Name: Date: ______ 1. The functional group present in carboxylic
advertisement

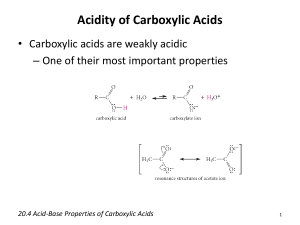
Name: __________________________ Date: _____________ 1. The functional group present in carboxylic acids is called a A) carbonyl group. B) carboxyl group. C) carboxylate group. D) carbohydroxyl group. 2. Which of the following statements concerning the structure of the functional group present in carboxylic acids is incorrect? A) Two oxygen atoms are present. B) A carbon-oxygen single bond and a carbon-oxygen double bond are present. C) A carbon-hydrogen bond is present. D) An oxygen-hydrogen bond is present. CH3 3. O The IUPAC name for the compound CH3 CH CH2 C A) 2-methyl-4-butanoic acid. B) 2-methyl-4-pentanoic acid. C) 3-methylbutanoic acid. D) 3-methylpentanoic acid. OH is 4. The common names for the C2 mono- and dicarboxylic acids are, respectively, A) formic acid and acetic acid. B) acetic acid and formic acid. C) oxalic acid and acetic acid. D) acetic acid and oxalic acid. 5. The common name for the C5 unbranched dicarboxylic acid is A) adipic acid B) glutaric acid C) pimelic acid D) succinic acid 6. Which of the following polyfunctional carboxylic acids is incorrectly characterized? A) tartaric acid, C4 dihydroxyacid B) malic acid, C4 hydroxyacid C) pyruvic acid, C3 ketoacid D) glyceric acid, C3 ketodiacid Page 1 7. Which of the following statements concerning the properties of carboxylic acids is incorrect? A) Short-chain monocarboxylic acids are liquids at room temperature. B) Carboxylic acids have higher boiling points than alcohols of similar molecular mass. C) Carboxylic acids cannot hydrogen bond to water. D) Carboxylic acids can hydrogen bond to each other. 8. Carboxylic acids may be prepared by oxidation of either A) ketones or aldehydes B) secondary or primary alcohols C) primary alcohols or aldehydes D) ketones or secondary alcohols 9. Which of the following statements concerning the acid strength of carboxylic acids is correct? A) all are weak acids B) their acid strength is equal that of strong mineral acid such as HCl C) aromatic acids are strong and nonaromatic acids are weak D) unbrached acids are strong 10. Which of the following statements concerning carboxylate ions is correct? A) they may be negatively or positively charged B) carboxylate ions formed from dicarboxylic acids carry a -2 charge C) they contain more carbon atoms than their parent acids D) they are always positively charged 11. Carboxylic acid salts may be converted to their "parent" carboxylic acids by reacting them with A) a strong base such as NaOH B) a strong acid such as HI C) an alcohol such as methanol D) a ketone such as acetone Page 2 12. Which of the following acids would produce a carboxylate ion with a minus two charge? A) B) C) D) 13. Which of the following is a general structural representation for an ester? A) B) C) D) 14. Esters are produced through the reaction of A) a ketone and an ether B) a carboxylic acid and an alcohol C) an aldehyde and a phenol D) a carboxylic acid and a ketone Page 3 O 15. The IUPAC name for the ester CH3 CH2 CH2 C O CH3 is A) butyl methanoate. B) methyl butanoate. C) methyl butyl ester. D) methyl carboxybutane. 16. The ester obtained by reacting benzyl alcohol and benzoic acid is called A) benzyl benzene B) benzyl benzoate C) phenyl benzoate D) benzyl benzate 17. When an ester is saponified, one reaction product is A) a base B) a carboxylic acid C) an aldehyde D) an alcohol 18. The monomers for the formation of a polyester are A) a dicarboxylic acid and a monoalcohol. B) a dicarboxylic acid and a dialcohol. C) two diesters. D) two monoesters. 19. Which of the following statements concerning acid anhydrides is incorrect? A) They undergo hydrolysis to produce the parent carboxylic acid. B) They are generally less reactive than the corresponding acid chloride. C) They have structures in which three oxygen atoms are present. D) They are produced by reacting two carboxylic acids with each other. Page 4 20. Which of the following is the general formula for a phosphate monoester? A) B) C) D) 21. Which of the following is a correct notation for the carboxylic acid functional group. A) B) C) D) more than one correct response E) no correct response 22. Which of the following carboxylic acids is paired with its correct IUPAC name? A) B) C) D) more than one correct response E) no correct response Page 5 23. In which of the following pairs of carboxylic acids are both members of the pair dicarboxylic acids? A) malonic acid and succinic acid B) glutaric acid and butyric acid C) oxalic acid and acetic acid D) more than one correct response E) no correct response 24. For which of the following biochemically important polyfunctional carboxylic acids is its accompanying characterization correct? A) fumaric acid; a keto acid B) pyruvic acid; an unsaturated acid C) lactic acid; a dihydroxy acid D) more than one correct response E) no correct response 25. Which of the