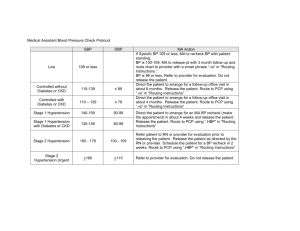
Enhanced Analysis on Route Summarization and Route
advertisement

ISSN:2229-6093
Haresh N Patel et al, Int.J.Computer Technology & Applications,Vol 5 (5),1682-1689
Enhanced Analysis on Route Summarization and Route
Redistribution with OSPF vs. EIGRP Protocols Using
GNS-3 Simulation.
Haresh N. Patel, Prof.Rashmi Pandey
Department of Electronics
& Communication Engineering
Vedica Institute of Technology, Bhopal
ABSTRACT
Routing protocol is taking an important role within
the Different internet era. A routing protocol
determines however the Routers communicate with
one another to forward the packets by taking the best
path to travel from a source node to a destination
node. During this paper we've explored two eminent
protocols specifically, Enhanced Interior Gateway
Routing Protocol (EIGRP) and Open Shortest Path
First (OSPF) protocols based on route redistribution
and route summarization using different techniques
to reduce routes, filter LSA Types and also reduce
size of LSA database, traffic of networks. In any
case, having a multiple protocol atmosphere makes
redistribution a necessity. Variations in routing
protocol characteristics, like metrics, administrative
distance, classful and classless capabilities will result
route redistribution. Though should be to those
variations for distribution to succeed. Then traffic of
the network is increase. This analysis will simulate
Networks using Route summarization, Stub area,
Totally Stub area , NSSA area, NSSA stub area
,NSSA totally Stub Area, Additionally greatly
reduces processor workloads, memory and
information measure demand.
is the process of aggregating routes to multiple
Index Terms
representing them by a smaller number of entries.
OSPF, EIGRP, Route Summarization, Route
Redistribution, Stub Area, Totally Stub area, NSSA
area, NSSA- Stub Area, NSSA-Totally Stub Area.
This allows you to reduce the memory requirements
1.
you must implement an effective hierarchical
A BRIEF LOOK ON ROUTE
SUMMARIZATION:
smaller networks that saving storage space in the
routing table and simplifying routing decisions.
Routes advertisements to neighboring gateways are
reduced. Route summarization within large and
complex networks can isolate topology changes from
other routers. This can improving the stability of the
network by limiting the propagation of routing traffic
after a network link fails. Example such as if a router
only advertises a summary route to the next router
then it does not advertise any changes to specific
subnets in the summarized range. This can reduce
any unnecessary routing updates following a
topology change. Hence that increases the speed of
convergence
and
allows
for
a
more
stable
environment.[2][3]
In it is most basic form; route summarization
is the taking of multiple route entries and
on a router, thereby improving performance. But in
order to use route summarization proper effectively,
addressing scheme that which can have a found
In Internet networking terminology, Supernet is a
impact on the performance and scalability of your
block of contiguous subnet works addressed as one
network. One of the biggest benefits of route
single subnet within the larger network. Supernets
summarization is the shrinking of the routing table,
perpetually have a subnet mask that's smaller than
which results in the reduced amount of memory
the masks of the component networks.[1] The size of
used. This also results in a router spending less time
routing tables has been rapidly increasing during the
looking for a route in its routing table and also
expansion of the Internet. Route summarization
results in having a smaller link-state database and
making the process of the SPF algorithm better.
Summarization also reduces the number of routing
updates sent because of link or network flaps. That
IJCTA | Sept-Oct 2014
Available online@www.ijcta.com
1682
ISSN:2229-6093
Haresh N Patel et al, Int.J.Computer Technology & Applications,Vol 5 (5),1682-1689
by summarizing networks, you in effect isolate all
summary routes at random boundaries by using
the flapping but it does have the disadvantage of
manual
other routers still sending data to the router that is
summarization can be applied anywhere in EIGRP
advertising
network.
domain, on every router and on every interface.
Troubleshooting will be easier with summarization
Summary route will live in routing table as long as at
configured since you are better able to isolate the
least one more specific route will exist.
the
summarized
route
summarization.
Manual
route
part of your network where issues may arise. One
If you want to use auto route summarization
drawback to be aware of with summarization is the
you have to do nothing because it is enabled by
lost of routing information. Which can result in sub-
default, otherwise use no auto-summary EIGRP
optimal routing if a network within the summarized
command to disable it. To do manual route
route were to go down. Assigning subnets according
summarization go to on interface and use { ip
to simple octet or bit boundaries allows you to make
summary-address eigrp as-number address mask
addressing and summarization easier to accomplish.
[administrative-distance] } command.[3][4]
Placing subnets in blocks that are a power of 2 also
helps optimize summarization.
