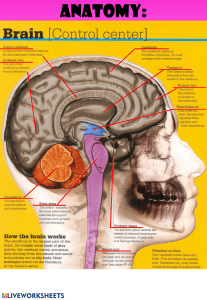
The human brain is one of the most complex and fascinating organs in the body. It is the command center of the central nervous system and plays a crucial role in controlling our thoughts, movements, and emotions. The brain has three main parts: the cerebrum, the cerebellum, and the brainstem. The cerebrum is the largest part of the brain and is responsible for processing information from our senses, controlling voluntary movements, and supporting language, learning, and memory. The cerebellum is located at the base of the brain and is primarily responsible for coordinating movement, balance, and posture. The brainstem connects the brain to the spinal cord and regulates vital functions such as breathing, heart rate, and blood pressure. The brain consists of billions of neurons that communicate with each other through electrical and chemical signals. These neurons are interconnected through a network of synapses, forming complex circuits that enable us to process and store information. The brain is also capable of plasticity, which allows it to adapt to changing environments and experiences. This plasticity is particularly important during childhood, as the brain undergoes significant development and growth. However, the human brain is not without its vulnerabilities. Neurological disorders such as Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, and schizophrenia can have a profound impact on brain function and behavior. Traumatic brain injury and stroke can also cause lasting damage to the brain and impair cognitive and motor function. In conclusion, the human brain is a remarkable organ that plays a critical role in our daily lives. Despite its incredible complexity and resilience, the brain is not invincible, and we must take care to protect it from injury and disease. Through ongoing research and study, we continue to deepen our understanding of the brain and uncover new ways to promote brain health and well-being.