Race and Ethnicity
advertisement

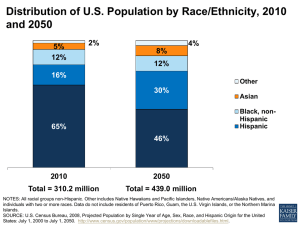
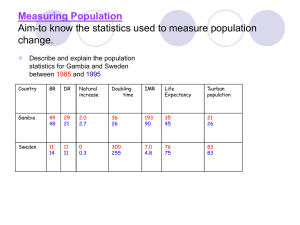
Race and Ethnicity What is Race? • The inherited physical characteristics that distinguish one group from another. • This is a reality, humans are different • Sociologists, think of race more as a social construct, determined by cultural factors rather than skin color. What are ethnic groups? • People who identify with one another on the basis of common ancestry and cultural heritage. – Having distinctive cultural characteristics •Language •Beliefs •Values •Traditions •Religion • Ethnic group of Thailand Race: Reality and Myth • Reality: Humans have physical distinctions • Myth: fabrications of the human mind. 1. Idea that any race is superior to another. – Hitler, Rwanda Genocide, and Imperialists 2. Idea that any race is “Pure” • Social Reality: People act on beliefs, not facts (act on stereotypes) History of Race in America Firm “color line’ existed between racial-ethnic groups (marriage and dating) The U.S. census classified people by their race Restrictive: Caucasian, Negro, Indian, and Oriental • Clip 3: Race an "idea constructed by society to further certain political economic goals," • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4UZS8Wb4S 5k&feature=related 2000 census was changed to include several races: (multiracial) (7 million Americans classified as multiracial 9 million 2012) http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=GLnO1-sRow 2010 Census • http://2010.census.gov/2010census/about/inte ractive-form.php • http://2010.census.gov/2010census/data/ • http://www.thesociologicalcinema.com/1/post /2012/03/being-garifuna-how-do-we-measurerace.html US Census • “Definition of Race Categories Used in the 2010 Census.” Starting in 1997, OMB required federal agencies to use a minimum of five race categories: White, Black or African American, American Indian or Alaska Native, Asian, and Native Hawaiian or Other Pacific Islander. For respondents unable to identify with any of these five race categories, OMB approved the Census Bureau’s inclusion of a sixth category—Some Other Race—on the Census 2000 and 2010 Census questionnaires. • “Definition of Hispanic or Latino Origin Used in the 2010 Census.” OMB requires federal agencies to use a minimum of two ethnicities: Hispanic or Latino and Not Hispanic or Latino. Hispanic origin can be viewed as the heritage, nationality group, lineage, or country of birth of the person or the person’s parents or ancestors before their arrival in the United States. People who identify their origin as Hispanic, Latino, or Spanish may be any race. Discussion Questions: Everyother • How do the women in the film feel in regards to the census? • After viewing the 2010 census how do you feel? • Do you believe, you can be more than one race? • Should the way you personally identify yourself be a political issue? • How is the meaning of race changing in the U.S? • Do you have the same racial attitudes as their parents/grandparents? • How do you imagine your own kids might view the concept of race? • Do you see any trends developing in racial attitudes? Minority and Dominant Groups • Minority Groups: people who are singled out for unequal treatment and who regard themselves as objects of collective discrimination. – Minority Group Can Be Racial or Ethnic – Not necessarily the numerical minority • Dominant Groups: those who do the discriminating….for they have the greater power, privileges, and social class. Shared Characteristics of Minorities • Membership into minority group at birth • The physical and cultural traits are looked down on by dominant group • Treated unequally by dominant group • Tend to marry within their own group • Have strong group solidarity Racial–Ethnic Identity • Some people are more aware of their race or ethnicity. • Some Americans are not aware of their ethnicity because of assimilation into mainstream America – Some may say “I am Heinz 57 – German and Irish, with a little Italian and French thrown in…and I think someone once said that I was 1/16 Amerian Indian, too.” Awareness of Ethnicity • Why do some people feel an intense sense of ethnic identity, while others feel hardly any? • Low Sense of ethnicity – Those who are part of dominant group in America are less aware of ethnicity – Tend to be the group with the greatest power – Are not subject to discrimination – Have a sense of “belonging” • Heightened Sense – – – – – Minorities are very aware of their ethnicity Have less power Different from the national identity Discriminated against Have a sense of not belonging Figure 12.1 A Sense of Ethnicity Source: By the author. Based on Doane 1997. Melting Pot Idea vs. Tossed Salad • Assimilation: blending or fusing of minority groups into the dominant society. – Members given full participation into society. – Either you conform or are suppressed. • Melting Pot the view that Americans of various backgrounds would blend into a sort of ethnic stew. • Tossed Salad the view visualizes American culture as being a bowl full of lots of different kinds of things, each contributing its own flavor and identity to the whole. – cultures and traditions exist side by side