The Biology of Sex: How We Become Male or Female.
advertisement
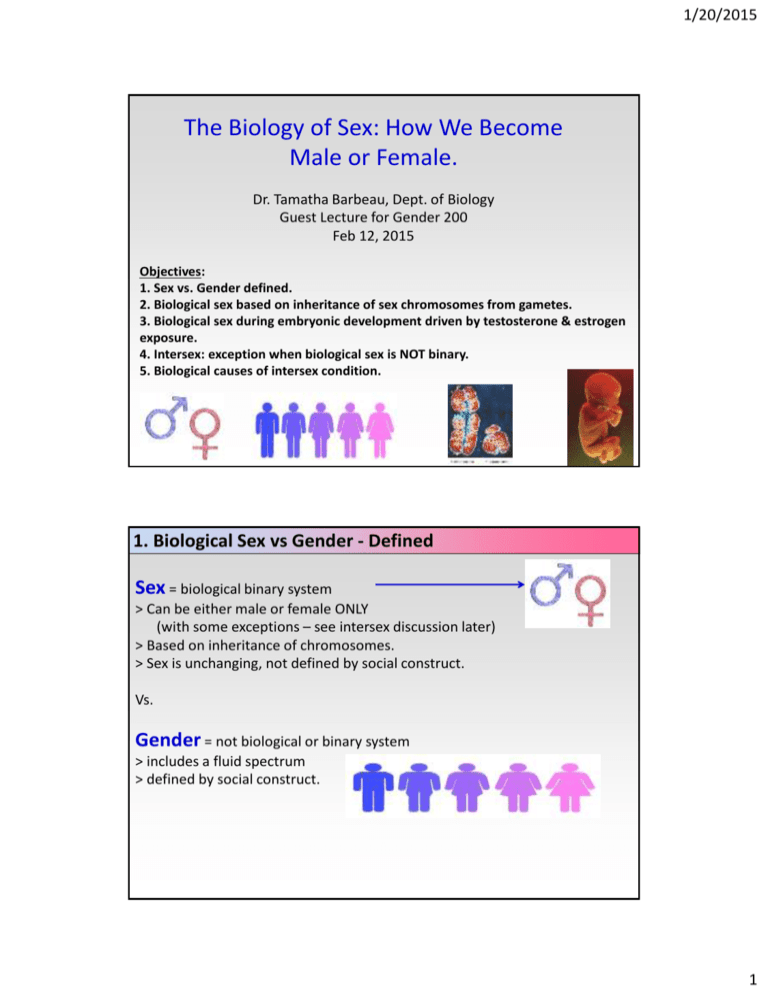
1/20/2015 The Biology of Sex: How We Become Male or Female. Dr. Tamatha Barbeau, Dept. of Biology Guest Lecture for Gender 200 Feb 12, 2015 Objectives: 1. Sex vs. Gender defined. 2. Biological sex based on inheritance of sex chromosomes from gametes. 3. Biological sex during embryonic development driven by testosterone & estrogen exposure. 4. Intersex: exception when biological sex is NOT binary. 5. Biological causes of intersex condition. 1. Biological Sex vs Gender - Defined Sex = biological binary system > Can be either male or female ONLY (with some exceptions – see intersex discussion later) > Based on inheritance of chromosomes. > Sex is unchanging, not defined by social construct. Vs. Gender = not biological or binary system > includes a fluid spectrum > defined by social construct. 1 1/20/2015 2. Biological Sex - based on inheritance of sex chromosomes from gametes. Gametes = sex cells (eggs or sperm) > have only 1 set of chromosomes > 23 chromosomes - represented as 1n: - 22 autosomes (code for all traits except sex) - 1 sex chromosome (code for sex) Egg 22 autosomes 1 sex chromosome (X) Sperm 22 autosomes 1 sex chromosome (X OR Y) 2. Biological Sex - based on inheritance of sex chromosomes from gametes. Sexual Reproduction > Involves production of gametes at sexual maturity. > Union of gametes with sex produces a zygote (fertilized egg). Mother (XX) Father (XY) 2 1/20/2015 3. Biological Sex – embryonic development. We start out w/ same non-specific gender. (genital tubercle, urethral folds, labial fold) 1. If have Y chromosome have following genes: SRY gene = sex determining region of Y. TDF gene = testis-determining factor. > Both genes start testes formation. >Testes produce testosterone (T), which turns - Wolffian duct becomes vas deferens, epididymis, & male glands - Labial folds → fused penis shaft & scrotal sac - Genital tubercle → penis - Urethral fold opens at head of penis 2. Absence of Y-genes = female genitalia > Ovaries develop > No testosterone, but Estrogen (E), which turns - Mullerian duct becomes uterus & fallopian tubes - Labial folds → labia major & minor - Genital tubercle → clitoris - Urethral fold → vaginal & urethral orifice Exposure to T or E affects all subsequent sexual development! The difference between male and female comes down to 1 double bond, found in T!!! 3 1/20/2015 Review • Biological sex vs gender defined. • Biological sex based on inheritance of sex chromosomes from gametes. > gametes = eggs or sperm > gametes produced during sexual maturity. > union of gametes produces a zygote • Biological sex – embryonic development > we all start from undifferentiated gonads > SRY & TDF genes on Y chromosome produce testes, which make T. > No Y chromosome - develop ovaries, which make estrogen. > influence of testosterone or estrogen controls development. 7 Natural cases of Intersex Animals Banana slugs, snails, earthworms = simultaneous hermaphrodites - Groupers & Clown fish (sequential hermaphrodites) 4 1/20/2015 Unusual cases of Intersex Animals 4. Intersex: exception when biological sex is NOT binary. Intersex = variety of conditions in which an organism is born with sexual anatomy that doesn’t clearly fit definition of male or female. 