Race & ethnicity - Hackettstown School District
advertisement

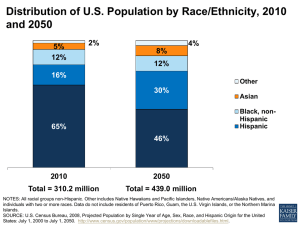
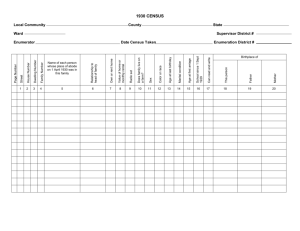
RACE & ETHNICITY Contemporary Social Issues Rachael Gorski 2016 INTRODUCTION ACTIVITY ■ What races are there in the United States? ■ Make a list! ■ When done, write your list on the board US Census Over Time ■ Census has accounted for race since its inception in 1790 ■ Categories of race (and other markers) reflect social conceptions of the time ■ 1790 Options: – Free white males – Free white females – All other free persons – Slaves ■ 2010 Options: – White – Black, African American, or Negro – American Indian or Alaska Native – Chinese – Japanese – Filipino – Korean – Asian Indian – Vietnamese – Other Asian – Native Hawaiian – Samoan – Guamanian or Chamorro – Other Pacific Islander – Mexican, Mexican American, Chicano – Puerto Rican – Cuban – Another Hispanic, Latino, Spanish Origin – *Hispanic is not a race, but is an ethnicity in a separate question – Some other Race 1790-1810 Census ■ Free White Males ■ Free White Females ■ All Other Free Persons 1850 Census ■ White ■ Slaves ■ Black ■ Mulatto 1820-1840 Census ■ Free White Males ■ Free White Females ■ Free Colored Males ■ Free Colored Females ■ Slaves ■ Black Slaves ■ Mulatto Slaves 1860 Census ■ White ■ Black ■ Mulatto ■ Black Slaves ■ Slaves accounted for on “Non-Population Schedules” that also recorded acreage, bushels ■ Mulatto Slaves of wheat & applies, # cows and swine, etc. ■ Indian 1870 Census ■ COLOR ■ Mulatto ■ White ■ Chinese ■ Black ■ Indian 1880 Census ■ Same 5 racial categories, but changed position to the FIRST indicator 1900 Census ■ Color or Race: White, Black (Negro or Negro Descent), Indian, Chinese, Japanese ■ Also asks how many children you had & how many alive + your place of birth & parents’ places of birth 1910 Census ■ Color or Race: White, Black, Mulatto, Indian, Chinese, Japanese, Other ■ Sex moves to first indicator; race to second ■ Now asks for native language in addition to places of birth 1920 Census ■ Color or Race: White, Black, Mulatto, Other, Indian, Chinese, Japanese ■ NEW – Filipino, Korean, Hindu 1930 Census ■ Color or Race: White, Negro, Other, Indian, Chinese, Japanese, Filipino, Korean, Hindu ■ NEW: Mexican ■ Deleted: Mulatto 1940 Census ■ COLOR OR RACE: – White – Negro – Indian – Chinese – Filipino – Hindu – Korean – Other, spell out in full ■ Also requests place of birth & parents’ places of birth Sorting People Activity ■ Need 2 brave volunteers ■ http://www.pbs.org/race/002_SortingPeople/002_01-sort.htm RACE V. ETHNICITY DEFINING RACE ■ Socially-constructed categories of people, usually based on color or physical features – Vary depending on time & place ■ Merriam-Webster Dictionary – A breeding stock of animals – A family, tribe, people, or nation belonging to the same stock – A category of humankind that shares certain distinctive physical traits U.S. RACES – 2010 CENSUS ■ White ■ Guamanian or Chamorro ■ Black, African American, or Negro ■ Other Pacific Islander ■ American Indian or Alaska Native ■ Chinese ■ Japanese ■ Filipino ■ Korean ■ Mexican, Mexican American, Chicano ■ Puerto Rican ■ Cuban ■ Another Hispanic, Latino, Spanish Origin ■ Asian Indian ■ *Hispanic is not a race, but is an ethnicity in a separate question ■ Vietnamese ■ Some other Race ■ Other Asian ■ Two or More Races ■ Native Hawaiian ■ Samoan PAST CLASSIFICATIONS ■ Caucasoid ■ Mongoloid ■ Negroid ■ Believed there were different types of humans ■ Terms are outdated & offensive today WHY DO WE HAVE RACE? ■ Some believe it’s based in biology – Helps organize & classify different people – Justifies differential treatment, racism, & discrimination – Results in differential intelligence, sexual behavior, birth rates, infant care, ethics, lifespan, law-abidingness, aggression, family