Chemical Properties and Changes Physical Property Chemical
advertisement

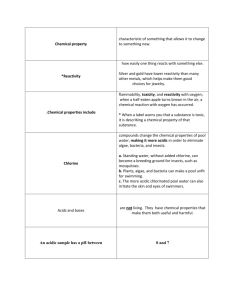
Property = a characteristic that gives a substance identity Chemical Properties and Changes Properties of Vinegar: - clear liquid - density is 1.08 g/mL -strong odor - reacts with baking soda - acidic Composition Physical Property = the ingredients or make-up of a substance, often represented by a chemical formula Water is composed of Hydrogen and Oxygen Emeralds are composed of Al, Be, Si and O Chemical Property • can be observed without changing composition • Only can be observed when composition changes. • depends only on the substance itself • “depends on its reaction with other matter” Diamonds are composed of Carbon only Methanol / Water Physical Property Chemical Property • can be described using the word “is” • can be described using the word “can” or “will” • (or will not, can not) Important Physical Properties: • • • • • Color Opacity Density Magnetism Conductivity – (ability to conduct heat or electricity) • Solubility – (ability to form a solution in water or other solvent) • Crystal Form Methanol / Water – (grain size, geometric shape of crystal) 1 What is a Chemical Reaction? There is only one chemical property: REACTIVITY Chemical Reaction: …whether something will react with (have a chemical reaction with) another substance. …a rearrangement of the atoms in a substance to produce new substances All chemical reactions can be written as: So, (review): chemical equations: REACTIVITY for example: Methanol + Oxygen Carbon Dioxide + Water REACTANTS PRODUCTS is a chemical property or: CH3OH + O2 REACTANTS CO2 + 2H2O PRODUCTS …that describes whether something will have a chemical reaction (chemical change) with another substance. pH: An important chemical property. Examples of Reactivity: pH = a measure of how acidic or basic a substance is. (it describes a reaction with water.) • Reaction with…____ • Flammability (reaction with O2) • pH (reaction with water…whether something is an ‘acid’ or a ‘base’) ACIDS BASES • Turn litmus paper red • React with bases to form salts and water • Taste Sour • Turn litmus paper blue • React with acids to form salts and water • Taste Bitter Solder / Mg 2 Which are Physical Properties? Which are Chemical Properties? pH = a measure of how acidic or basic a substance is. (it describes a reaction with water.) ACIDS Physical Change • No new substances are formed. • No change in chemical formula Examples; - Crushing into Powder - All Phase Changes BASES Chemical Change • = “chemical reaction” • New substances are formed. • Chemical Formulae are new or changed, Examples; - Wood Burning (Combustion) -Iron Rusting (Oxidation) Ice Melting: Chemical or Physical Change? • • • • • • • • • • Hardness…………………… Color………………………. Reactivity with HCl………. Magnetism………………... Density……………………. pH…………………………. Flammability……………… Boiling Point……………… Corrosiveness……………… Melting Point……………… Physical Physical Chemical Physical Physical Chemical Chemical Physical Chemical Physical Q: How can we tell if a chemical change has occurred? A: Look for evidence… 5 Signs of a Chemical Reaction: • • • • • Formation of a gas Formation of a solid Unpredictable Color Change Radiant Energy (Light) Thermal Energy (Heat) Phase Changes and Kinetic Theory • Composition does not change; it is still water (H2O). No new substances are formed, so no chemical change. PHASE CHANGE = PHYSICAL CHANGE 3 When a candle melts, some of the wax turns to a liquid and runs down the side. Is this a chemical change or a physical change? Why? • Does the candle become a new substance? • It was wax; it is still wax; liquid wax is still wax Physical Change Is lighting a match a chemical change Enough! or a physical change? Why? • Is a new substance produced? • Does a color change occur? • Is heat and light given off? • Is a gas produced? Chemical Change 4