Levels of organization: Chemical level: Simplest level (smallest
advertisement

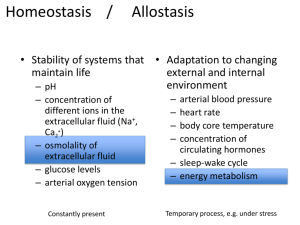
Levels of organization: Chemical level: □ Simplest level (smallest components) includes atoms & molecules □ Building blocks of matter Organelles: □ Atoms & molecules assemble to form specialized structures within the cell with a variety of shapes, sizes, & functions □ Includes: nucleus, mitochondria, ribosomes Cellular level: □ Composed of a variety of different organelles that assemble together. Basic structural & functional unit of an organism. Same common function, vary in size & shape, each type having its own unique function. □ Includes: muscle cells, nerve cells, blood cells Tissue level: □ Groups of similar cells that have a common function. □ Includes: Epithelial tissue, Connective tissue, Muscle tissue, Nervous tissue Organ level: □ Composed of two or more different types of tissues. They perform specific functions and have defined shapes. □ Includes: Stomach, brain, heart, lungs Organ system level: □ Made of two or more different but related organs that have a common function □ Includes: Digestive system, Cardiovascular system Organism level: □ The sum total of all structural levels working together. Homeostasis 1) Definition: Maintaining relatively constant internal conditions (dynamic balance within narrow ranges) even though outside is in constant change 2) Why is it called a “feedback” system. In other words what is fed back? The RESULT of a process to restore homeostasis is fed back as the new STIMULUS(STRESS) 3) Read the example below (Osmoregulation). Select a part(phrase) from the example that provides an example of each term that follows: Control Center, Variable (Controlled Condition), Stimulus (Stress), Receptor (Monitor), Effector, Response, Result, and Feedback. Osmoregulation Osmoregulation is the regulation of water concentrations in the bloodstream, effectively controlling the amount of water available for cells to absorb. Due to exercise excessive sweating causes a decrease in water concentration in the body. Osmoreceptors that are capable of detecting water concentration are situated on the hypothalamus in the brainstem. The hypothalamus sends chemical messages to the pituitary gland (in the brain) next to it. The pituitary gland secretes anti-diuretic hormone (ADH), which targets the kidney responsible for maintaining water levels. When the hormone reaches its target tissue, it alters the tubules of the kidney to become more permeable to water. If more water is required in the blood stream, high concentrations of ADH make the tubules more permeable thus increasing the volume of water in the bloodstream. The osmoreceptors in the hypothalamus reevaluate the new water concentration and determine what the next step is. Control Center: __________pituitary gland________ Variable (Controlled Condition): Osmoregulation = regulation of water concentrations in the bloodstream Stimulus (Stress): exercise causing a decrease in water concentration Receptor (Monitor): Osmoreceptors in the hypothalamus Effector: _______kidney___________ Response: tubules of the kidney to become more permeable to water. Result: increasing the volume of water in the bloodstream. Feedback: the result is fedback as the new stimulus (New water concentration is reevaluated by the Osmoreceptors in the hypothalamus) and/or Negative Feedback because the Result conteracts the Stimulus