cohesion, brain size…. – EMBEDDED IN OUR CULTURE ■ It’s NOT based in biology – 1950 – UNESCO reported all humans belong to the same species & race is not a biological reality, but a myth! – NO inherent relationship between “race” and intelligence, economic practices, lawabidingness – Also NO relationship between “race” and nose size, height, blood group, skin color, etc.! – Not genetically identified – “races” inbreeding for hundreds of thousands of years ■ Socialized to believe in race – Impacts where you live, go to school, profession, who you interact with, your treatment, healthcare, justice system …. – Policies keep leaders & followers in control (Examples: Spanish Inquisition, Holocaust, Segregation) RACE IS AN ILLUSION… ■ Modern Idea – ancients did not divide people according to physical differences, but according to religion, class, or language ■ No genetic basis – no one trait or gene distinguishes all members of one ‘race’ from another ■ Slavery predates race – enslaved people not because of physical characteristic, but conquest of war ■ “Race” helped justify slavery & social inequalities – explained why some people could be denied rights & freedoms ■ Human “sub-species” don’t exist – unlike in animals ■ Skin color is only skin deep – traits inherited independently from one another; genes for skin color are unrelated to hair texture, eye shape, blood type, athletic ability… ■ Most genetic variation is within, not between “races” – 85% of genetic variation exists within local population; two random Koreans are as genetically different as a Korean and an Italian ■ RACISM IS REAL – different races have different opportunities and resources; there ARE advantages to being white ■ Colorblindness will NOT end racism – pretending race doesn’t exist is NOT the same as creating equality – Race is more than stereotypes & individual prejudice – Need to identify & remedy social policies that give advantages to some groups over others …BUT IT DOES HAVE MAJOR EFFECTS ■ **We’ll go into more detail with these ideas later in the unit** – students Quality of schools by neighborhood ■ Different jobs available ■ Institutional Racism – “Black-sounding” name on resume makes – Racial profiling a difference – Higher incarceration rates ■ Poverty Rate – Lower quality of health services – American Indian 27%; Black 26%; ■ Increased Adolescent Risk Behaviors Hispanic 23%; white 11% – Blacks more likely to have sex ■ Earning Potential: Median Income – Black & Hispanic more likely to engage in – Asian $68,636 violence – White $57,009 – But, whites more likely to smoke & drink – ALL %51,017 ■ White privilege – Hispanic $39,005 – Unintentional “perks” for white people – Black $33,321 – Range from “nude” color clothing ■ Educational Attainment matching skin tone to not being harassed by store security officers – SAT questions benefit affluent (white) ETHNICITY ■ Group of people with common culture or heritage ■ Based on – National origin – Religion – Language – Customs – Values ■ Self-identified – Are you an American or are you Polish? – Are you Hispanic or are you Mexican? – Are you Israeli or are you Jewish? ■ Can be same ethnicity, but different race REMEMBER: Ethnicity is associated with culture, whereas race is associated with, but not proven by, biology. DISCUSSION ■How does race impact your life? ■What race and ethnicity do you identify as? ■How does ethnicity impact your life? EVOLUTION OF RACE In the United States Before 1787 ■ 1300 – Origin of the word slave ■ 1680 – “White” appears in colonial laws ■ 1705 – Virginia slave codes passed ■ 1765 – Slaves lobby for freedom in American Revolution ■ 1776 – Birth of “Caucasian” ■ 1781 – Jefferson suggests black inferiority 1790-1854 ■ 1790 – Racial categories appear on first US Census ■ 1790 – Naturalization reserved for