5 1/20/2015 4. Intersex: exception when biological sex is NOT binary. > Approx. 1% (1 out of 100) of humans born intersex. 4. Intersex: exception when biological sex is NOT binary. Signs of human intersex: “Hypospadia” = male urethral opening anywhere except at head of penis. Micropenis Hypospadia “Micropenis” = smaller than normal penis. OR “Clitoromegaly = larger than normal clitoris. Clitoromegaly & hypospadia 6 1/20/2015 5. Biological Causes of Human Intersex Condition: 1. Nondisjunction of sex chromosomes (during meiosis) – Meiosis problem. 2. Kallman syndrome (hypogonadism) – Brain problem. 3. Androgen-insensitivity syndrome (AIS) – Tissue problem. 4. Congenital adrenal hyperplasia (CAH) – Adrenal gland problem. 5. 5-alpha reductase deficiency – Enzyme problem. 6. Exposure to endocrine disruptors – Environmental problem. 1) Nondisjunction of sex chromosomes in meiosis. = failure of sex chromosomes to separate during egg & sperm production. > May affect as many as 25% of all ova and 2% of all sperm! (http://www.uic.edu/classes/bms/bms655/lesson9.html > Egg or sperm has extra or too few sex chromosomes. > Ex.: I. Klinefelter syndrome = XXY male (extra X chromosome) Have testes & male appearance with some degree of “feminized” features 1 out of 1000 births May/may not also have: Gynocomastia = female breast development Hip development - due to estrogen changing fat deposition. Poor muscle development II. Turner syndrome = XO female (missing a sex chromosome) Female appearance May/may not also have: Short, wide neck Might have fertility problems 7 1/20/2015 1) Nondisjunction of sex chromosomes in meiosis (Klinefelter & Turner Syndromes) Egg development in meiosis Sperm development in meiosis Klinefelter XXY male Turner Syndrome (XO) 2) Kallmann Syndrome (“hypogonadism”) = failure of brain (hypothalamus) to stimulate gonads. > 1 out of 4,000 births > No GnRH from hypothalamus. > Then no pituitary LH & FSH (hormones that stimulate gonads). > Without LH & FSH – testes don’t make T, ovaries don’t make E. > Male (XY) baby born intersex. > Both males and females with Kallman syndrome require hormone replacement therapy and fertility treatments. 8 1/20/2015 3) Androgen Insensitivity Syndrome (AIS) Complete AIS = Genetic (XY) male with normal testes and testosterone, but tissues don’t respond to testosterone. > 1 out of 13,000 births > Born either partial AIS or complete AIS. External genitals feminized to variable extent: - Micropenis - Clitoromegaly - Hypospadia - Unfused scrotal skin or actual labia. - No internal female organs > At puberty un-used T converted to E, get breasts & hips Partial AIS – partial fusion of scrotal skin, micropenis or enlarged clitoris 4) Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia (CAH) = fetal adrenal gland tumor causes excess adrenal gland growth & T production. > 1 out of 13,000 births > In genetic (XY) male – not problem. > In genetic (XX) female – causes intersex External genitals feminized to variable