2.
OSPF ROUTE SUMMARIZATION
Area border routers (ABRs) send summary link
advertisements to describe the routes to other areas.
It is depending on the number of destinations and an
area can get flooded with a large number of link-state
records. This can utilize routing device resources to
minimize the number of advertisements that are
flooded into an area. You can configure the ABR to
combine or summarize a range of IP addresses and
send reachbility information about these addresses in
a single link-state advertisement (LSA). You can
summarize one or more ranges of addresses where all
routes that match the specified area range are filtered
at the area boundary and the summary is advertised
in their place.[1][2]
For an OSPF area, you can summarize and filter
inter-area prefixes. All routes that match the
specified area range are filtered at the area boundary
and the summary is advertised in their place. For an
OSPF not-so-stubby area (NSSA), you can only filter
NSSA external (Type 7) LSAs before they are
translated into AS external (Type 5) LSAs and enter
the backbone area after all external routes learned
within the area that do not fall into the range of one
of the prefixes are advertised individually to other
areas.
3. EIGRP AUTOMATIC & MANUAL
SUMMARIZATION
By default EIGRP has auto summarization enabled.
This means that it will summarize to class full
addresses at network boundaries. Leaving auto
summarization enabled can cause a lot of troubles
occur in the network. EIGRP has the ability to create
IJCTA | Sept-Oct 2014
Available online@www.ijcta.com
4.
OSPF AND EIGRP ROUTE
REDISTRIBUTION
Mutual route redistribution is the process where two
dynamic routing protocols exchange their routes with
each other. Example such as when you route
redistribute EIGRP into OSPF then all routes in the
EIGRP Autonomous system will be in the OSPF
database that show up as OSPF routes in the OSPF
domain. Same with EIGRP when you redistribute
OSPF into EIGRP then all the routes from OSPF will
be carried over to EIGRP and advertised throughout
the autonomous system.
Mutual route redistribution is a common when
companies acquire other companies that use different
routing protocols. In such case Company XYZ Inc.
acquires Company ABC Inc. however XYZ Inc. uses
OSPF and ABC Inc. uses EIGRP. After the
acquisition, the Chief Technology Officer mandates
that there be full network communication between
the newly merged companies. In this case you need
to perform mutual redistribution to ensure XYZ Inc.
has routes to ABC‟s network and vice-versa.
5. PROPOSED METHODOLOGY
5.1 Route Summarization
5.1.1 Using Route Summarization to reduce the
size of routing table:
Route summarization offers many vital advantages
over flat routing. Route summarization can reduce
the latency in a complex network, when many
routers are involved in the networks. It will also
reduced number of routing entries, the overhead for
routing protocols is reduced. Network stability will
be improved by reducing or eliminating unnecessary
1683
ISSN:2229-6093
Haresh N Patel et al, Int.J.Computer Technology & Applications,Vol 5 (5),1682-1689
routing updates after part of the network undergoes a
change in topology. Route summarization also
reduces processor workloads, memory necessities
and bandwidth demand.
A Different AS with a large number of networks,
OSPF router should keep the LSA of every other
router in its LSDB. Every router in a large OSPF AS
has a large LSDB. The SPF calculation of a LSDB
can require a substantial amount of processing. Also,
the resulting routing table will be large, containing a
route to each network in the AS. In an effort to
reduce the size of the LSDB and the process
overhead for the SPF tree and routing table
calculation, OSPF permits the AS to be divided up
into groups of networks called areas.
5.1.2 Using Stub Area to filter LSA Type 5 and to
reduce size of routing table:
Does not accept information about external to the
AS. If routers need to route to networks outsides an
AS, They will use a defaults route (0.0.0.0).This kind
of area reduces the size of link state database, and
result of that it will reduces the memory requirement
of the routers inside that area. External networks
LSA type 5s are not allowed to be flooded into a stub
area, to get to external route networks, routers will
use the default route.
5.1.3 Using Totally Stubby Area to filter LSA
Type 3, 4, 5 and reduce size of routing table:
Does not accept external AS route, or summary
routes from other areas internal to the AS. A defaults
route is injected for reachbility to other networks
outside that area. Cisco Proprietary solution. It can
only be used if all the routers are CISCO.
Flooded LSAs are: LSA type1, and LSA type2.
5.1.4 Using Not So Stubby Area (NSSA Area) to
allows LSA Type 1, 2, 3, and 7:
Many service providers have OSPF areas that they
have only one exit point, but the areas consist an
ASBR
Solution: Not-So-Stubby Areas (NSSAs) .The
ASBR originates a Type 7 LSA. The ABR converts
from Type 7 to Type 5. It‟s Hybrid Stub area that can
accept external route with using LSA type 7s. LSA
Type 7s can be originated and advertised throughout
a NSSA.