following functional groups is always found at the end of a carbon chain? A) aldehyde B) carboxylic acid C) ketone D) more than one correct response E) no correct response 26. Which of the following statements concerning the boiling points of carboxylic acids is correct? A) They are higher than those of corresponding alcohols. B) They are lower than those of corresponding alkanes. C) They are lower than those of corresponding aldehydes. D) more than one correct response E) no correct response 27. Which of the following compounds could not be oxidized to a carboxylic acid? A) propanal B) 2-methyl-1-propanol C) 2-methyl-2-propanol D) more than one correct response E) no correct response Page 6 28. Which of the following carboxylic acids possesses two acidic hydrogen atoms? A) butanedioic acid B) 2-methylbutanoic acid C) succinic acid D) more than one correct response E) no correct response 29. In which of the following pairs of compounds does the first listed compound have a greater solubility in water than the second listed compound? A) hexanoic acid, methanoic acid B) sodium butanoate, butanoic acid C) pentanoic acid, potassium pentanoate D) more than one correct response E) no correct response 30. The general structural difference between a carboxylic acid and an ester is the same as that between an A) alcohol and an ether. B) aldehyde and a ketone. C) alkane and an alkene. D) more than one correct response E) no correct response 31. Which of the following esters is paired with an incorrect IUPAC name for it? A) B) C) D) more than one correct response E) no correct response Page 7 32. Which of the following pairings of ester common and IUPAC names is correct? A) ethyl propionate and propyl ethanoate B) propyl acetate and propyl ethanoate C) ethyl butyrate and butyl ethanoate D) more than one correct response E) no correct response 33. Which of the following compounds is a constitutional isomer of ethyl ethanoate? A) methyl methanoate B) ethyl propanoate C) butanoic acid D) more than one correct response E) no correct response 34. For which of the following types of carboxylic acid derivatives is the parent carboxylic acid(s) a product of the derivative's hydrolysis? A) acid anhydride B) acid chloride C) ester D) more than one correct response E) no correct response 35. Which of the following types of inorganic esters would contain two oxygen-carbon single bonds? A) diphosphate monoester B) phosphate triester C) diphosphate diester D) more than one correct response E) no correct response Use the following to answer questions 36-45: In each of the following multiple-choice questions, characterize EACH of the three given statements as being TRUE or FALSE and then indicate the collective true-false status of the statements using the choices a) All three statements are true. b) Two of the three statements are true. c) Only one of the statements is true. d) None of the statements is true. Page 8 36. Statements: (1) The compound ethanoic acid contains two carbon atoms and two oxygen atoms. (2) Unsubstituted short-chain monocarboxylic acids are completely miscible with water. (3) The two reactants in an esterification reaction are a carboxylic acid and an aldehyde. A) All three statements are true. B) Two of the three statements are true. C) Only one of the statements is true. D) None of the statements is true. 37. Statements: (1) The boiling points of esters are much higher than those of corresponding carboxylic acids. (2) The compound benzoic acid is a heterocylic compound. (3) In linear form, the ester functional group can be represented as -COOR. A) All three statements are true. B) Two of the three statements are true. C) Only one of the statements is true. D) None of the statements is true. 38. Statements: (1) The compound 4-oxobutanoic acid contains both a carboxyl group and a carbonyl group. (2) Aldehyde oxidation is a method for preparing a carboxylic acid. (3) Both IUPAC and common names for esters consist of two words. A) All three statements are true. B) Two of the three statements are true. C) Only one of the statements is true. D) None of the statements is true. 39. Statements: (1) A carboxylic acid and its corresponding carboxylate ion differ in the number of oxygen atoms they contain. (2) In ester hydrolysis, the carbon-oxygen double bond breaks producing an alcohol and a carboxylic acid. (3) The acronym PET stands for polyester(terephthalate). A) All three statements are true. B) Two of the three statements are true. C) Only one of the statements is true. D) None of the statements is true. Page 9 40. Statements: (1) Hydrogen bonding is not possible between carboxylic acid molecules. (2) The alpha-carbon atom in a carboxylic acid is the carbon atom to which the carboxyl group is attached. (3) Sodium butanoate and ethyl butanoate are both examples of esters. A) All three statements are true. B) Two of the three statements are true. C) Only one of the statements is true. D) None of the statements