Print › Ch. 11 - The Cardiovascular System | Quizlet
advertisement

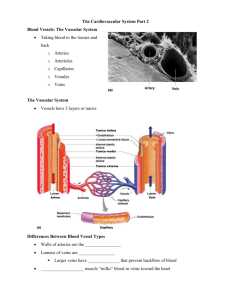
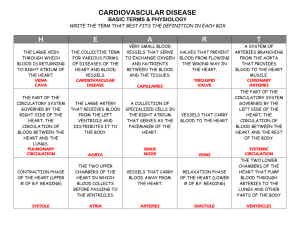
apex point, tip of heart; rests on diaphragm arteries vessels that carry blood away from the heart. arterioles blood vessels that are smaller branches off of arteries atria 2 upper chambers of the heart atrioventricular (AV) bundle (bundle of His) extends from the AV node into and through the interventricular septum atrioventricular (AV) node base of heart bicuspid valve blood pressure bradycardia relays the impulse to contract from the atria to the ventricles; delays signal 0.1 seconds broader area of heart's outline located at the 3rd right and left intercostal space; blood vessels enter and exit also known as the mitral valve, is the left atrioventricular valve. It consists of two cusps of endocardium. measurement of the force exerted by the heart against the arterial walls when the heart contracts and relaxes; systole/diastole a heart rate below 60 beats per minute. capillaries the smallest of the blood vessels and the sites of exchange between the blood and tissue cells. cardiac output amount of blood pumped out of a ventricle in one minute. chordae tendineae tendinous strings that extend from the cusps of the AV valves to the papillary muscles of the heart, thus preventing valve inversion. coronary artery the artery that branches from the aorta to supply blood to the heart diastole period of the cardiac cycle when either the ventricles or the atria are relaxing. ductus arteriosus ductus venosus a blood vessel in a fetus that bypasses pulmonary circulation by connecting the pulmonary artery directly to the ascending aorta blood entering the fetus through the umbillical vein is conducted via the ductus venosus into the interior vena cava to bypass the hepatic circulation electrocardiogram a record of the electrical activity of the heart that, if abnormal, may indicate heart disease endocardium the membrane that lines the cavities of the heart and forms part of the heart valves epicardium visceral layer of serous pericardium foramen ovale connects the left and right atria, allowing blood to flow directly from the right to the left side of the heart hepatic portal circulation transfers nutrient rich blood from intestinal capillary bed to a hepatic capillary bed interventricular septum wall that separates the right and left ventricles intrinsic conduction system SA node, AV node, Av bundle, bundle branches, perkinje fibers; coordinates the heart's basic rhythm ligamentum arteriosum remnant of the prenatal ductus arteriosis mediastinum central compartment of the thoracic cavity; contains the heart, the great vessels of the heart, esophagus, trachea, phrenic nerve, cardiac nerve, thoracic duct, thymus, and lymph nodes of the central chest myocardium layer of the heart wall composed of cardiac muscle. pericardium double-layered serosa enclosing the heart and forming its superficial layer. peripheral resistance a measure of the amount of friction encountered by blood as it flows through the blood vessels. pulmonary circulation system of blood vessels that carry blood to and from the lungs for gas exchange. purkinje fibers modified cardiac muscle fibers of the conduction system of the heart. renin substance released by the kidneys that is involved with raising blood pressure sinoatrial (SA) node pacemaker of the heart; located in the right atrium wall stroke volume the volume of blood pumped out by a ventricle with each heartbeat systemic circulation system of blood vessels that carries nutrient and oxygen-rich blood to all body organs. systole contraction of the heart tachycardia a heart rate over 100 beats per minute. tricuspid valve valve between the right atrium and the right ventricle tunica externa outer layer of a blood vessel which connects it to surrounding tissues tunica intima This is the name for the inner endothelial lining of blood vessels that includes a thin connective tissue layer as well tunica media valves middle layer of artery; made up of smooth muscle fibers and thick layer of elastic connective tissue flap of tissue in the heart between large arteries/chambers that prevents blood from flowing backwards vasoconstriction narrowing of blood vessels. veins blood vessels that return blood toward the heart from the circulation.