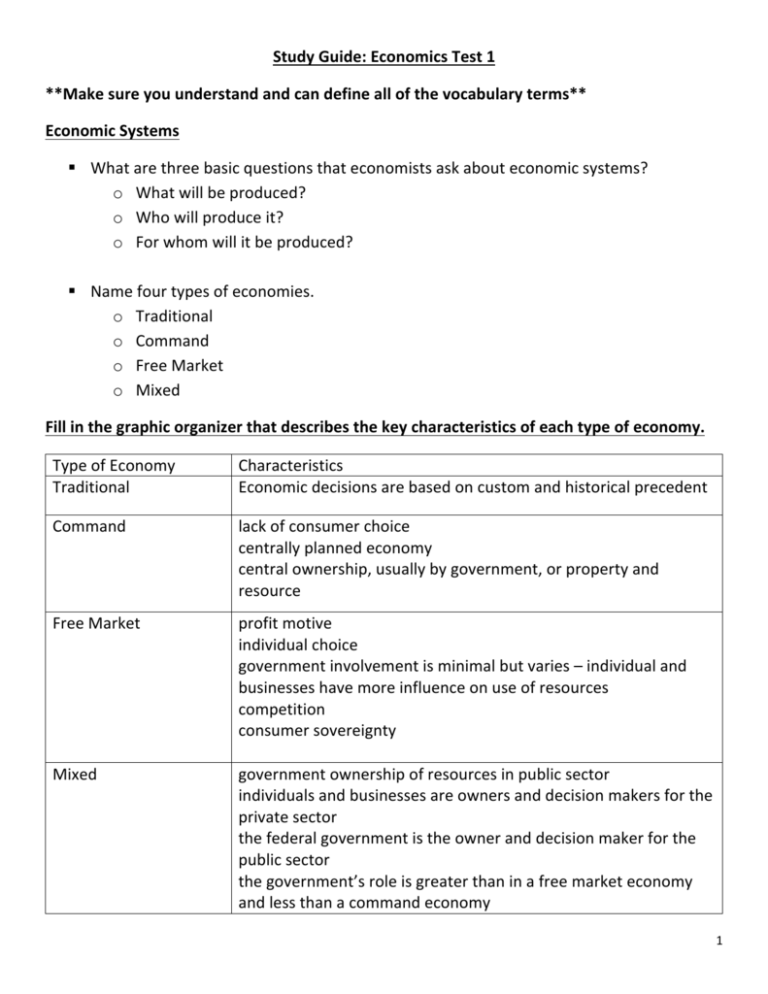
Study Guide: Economics Test 1 **Make sure you understand and can define all of the vocabulary terms** Economic Systems § What are three basic questions that economists ask about economic systems? o What will be produced? o Who will produce it? o For whom will it be produced? § Name four types of economies. o Traditional o Command o Free Market o Mixed Fill in the graphic organizer that describes the key characteristics of each type of economy. Type of Economy Traditional Characteristics Economic decisions are based on custom and historical precedent Command lack of consumer choice centrally planned economy central ownership, usually by government, or property and resource Free Market profit motive individual choice government involvement is minimal but varies – individual and businesses have more influence on use of resources competition consumer sovereignty government ownership of resources in public sector individuals and businesses are owners and decision makers for the private sector the federal government is the owner and decision maker for the public sector the government’s role is greater than in a free market economy and less than a command economy Mixed 1 § Describe four important characteristics of the United States Economy. o Profit o consumer sovereignty o competition o Private property § Give two or three examples of incentives that companies/businesses offer to consumers to encourage them to change their buying behavior: o buy one get one free o extended warranties o bundles § In free market (mixed) economies, most individuals are motivated by profits and their own self-­‐interest. § Explain two relationships between Supply and Demand and what it does to price (eg. ‘If Supply is high, but Demand is low’ and ‘If Supply is low but Demand is high’): o increased supply tends to lower price o Increased demand tends to increase price § What are four synonyms for the term ‘competition’? o Rivalry o Contest o Match o Battle § Describe four benefits to consumers of COMPETITION in the marketplace: o lower prices o higher quality o more choice o drives innovation § Interaction between Supply & Demand determines price. § Compare who makes most decisions in the public sector vs. the private sector. o Public sector – government officials o Private sector – individuals and businesses 2 § Regulations, laws, setting tax and interest rates, and looking out for public and consumer safety are all examples of: government involvement § Why is some government interference and regulations in the economy good? o protects consumers from unfair or unsafe business practices, o protects labor force, o minimizes fraud, o corruption and unfairness in the market, o protects resources • What are some things that are not desirable about too much government interference/regulations? o hinders innovation, o adds cost to production, o limits use of resources • What is the significance of private property ownership in free markets? Why is it so important? o Individuals and business can own and decide how to use resources o Higher entrepreneurial spirit • Describe what you have learned about the role of ‘Profits’ in the marketplace: o sellers incentive is to make more money o profit drives what is produced, how it is produced, and how much is produced o profit motivates behavior Compare and Contrast the three major types of business organizations. What are the advantages and disadvantages of sole proprietorship, partnership, and corporation? (Give examples to support). o Sole proprietorship-­‐ Pros= (you keep all profits; easy to set up; more options to do what you want; work by yourself) (Cons=you get overwhelmed with a lot of work for one person; difficult to expand/manage; if you fail, you might lose everything you put into it; you don’t have help/feedback) o Partnership-­‐ Pros= (Share the work/responsibilities with others; you have others to lend their creative ideas and skills; split the costs to run the business) (Cons= disagreements about direction of the company, splitting profits) 3 o Corporation= Pros= (You have many resources to succeed; you can sell shares/stocks to raise more capital for the company; you have the opportunity to go global; has legal protections) (Cons= If the company does poorly many people are affected; difficult to manage) Circular Flow of Money: • What is money? o A medium of exchange generally accepted as payment for goods and services • What are three types of money? o Cash/currency, o coins, checks, o debit cards, credit cards • Why does the United States issue coins and currency? o In order to facilitate trade • What is a U.S. Federal Reserve Note? o A bill, o a note o legal tender Businesses and Households: § Where do businesses get their income from? o Households/consumers purchase goods and services; investment income § Where do households get income (money to spend) from? o From working for businesses or self-­‐employed or investment income Banks: § What is the purpose of financial institutions (such as banks)? o They receive deposits, make loans, keep money safe, and facilitate transfers of funds § How do financial institutions encourage consumers to save and invest money? o They offer incentives such as interest 4 Draw your own version of the ‘Circular Flow’ between households, businesses, banks, and the national government. Make sure you label all relationships. Globalization: § Why do nations and states trade? o To get goods and services they can’t produce efficiently; o to buy goods and services at a lower cost or opportunity cost o to sell to other countries; to create jobs and economic growth § How does technology impact global trade? o Increases global flow of information, capital, goods, and services o often lowers cost of production o increases speed and efficiencies 5