whites ■ 1825 – “Blood Degree” measures who is Indian ■ 1833 – Abolition strengthens idea of race ■ 1839 – Skulls measured to prove racial hierarchy ■ 1854 – Nonwhites barred from testifying at trials ■ 1854 – Frederick Douglass challenges race scientists 1857-1904 ■ 1857 – African Americans denied citizenship in Plessy v. Ferguson ■ 1859 – Evolution shapes race debate ■ 1868 – 14th Amendment guarantees equal rights (by race) ■ 1883 – Birth of eugenics ■ 1887 – Jim Crow segregation begins ■ 1898 – Birthright citizenship begins ■ 1899 – “The White Man’s Burden” published ■ 1899 – Europeans ‘note quite white’ (southern & eastern Europeans discriminated against in employment) ■ 1904 – Race on parade – displays at fair in St. Louis 1905-1935 ■ 1905 – African Americans demand equal rights (WEB Du Bois Niagara Movement) ■ 1911 – Universal Race Congress held at U. London (WEB Du Bois & Franz Boas attend) ■ 1913 – Land laws discriminate against Asians ■ 1922 – Courts decide who is white for naturalization purposes ■ 1924 – Changing definitions of who is black (“One Drop” Rule) ■ 1924 – Immigration quotas favor ‘Nordics’ ■ 1930 – Mexican added to Census categories ■ 1934 – Indians base membership on blood degree ■ 1935 – Minorities denied Social Security & excluded from unions 1950 - 2000 ■ 1950 – UNESCO statement denies biological concept of race ■ 1954 – Legal segregation ends with Brown vs. Board ■ 1967 – Laws against interracial marriage invalidated (antimiscegenation laws) in Loving vs. Virginia ■ 1977 – Government defines race/ethnic categories, meaning to aid agencies, but are arbitrary, inconsistent, & based on assumptions ■ 1985 – Minorities lead nationwide union campaign ■ 1994 – Black-white wealth gap studied ■ 2000 – Census allows for more than one race MAJORITY-MINORITY RELATIONS MINORITY GROUP ■ People singled out for unequal treatment ■ Regard themselves as objects of collective discrimination ■ Often numerically a minority – US Examples from 2010 Census & 2014 Estimates: – Hispanic or Latino 17.4% – African Americans 13.2% – Asian Americans 5.4% – Native Americans 1.2% – Muslims (in America) ■ Sometimes NOT statistically a minority, but lack political resources for power – US Example: women – Historical Example: blacks in South Africa during apartheid CHARACTERISTICS OF MINORITY GROUPS ■ Physically or culturally distinct from dominant group ■ Victims of unequal treatment ■ Share strong bond / loyalty to group ■ Tend to marry within the group DOMINANT GROUP ■ People who have power over the minority group – Economic Power – Political Power – Social Power – US Example: 77% population White ■ Not always a numerical majority – Example: white British in colonial India – Example: whites in apartheid South Africa NEGATIVE RELATIONS ■ Subjugation – maintain control over a group through force – Spanish conquistadors in the New World – Saddam Hussein’s oppression of Kurds through violence & intimidation ■ Ethnic Cleansing – forced removal and/or slaughter of a minority group – Trail of Tears of the Cherokee Nation, 1838-1839 – Armenian “Genocide” – Ottoman Empire, 1915-1923 – Srebrenica, 1995 – *Videos at end of class ■ Genocide – systematic extermination of a minority group with intent of destroying the entire population – The Holocaust, 1936-1945 – Rwanda Genocide, 1994 SEGREGATION ■ Separation of minority and majority groups ■ De Jure Segregation – based on or caused by laws – “Separate but equal” facilities in the United States – Apartheid ■ De Facto Segregation – separation results from informal norms – Mostly black neighborhoods / mostly white neighborhoods – Lunch tables – Dating LEGAL PROTECTIONS FOR MINORITIES ■ Basic function of government is to protect minority rights when dominant groups attempt to infringe upon them ■ US Examples: – Brown vs. Board ruling, 1954 – Civil Rights Act, 1964 – Voting Rights Act, 1965 – Affirmative Action policies – Obergefell vs. Hodges ruling, 2015 WHEN GROUPS MEET ■ Assimilation – blending of culturally distinct groups into a single group with common culture & identity – “Melting Pot” – Can be voluntary ■ Choosing to ‘Americanize” your name; learn English – Can be forced ■ ■ Required to learn language for citizenship 1910-1970 Australia removed aboriginal children from their homes & had them raised by whites ■ Multiculturalism – encouragement of ethnic variation or diversity by the dominant group – “Salad Bowl” – “Pluralism” – Respect each group AN AMERICAN DILEMMA ■ 1944 – Sociologist Gunnar Myrdal commissioned to study race relations ■ Concluded there is a gap between what people believe and how they behave >> “an American dilemma” ■ Believe – freedom, equality, inalienable rights, dignity … ■ Behavior– segregation of blacks, Native Americans, Japanese internment camps … ■ Discuss – do you think this dilemma still exists today? What values do people claim to believe in? Does their behavior contradict their beliefs? ETHNIC CLEANSING VIDEOS ■ Ethnic Cleansing in Bosnia [7 min] https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=VbNocQORWQ8 ■ Ethnic Cleansing in the Central African Republic [3:25 min] https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=sG8Fsu9e8oI ■ Iraq: Ethnic Cleansing [3:22 min] https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=v3nTz1Bc6X0 PREJUDICE & DISCRIMINATION Different branches of the same hate tree INTRODUCTION ACTIVITY ■ List stereotypes of the minority group your row is assigned ■ List ways in which the group has been treated differently (past or present) ■ African Americans ■ Hispanics ■ Asian Americans ■ Native Americans ■ Women ■ Disabled ■ LGBT RACISM ■ Belief one’s own race or ethnic group is superior to other races ■ Can be subtle ■ Can be direct ■ Doesn’t have to be overt discrimination ■ Manifests in two forms: prejudice & discrimination PREJUDICE ■ Attitudes towards members of a group ■ Judgment applied to whole group based on single perception/stereotype STEREOTYPES ■ Oversimplified, exaggerated, or unfavorable generalizations about groups of people ■ Often had some truthful origin – Example “stupid Poles” arose because Polish immigrants were uneducated ■ Can lead to self-fulfilling prophecy – prediction that results in behavior that makes the behavior come true – Example: if group is seen as lazy, they will not get hired for high-end work. Because they did not earn high-end work, they will end up in lower end jobs & often find themselves on the streets in between jobs DISCRIMINATION ■ Unfair treatment directed against someone ■ Based on: – Height – Weight – Age – Income – Race – Ethnicity – Marital status – Sexual orientation – Religion – Disability – Politics ■ You CAN discriminate without being prejudiced & be prejudiced WITHOUT discriminating! TYPES OF DISCRIMINATION ■ Individual Discrimination – by individuals or small groups against individuals or small groups – Burning a cross – Not renting apartment to minority – Spray-painting swastikas ■ Institutional Discrimination – woven into fabric of society or organizations – Policies designed to the advantage of dominant group – Plessy v. Ferguson >> separate but equal – Virginia Military Institute didn’t admit women until 1996 – Rodney King beaten by police in 1992 >> all white jury acquitted the police MERTON’S TYPOLOGY OF PREJUDICE & DISCRIMINATION ■ It is possible to discriminate without being prejudiced and vice versa! Prejudiced? Yes Prejudiced? No Discrimination? Yes Active Bigot [KKK] Discrimination? No Timid Bigot don’t want to look bad with discriminatory behavior [Shop owner who doesn’t discriminate because it would hurt business] Fair-Weather Liberal Discriminates based on