LSA Type 7s then will be translated in to LSA Type
5s by the ABR and flood in to the area 0. NSSA can
only receive the LSA Types 1, 2, 3 and 7. Prior to
NSSA, if an area had external route, that area could
not be set to STUB of any Kind.
5.1.5 Using NSSA Stub Area to advertise a default
route manually:
By default, stub ABRs are advertise a default route.
By default, NSSA ABRs don't.
To force NSSA to advertise a default route.
5.1.6 Using NSSA Totally Stub Area to reduce
size of routing table to filter LSA Type 7:
IJCTA | Sept-Oct 2014
Available online@www.ijcta.com
After you define the NSSA totally stub area, Area
has these characteristics in addition to the NSSA
characteristics: No type 3 or 4 summary LSAs are
allowed in Area. This means no inter-area routes are
allowed in Area. A default route is injected into the
NSSA totally stub area as a type 3 summary LSA.
5.2 Route redistribution:
The use of a routing protocol to advertise routes that
they are learned by another routing protocol such as
static routes or directly connected routes is called
redistribution. Whereas running one routing protocol
throughout your entire IP internetwork is desirable,
multi-protocol routing is common for variety of
reasons, such as company mergers, multiple
departments managed by multiple network
administrators and multi-vendor environments.
One-Point redistribution defines one redistribution
point between two routing protocols. By this we
mean routes redistributed on only one router. The
distribution can be: [A] One-way [B] Two-way. Oneway route redistribution requires the use of a default
route or static routes. Here Experimental Analysis in
first lab identify one way route redistribution. Twoway route redistribution when performed on two or
more separate routers both running routing protocols.
Here Experimental Analysis in second lab identify
two way route redistribution.
6. SIMULATION
GNS3 is a Graphical Network Simulator that allows
emulation of complex networks. You familiar about
with Virtual Box or Virtual PC, VMWare that are
used to emulate various operating systems in a
virtual environment. This software is used to emulate
Cisco ASA and Cisco IPS, PIX firewalls, Juniper
routers as well as hosts Like Linux, Windows, Mac
OS X, FreeBSD etc.
Simulation is performed using GNS3 software. In
this paper, there are 4 typologies to be simulated
based on route redistribution, route Summarization,
OSPF Stub and NSSA Area. Each topology consists
of four routers and each router is connected to
several computers through network switch. Each
network topology simulated using IPv4 addressing
mode with OSPF and EIGRP Protocols.
In the first topology, each router is connected to
other router through network switches and devices.
This topology is also called multi-access network.
To perform Static Vs Defaults Vs OSPF and
Injecting Default Route with Route Redistribution
using OSPF Routing Protocol.
In Figure 1: R1 is Acting as the ISP and R2 is the
Edge router for company that is running OSPF
internally R2, R3, R4 .R1 will have static route
towards all the company networks. R2 will have
1684
ISSN:2229-6093
Haresh N Patel et al, Int.J.Computer Technology & Applications,Vol 5 (5),1682-1689
default route pointing toward R1.R2 should inject the
default route in to R3 and R4.
In Figure 2: Performing Mutual redistribution
between EIGRP and OSPF. Run EIGRP between R1
and R2.Run OSPF between R2, R3 and R4.Also
Both Protocols have different Autonomous System.
In figure 3: configure OSPF in Multi-area
configuration based on the network diagram.
Advertise all the loopbacks on all the routers. Verify
the different types of routes in a Multi-area
configuration. Perform Route summarization such
that all the loopbacks from Area 10 and Area 100 are
summarized.
After Route Summarization, Configuration of
Stub area and totally stub area build on this
topology. Here loopback advertise using
redistribution and to filter LSA type 3, 4, 5.
Figure 2: Route redistribution between OSPF vs.
EIGRP with Different Autonomous System.
Figure 3: Multi-Area Connection Using Route
Summarization.
Figure 1: Injecting Default Route using OSPF
Protocol.
IJCTA | Sept-Oct 2014
Available online@www.ijcta.com
1685
ISSN:2229-6093
Haresh N Patel et al, Int.J.Computer Technology & Applications,Vol 5 (5),1682-1689
Figure 4: Configuring Not-So-Stubby Area
In figure 4: configure OSPF in Multi- area
configuration based on the network diagram.
Configure Area 10 as a NSSA Area to prevent
External routes from the backbone getting
injected into it. Make sure that everybody
outside of Area 10 has reachbility to external
routes injected by the ASBR in Area 10.
In Configure Area 10 a NSSA-Stub to
maintain reachbility to the external routes from
the Backbone. In Configure Area 10 as a NSSATotally area to block the Inter-area routes as
well from getting injected into area 10.
