1 Macromolecules AP Biology 2015
advertisement
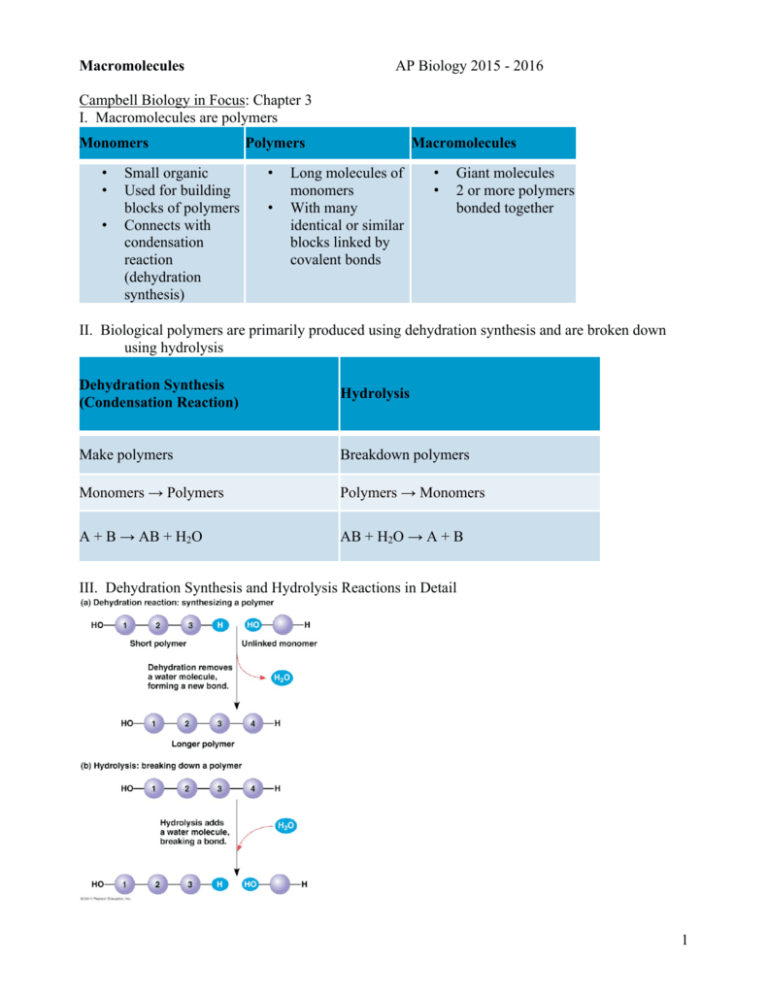
Macromolecules AP Biology 2015 - 2016 Campbell Biology in Focus: Chapter 3 I. Macromolecules are polymers Monomers • • • Small organic Used for building blocks of polymers Connects with condensation reaction (dehydration synthesis) Polymers • • Macromolecules Long molecules of monomers With many identical or similar blocks linked by covalent bonds • • Giant molecules 2 or more polymers bonded together II. Biological polymers are primarily produced using dehydration synthesis and are broken down using hydrolysis Dehydration Synthesis (Condensation Reaction) Hydrolysis Make polymers Breakdown polymers Monomers → Polymers Polymers → Monomers A + B → AB + H2O AB + H2O → A + B III. Dehydration Synthesis and Hydrolysis Reactions in Detail 1 IV. Proteins A. 50% dry weight of cells B. Contains: C, H, O, N, S C. Functions: i. Enzymes (lactase) ii. Defense (antibodies) iii. Storage (milk protein = casein) iv. Transport (hemoglobin) v. Hormones (insulin) vi. Receptors vii. Movement (motor proteins) viii. Structure (keratin) 2 D. Levels of Protein Structure i. Primary a. Amino acid (AA) sequence b. 20 different AA’s c. peptide bonds link AA’s d. Amino acid structure 1. R group = side chains Properties: hydrophobic, hydrophilic, ionic (acids & bases), large, small 2. “amino” : -NH2 3. “acid” : -COOH 3 e. formation of peptide bonds 4 ii. Secondary: 3D structures formed by hydrogen bonding a. Gains 3-D shape (folds, coils) by H-bonding b. Alpha (α) helix, Beta (β) pleated sheet iii. Tertiary a. Bonding between side chains (R groups) of amino acids b. H bonds, ionic bonds, disulfide bridges, van der Waals interactions 5 iv. Quaternary: two or more polypeptides bond together v. Overview of the four levels of protein structure 6 E. Protein folding is very complex i. Chaperonins are proteins that assist in the folding of other proteins ii. Strong acids/bases, hydrophobic solvents and temperature changes can all change or denature a protein so that it is no functional. iii. A change in the shape of a protein may create a change in function 7 V. Nucleic acids A. Functions: 1. stores hereditary information 2. contains the instructions for making proteins 3. assists in creating proteins 4. indicates when certain proteins are created 5. allows only certain proteins to be created in specialized cells B. Differences between DNA and RNA DNA RNA • • • • • Double-stranded helix N-bases: A, G, C, Thymine Stores hereditary info Longer/larger Sugar: deoxyribose • • • Single-stranded N-bases: A, G, C, Uracil Carry info from DNA to ribosomes • tRNA, rRNA, mRNA, RNAi • Sugar: ribose C. Nucleotides - the monomers of nucleic acids Nucleotide = Sugar + Phosphate + Nitrogen Base 1. Phosphate 8 2. Sugar Purines 3. Nitrogenous base Pyrimidines • • Adenine Guanine • • • Cytosine Thymine (DNA) Uracil (RNA) • Double ring • Single ring 9 D. Information flow in a cell DNA → RNA → Proteins VI. Carbohydrates A. Fuel and building material B. Include simple sugars (fructose) and polymers (starch) C. Typical ratio of 1 carbon: 2 hydrogen: 1 oxygen or CH2O D. monosaccharide → disaccharide → polysaccharide E. monosaccharides = monomers (eg. glucose, ribose) and used for energy storage 10 Glucose structure F. Disaccharides (used for energy storage) 11 G. Polysaccharides: i. Functions: storage (plants-starch, animals-glycogen) and structure (plant-cellulose, arthropod-chitin) ii. Cellulose vs. Starch a. There are two forms of glucose: b. Starch uses α-glucose while cellulose uses β-glucose (just know that starch has all the glucose molecules in the same orientation, which makes it easy to digest while cellulose alternates orientation which makes it difficult to digest.) c. Glycogen (animal starch) and plant starches are slightly different 12 d. Cellulose is used as a structural polysaccharide in plants.... ....while chitin is used in fungal cell walls and in exoskeletons of arthropods 13 VII. Lipids A. Fats (triglyceride): store energy i. consist of glycerol and 3 fatty acids ii. fatty acids come in saturated, unsaturated, polyunsaturated forms Saturated “saturated” with H In animals Solid at room temp. Eg. butter, lard Unsaturated Polyunsaturated Have some C=C, result in kinks In plants Liquid at room temp. Eg. corn oil, olive oil 14 B. Steroids: cholesterol and hormones C. Phospholipids: lipid bilayer of cell membrane and consist of hydrophilic head, hydrophobic tails 15