convenience [Shop owner doesn’t hire blacks to help business interests] All-Weather Liberal Sees all groups as equals in theory & practice Very educated, non-traditional, open-minded individuals PREJUDICE & DISCRIMINATION ACTIVITY ■ Write a short story displaying each of the 4 typologies theorized by Merton: – Active Bigot – Fair-Weather Liberal – Timid Bigot – All-Weather Liberal ■ Activity #2 – What Would You Do? Videos & Discussion – Latino Hate Crime [8 min] https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ru1F29vuVKI – Racial Profiling in Store [9 min] https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=vpUAlmW72QM – Bashed for Adopting Black Children [11 min] https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=J47tcBcU3Rs RACE RELATIONS IN U.S. Black – White Differences of Opinion RACE RELATIONS IN USA – DECLINING? ■ Only 34% of Americans said race relations are ‘fairly good’ or ‘very good’ – a 20 year low ■ 2 Black Billionaires – Oprah & Michael Jordan – ~500 white billionaires ■ 9.8% over-25 have a degree – 14.4% whites have bachelor’s degree ■ 75% white Americans have only white friends – 65% of black Americans have only black friends ■ 10.9% black unemployment rate – 4.8% white Americans; overall average 5.8% ■ 37% male prison inmates are black – Only 13% of population >> inmates are disproportionately black – 32% white – 22% Hispanic ■ 65% African Americans think “Black Lives Matter” focuses on racial discrimination – 25% of whites ■ 59% of whites think it distracts from real issues – 26% African Americans Video Clip ■ CNN: Race Relations in the United States [8 min] https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_BOlc7r_3ao BLACK LIVES MATTER BACKGROUND INFORMATION ■ Black Lives Matter = national organization working for the validity of Black life – Rebuild the Black liberation movement – Broadening the conversation around state violence – Also affirms lives of Black queer & trans folks, undocumented folks, folks with police records, women, etc. – Goes beyond extrajudicial killing of black people: ■ ■ ■ ■ 2.8M black people imprisoned = state violence Assault on black women and families Black LGBT individuals bear a “unique burden” from a hetero-patriarchal society 500,000 are undocumented immigrants ■ Began in 2012 with murder of Trayvon Martin – George Zimmerman was acquitted of the murder of 17-year-old Trayvon, an unarmed black teenager, in Florida ■ Impetus seen more after Ferguson, MO in August 2014 – Protests after police killed Michael Brown ■ Builds momentum with each instance of police brutality and deaths of black people in custody – Protests & Rallies – Social Media Campaigns INTRO VIDEO CLIP ■ Bill O’Reilly Takes on Two Black Lives Matter Activists [10 min] https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=E5HsBVmGKB8 TWO VIEWS ■ Bringing attention & empowerment to the Black community, and for all people – Saying “All Lives Matter” loses effect; no longer focused on the programs of repression against Blacks – African Americans DO suffer from police brutality – They ARE disproportionately incarcerated for crimes that whites usually do not see jail time for – African Americans, especially single mothers, ARE more likely to be in poverty – These social inequalities & systemic racism SHOULD be addressed ■ “All Lives Matter” – Feel that the movement asserts Black superiority & preference over lives of whites and other minorities – Some protestors are radical – “What do we want? Dead Cops!” – Also criticize Black Lives Matter for lack of consistent, clear, cohesive goals & organization ARTICLES & DISCUSSION ■ Read the articles: – TIME Person of the Year Runner Up – The Myth of Black Lives Matter – All Lives Matter Is and Always Was Racist – “Using White Privilege for Positive Change” ■ Discuss them with your peers