extent: - Micropenis Enlarged “phallic” clitoris, fusion of labial - Clitoromegaly folds, urethral opening towards clitoris - Hypospadia - Unfused scrotal skin or actual labia. > No internal male organs > Masculinized brain 9 1/20/2015 5) 5- reductase deficiency = Genetic (XY) male has lacks enzyme to convert T into DHT. > DHT needed for normal penis development External genitals feminized : - Micropenis - Clitoromegaly - Hypospadia - Unfused scrotal skin or actual labia > has internal testes > has masculinized brain 6) Exposure to Endocrine-Disrupting Contaminants (EDCs) > EDCs = man-made chemicals that mimic body’s own hormones or interfere with their functions. > Most known EDCs are estrogenic (act like estrogens on body). > Very small doses cause big developmental problems to developing fetus. Lots of EDCs! - Bisphenol A (BPA) - Phthalates - Pesticides (DDT) - Atrazine - many, many more … 10 1/20/2015 A) Bisphenol-A (BPA) = chemical used in making plastics. > Found in soda bottles, plastic utensils, Tupperware. > Estrogenic by activating estrogen receptors on tissue. Effects in lab animal in-utero (during development) : - Alters development of genitals (intersex) - Reverses sex differentiation of brain - Damages eggs (chromosomes) Effects in adult lab animals: - Decreases maternal behavior - Predisposes breast cells to cancer - Predisposes prostate cells to cancer A) Bisphenol-A (BPA) = chemical used in making plastics. 11 1/20/2015 B) Phthalates > Phthalates used to make soaps, makeup, plastics (other everyday items) can disrupt the development of male baby reproductive organs in utero. > ~95% of Americans have detectable phthalates in urine. > Shown to be estrogenic (feminizes male fetuses in utero = intersex). > Women with high urine phthalate metabolites more likely to give birth to baby boys with undescended testicles, or small testicles, and small penises (____________________). > Young girls with early breasts (thelarche) & puberty. 23 month old Puerto Rican with premature breasts (thelarche) B) Phthalates Short List of Products Containing Phthalates: Baby toys (plastic) Backpacks Beach balls Bubble bath Cleaning agents Coatings for tablets Computers Deodorant Disinfectant DVD players Electrical cables Garden hoses Hair gels and mousse Hairspray Ink Insect repellent IV fluid bags Lipstick Mobile phones Moisturizers Nail polish Paint Perfume Plastic raincoats Portable music players PVC flooring Shampoo Shaving foam Shower curtains Soap Sunscreens Toothbrushes Trainers Japan, Austria, Greece, Norway, Vinyl blinds Sweden, Finland, Germany have Wallpaper (PVC) banned PVC toys w/phthalates for Washing-up liquid children < 3yrs. Wellington boots Not banned in USA. 12 1/20/2015 Review 6 ways sexual development can lead to intersex condition: 1. Problem in meiosis – Non-disjunction of sex chromosomes in eggs or sperm can produce Klinefelter & Turner Syndromes 2. Hypothalamic (brain) problem – Kallmann Syndrome 3. Problem with tissue testosterone receptors – AIS 4. Problem with adrenal glands – CAH 5. Enzyme problem – 5- reductase deficiency 6. Exposure to endocrine-disrupting contaminants (EDCs) 26 13