is true. 41. Statements: (1) Structurally, the difference between malonic acid and succinic acid is a -CH2- grouping. (2) A carboxylic acid salt is generally more soluble in water than the carboxylic acid from which it is obtained. (3) Ester hydrolysis and ester saponification are “reverse” reactions of each other. A) All three statements are true. B) Two of the three statements are true. C) Only one of the statements is true. D) None of the statements is true. 42. Statements: (1) “Pleasant odor” is a general characteristic of esters. (2) Citric acid is both a tricarboxylic acid and a ketoacid. (3) Esters and carboxylic acids with the same number of carbon atoms and the same degree of saturation are constitutional isomers. A) All three statements are true. B) Two of the three statements are true. C) Only one of the statements is true. D) None of the statements is true. 43. Statements: (1) Hydrolysis of a mixed acid anhydride produces two different carboxylic acids as products. (2) Short-chain unsubstituted monocarboxylic acids are strong acids while their longer-chain counterparts are weak acids. (3) The parent alcohol for the ester methyl acetate is methyl alcohol. A) All three statements are true. B) Two of the three statements are true. C) Only one of the statements is true. D) None of the statements is true. Page 10 44. Statements: (1) Pyruvic acid is the keto-derivative of propanoic acid. (2) Reaction of a carboxylic acid with a thiol produces a thioester, a compound containing two carbon-sulfur single bonds. (3) One of the products of an esterification reaction is water. A) All three statements are true. B) Two of the three statements are true. C) Only one of the statements is true. D) None of the statements is true. 45. Statements: (1) Nitroglycerin is an example of a phosphate triester. (2) In the body, aspirin is converted to salicylic acid, which is the “active” ingredient. (3) Both ibuprofen and aspirin are propanoic acid derivatives. A) All three statements are true. B) Two of the three statements are true. C) Only one of the statements is true. D) None of the statements is true. Use the following to answer questions 46-50: For each pair of compounds, select a correct characterization from the response list. Responses may be used more than once or need not be used at all. a) have the same molecular formula but are different compounds b) both contain a carbon ring system c) contain the same number of carbon atoms but are not constitutional isomers d) two names for the same compound 46. Methyl propanoate Propyl methanoate 47. Acetic acid Ethanoic acid 48. Butanedioic acid Butanoic acid 49. Benzoic acid Propyl butanoate 50. 2-Methylpentanoic acid β-Methyl valeric acid Page 11 Use the following to answer questions 51-55: For each of the compound characterizations, select from the response list the number of constitutional isomers that exist. Responses may be used more than once or need not be used at all. a) two b) three c) four d) five 51. Saturated four-carbon ester 52. Saturated four-carbon monocarboxylic acid 53. Saturated four-carbon dicarboxylic acid 54. Chlorobenzoic acid 55. Molecular formula of C3H6O2 Use the following to answer questions 56-60: For each pair of carboxylic acids, select a correct characterization from the response list. Responses may be used more than once or need not be used at all. a) Both are dicarboxylic acids. b) Both are C3 acids. c) Both are monohydroxy acids. d) Both are unsubstituted monocarboxylic acids. 56. Fumaric acid, Succinic acid 57. Citric acid, Lactic acid 58. Glyceric acid, Pyruvic acid 59. Valeric acid, Caproic acid Page 12 60. Oxalic acid, Glutaric acid Use the following to answer questions 61-65: Identify the missing reactant in each of the reactions using the response list. Responses may be used more than once or need not be used at all. a) water b) base in water c) alcohol d) carboxylic acid 61. Acid + ? carboxylate ion + H3O+ 62. Acid + ? acid salt + H2O 63. Acid + ? ester + H2O 64. Ester + ? acid salt + alcohol 65. Ester + ? acid + alcohol Use the following to answer questions 66-70: For each of the inorganic esters, select from the response list the combination of reactants needed to produce the ester. Responses may be used more than once or need not be used at all. a) one acid molecule one alcohol molecule b) one acid molecule two alcohol molecules c) two acid molecules one alcohol molecule d) three acid molecules one alcohol molecule Page 13 66. O RO P O O OH 67. P OH O O P OH OH O RO P OR OH 68. O HO S OR O 69. O RO N O 70. O CH2 O N O O CH O N O O CH2 O N O Page 14 Answer Key 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. 31. 32. 33. 34. 35. 36. 37. 38. 39. 40. 41. 42. 43. 44. B C C D B D C C A B B B C B B B D B D C D C A E D A C D B D D B C D C B C A D D B B B A Page 15 45. 46. 47. 48. 49. 50. 51. 52. 53. 54. 55. 56. 57. 58. 59. 60. 61. 62. 63. 64. 65. 66. 67. 68. 69. 70. C a d c c a c a a b b a c b d a a b c b a d b a a d Page 16