Systematic Approach to 12 Lead EKG Interpretation
advertisement

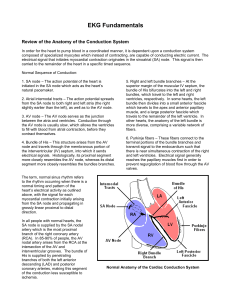
Systematic Approach to 12 Lead EKG Interpretation Maureen Knechtel MPAS, PA-C Wellmont CVA Heart Institute Objectives 1. 2. 3. 4. Establish a concise approach to EKG interpretation Gain confidence in the ability to correctly and thoroughly interpret an EKG Use EKG findings to guide clinical management Know when to refer based on EKG findings Disclosure Statement of Financial Interest I, Maureen Knechtel, do not have a financial interest/arrangement or affiliation with one or more organizations that could be perceived as a real or apparent conflict of interest in the context of the subject of this presentation. Follow a System Rate Rhythm Axis Infarction Block Rate Rate Large box = 200 ms Find R wave on thick line Count to next thick line to estimate HR Rate If less than 40 bpm, divide rhythm strip in 2 and multiply number of QRS complexes by 10 Rhythm: Regular or Irregular Axis Lead I: QRS positive = axis points to Lead aVF: positive: axis in lower left quadrant: axis normal Lead aVF: negative: axis in upper left quadrant: left axis deviation Axis quadrants: defined by intersection of leads I and aVF Normal: 0 to +90 Right Axis Deviation: +90 to +180 Left Axis Deviation: -1 to -90 Axis Lead I: QRS negative = axis points to Lead aVF: positive: axis in the lower right quadrant: right axis deviation Lead aVF: negative: axis indeterminate Axis Axis Causes of Axis Deviation Left Axis Inferior MI LVH Obesity LBBB LAFB Ischemia and Infarction Right Axis Lateral MI RVH Tall, thin frame COPD RBBB LPFB Ischemia and Infarction EKG Leads Myocardial Distribution Reciprocal Changes (Injury Pattern) RCA II, III, aVF Inferior Wall Lateral Leads LAD V1-V4 Anterior Wall Inferior Leads Left Circumflex I, aVL, V5-V6 Lateral Wall Ischemia Diminished blood flow causes a delay in the depolarization and repolarization pattern T wave inversion, ST depression Injury ST segment elevation Define in millimeters from baseline 2 mm = clinically significant Infarct Q waves = no depolarization, scar tissue Inferior Leads Reciprocal Changes Posterior Ischemia Coronary Blood Supply and the Conduction System Block Coronary Artery Conduction System Right Coronary SA Node, AV Node Left Anterior Descending Right Bundle Branch Left Bundle Branch Left Circumflex SA Node (less common) AV Node (less common) Inferior wall MI can be complicated by sinus arrest or complete heart block Anterior infarction can be complicated by new bundle branch block or complete heart block LAD supplies interventricular septum 1st Degree AVB 2nd Degree AVB (Type 1 and 2) 3rd Degree RBBB LBBB First Degree AVB 2nd Degree Type I 2nd Degree Type II 3rd Degree AV Block RBBB RBBB QRS > 120 ms Findings due to slow, rightward spread of ventricular depolarization from LV Can occur in structurally normal heart or any condition that affects R heart R wave: LV activation V6: RS R wave: LV activation S wave: RV activation LBBB QRS > 120 ms Findings due to slow, leftward spread of ventricular depolarization from RV More likely associated with structural heart disease V1: QS Q: RV activation S: LV activation V6: Tall R wave, +/R wave: RV activation LBBB Ischemia and LBBB LBBB affects early and late phases of ventricular depolarization LBBB is reflected by Q waves, ST segment and T wave changes These are the same findings that can be present in ischemia and infarction ST Elevation Discordant with QRS Ischemia and BBB ST elevation > 1mm in leads with a positive QRS complex (QRS concordant with ST segment) ST elevation > 5 mm in leads with a negative QRS complex (QRS discordant with ST segment) ST depression > 1 mm in V1 to V3 Obtain serial EKGs if you are suspicious of an acute event Obtain serial EKGs if you are suspicious of an acute event Left Hemiblock Diagnose by: Axis deviation QRS patterns QRS duration may be normal LAFB Left Anterior Fascicle Anterolateral LV Delay in electrical activation shifts general axis towards left Left axis deviation -30 or more negative QRS negative inferior: rS QRS positive lateral: qR LAFB LPFB LPFB Left Posterior Fascicle Inferoseptal portion of LV Delay in electrical activation shifts axis towards right Right axis deviation +120 or more positive QRS negative lateral: rS QRS positive inferior: qR Prolonged QTc QT > ½ the R-R Interval Examine drug list: Antipsychotics Antidepressants: SSRIs Antibiotics: fluoroquinolones and macrolides Antifungals Antiarrhythmics www.torsades.org QTc prolongation Summary Always follow a pattern in order to correctly and efficiently interpret a 12 lead EKG Examine the EKG leads as groups Use EKG clues to guide clinical management and refer when high risk findings are present