7. ANALYSIS
After Analysis of Topology 1(figure-1).we can
see injecting default route (Routing table 7.3)
With route redistribution. Advertising route
from Source Router R1 to Destination Router
R2.
Analysis of Topology 2 (figure -2) identify
Route redistribution between OSPF and EIGRP
with different AS. We can see in the routing
table 7.4 injected External routes of R3 and R4
Using route redistribution.
Analysis of Topology 3(Figure-3) identifies
Route Summarization with OSPF multi area
connection. After summarization we can see
Reduce size of routing table. (Routing table 7.5)
Routing table 7.6 indentify configuration of
Stub area and to filter LSA Type 5.more reduce
size of routing table. Routing table 7.7 identify
configuration of Totally Stub area and to filter
LSA type 3, 4, and 5. Furthermore reduce size
of routing table. We can see route on routing
table.
Analysis of Topology 4(Figure-4) identifies
Configuration of NSSA Area. (Routing table
7.8) NSSA Area does not provide default route
so we can manually configure default route
using NSSA Stub area. After filter LSA type 7
using NSSA Totally Stub area.
Routing Table 7.1- of Router R1 (Figure -1)
Routing Table 7.2- of Router R4 (Figure -1)
IJCTA | Sept-Oct 2014
Available online@www.ijcta.com
1686
ISSN:2229-6093
Haresh N Patel et al, Int.J.Computer Technology & Applications,Vol 5 (5),1682-1689
Routing table 7.3 – of Router R2 (Figure -1)
Routing table 7.4 – of Router R4 (Figure -2)
Routing table 7.5 – of Router R4 (Figure -3) – After route Summarization
IJCTA | Sept-Oct 2014
Available online@www.ijcta.com
1687
ISSN:2229-6093
Haresh N Patel et al, Int.J.Computer Technology & Applications,Vol 5 (5),1682-1689
Routing table 7.6 – of Router R4 (Figure -3) – After Configured STUB Area.
Routing table 7.7 – of Router R4 (Figure -3) – After Configured Totally STUB Area.
Routing table 7.8 – of Router R2 (Figure -4) – After Configured NSSA Area.
IJCTA | Sept-Oct 2014
Available online@www.ijcta.com
1688
ISSN:2229-6093
Haresh N Patel et al, Int.J.Computer Technology & Applications,Vol 5 (5),1682-1689
8. CONCLUSION
In this paper, performance analysis based on
route summarization and route redistribution
using OSPF and EIGRP protocols. Which may
be achieved that shown within simulation result
and routing table analysis. Finally, Reduces the
amount of information stored in routing tables,
also reduce CPU and Memory utilization of
networks. To makes the routing process more
efficient. To reduce the network convergence
time
Reduced Frequency of SPF calculation:
detailed routing information is kept within each
area so it‟s not necessary to flood all Link-state
changes to all other areas, thus not all routers
need to run the SPF calculations.
Smaller Routing Table: Because detailed
routing information is kept within an area, the
routers within an area will have smaller routing
table.
Reduced Link-state Updates: LSU is can
contain a variety of LSA types, instead of
sending an LSU about each network within an
area, you can advertise a single or fewer
summarized routes between areas to reduce
overhead associated with LSU.
[5] Franck Le,” Understanding Routing
Redistribution”,
International
conference,
Beijing, China, 2008.
[6] W.T.Zaumen and J.J. Garcia-Luna-Aceves,
Dynamics of Link-State and Loop-Free DistanceVector Routing Algorithms," Journal of
Internetworking, Wiley, Vol. pp. 161-188, 3rd
December 1992
[7] J.J. Garcia-Luna-Aceves,„Method and Apparatus
for Distributed Loop-Free Routing in Computer
Networks,„U.S.
Patent
application,
SRI
International, Menlo Park, California, 1993
[8]
Bob Albrightson , J.J. Garcia-LunaAceves,Joanne Boyle.,3rd March,„EIGRP routing
protocol based on distance vectors„, Journal of
internetworking ,Wiley,Vol pp 200- 205, 2001.
9. ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
I would like to sincere thanks to their family
members and their Guide, Principal and
Director,
HOD
of
Electronics
and
Communication department of Vedica Institute
of Technology (VIT), Bhopal for encouraging us
for this research work.
10. REFERENCES
[1] "CCNP ROUTE 642-902 Official
Certification Guide, by Wendell Odom" 2014
[2] CCNA Routing and Switching Study Guide:
Exam 100-101, 200-101, 200-120 (15 Oct 2013).
[3] TODD LAMMLE (AUTHOR), CCNA
AND SWITCHING S TUDY GUID, 2013
ROUTING
[4] Alex A. Stewart and Marta F. Antoszkiewicz,
“Route Analysis and Management System”,
2009.
IJCTA | Sept-Oct 2014
Available online@www.ijcta.com
1689